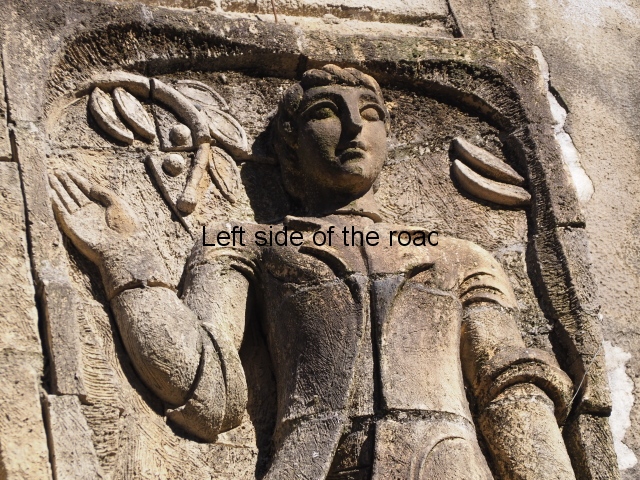Telephone exchange mural – Tskaltubo
More on the Republic of Georgia
Telephone exchange mural – Tskaltubo
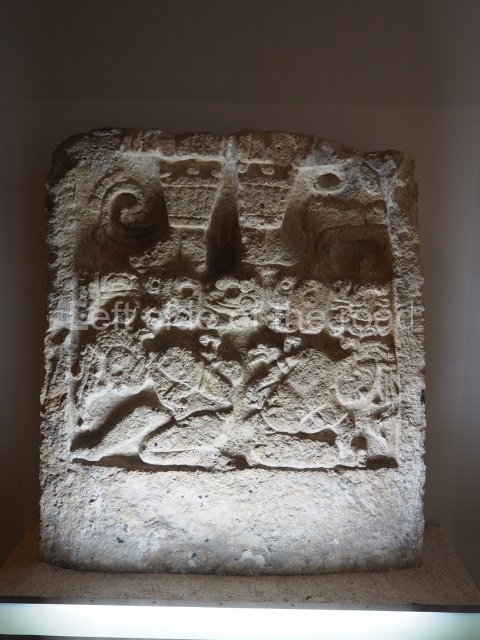
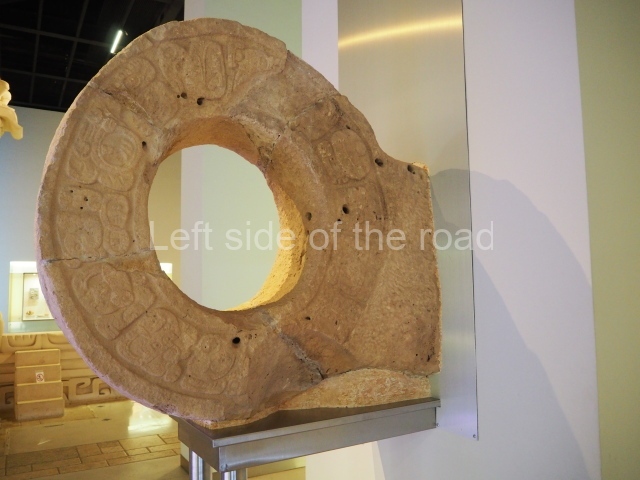
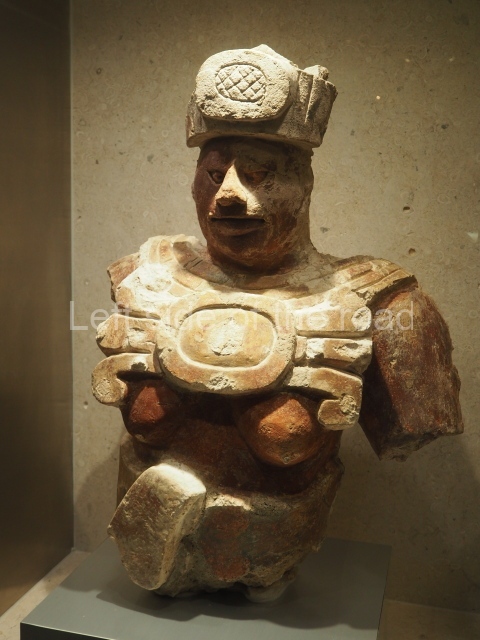
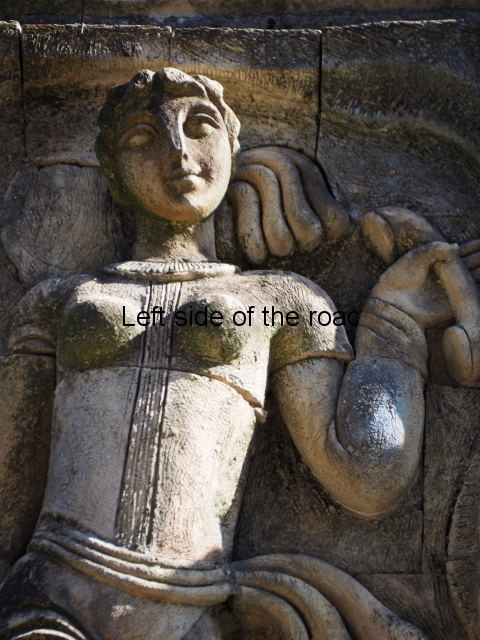
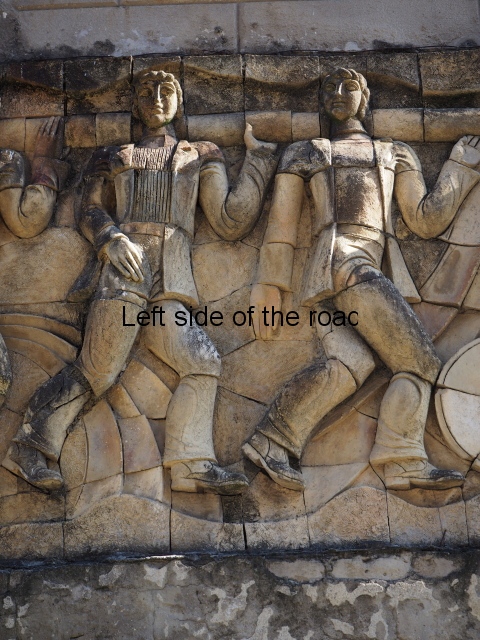
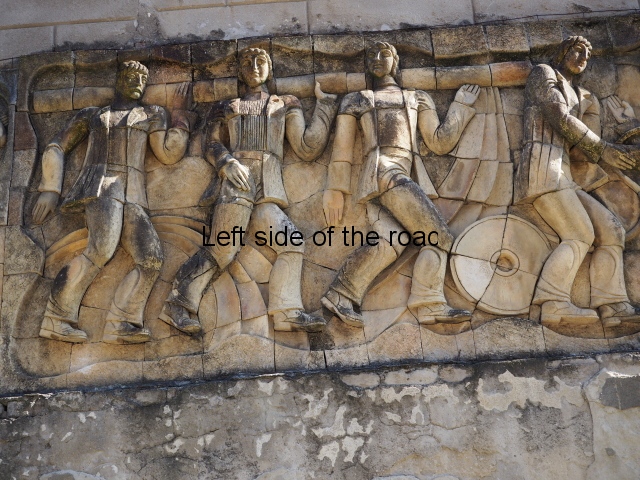
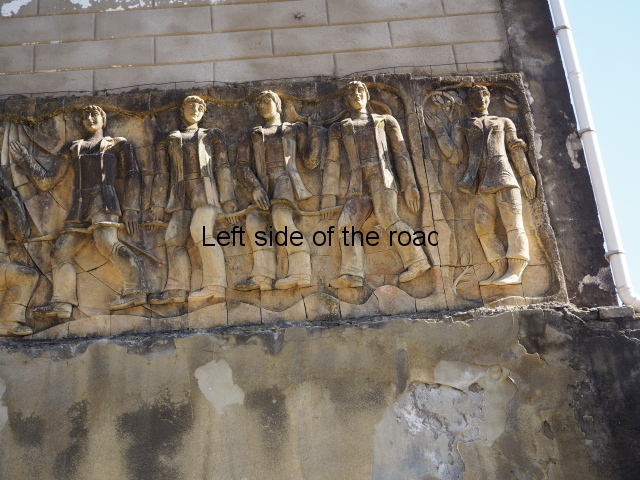
The terracotta mural portraying a group of telecommunications workers is an interesting, and in some aspects quite charming, piece of public art which is probably missed by the vast majority of visitors to the once immensely popular, and populous, spa town of Tskaltubo, not far from the city of Kutaisi in western Georgia.
Socialist Realist?
I am presenting it here for its curiosity value alone and do not plan to look too deeply into what is depicted as I don’t consider it fits into the definition I’ve been following of Socialist Realist art.
Just because a piece of art is produced and put on show in a country that calls itself ‘socialist’ doesn’t then – automatically – mean that it is a ‘Socialist Realist’ work of art. Realist yes, even social realist, but not Socialist Realist.
This mural, showing workers doing their job, is radically different from the mural that sits above the main entrance to Spring No. 6 – which is only a few minutes walk away.
That mural, which represents a visit of Joseph Stalin to the town in the early 1950s, had a very specific rationale. It was produced to demonstrate a unity between the people in one of the Republics on the edge of the vast USSR with the leadership in the capital of Moscow.
On the other hand the mural on the wall of the telephone exchange is mere decoration. Charming though it may be.
The terracotta mural is of a much later date (although the exact one I don’t know – but would guess 1970s at the earliest). And that’s important. Three years after the death of Stalin in 1953 the then leader of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, Nikita Khrushchev, not only denounced Joseph Stalin as an individual he basically attacked all the gains and victories that had been achieved since the October Revolution of 1917. He didn’t say that (after all he was a traitor to Marxism-Leninism and had to hide his revisionism from the assembled delegates at the 20th Party Congress) but all that happened during his time at the head of the Party and country, as with subsequent ‘leaders’ until 1990, was to turn back the construction of Socialism and allow the re-establishment of capitalism in the world’s first ‘Communist State’.
So those works of art produced from the mid-1950s onwards weren’t produced to aid the development of Socialism but to reflect the capitalist road on which the Soviet Union was now following. I will accept that there might have been works of art that challenged the change of direction but they still couldn’t be considered Socialist Realist as the economic base of the country was no longer socialist.
The Mural
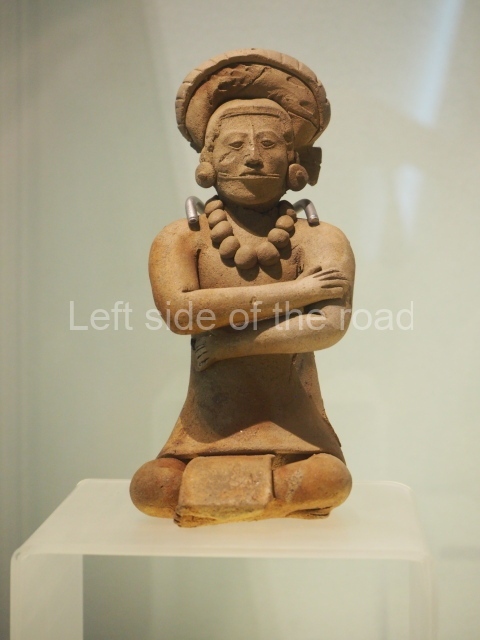
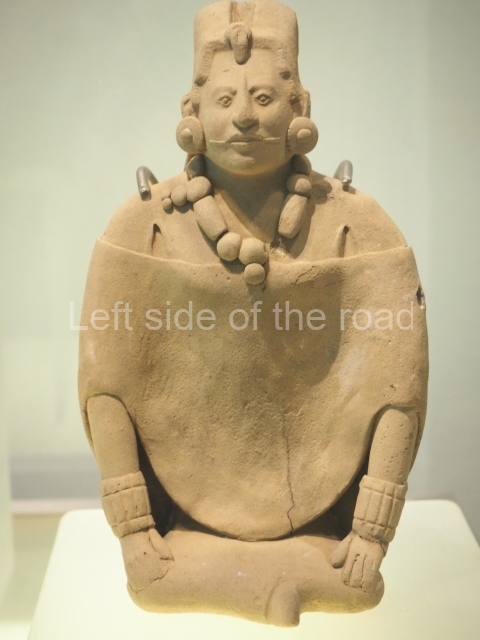
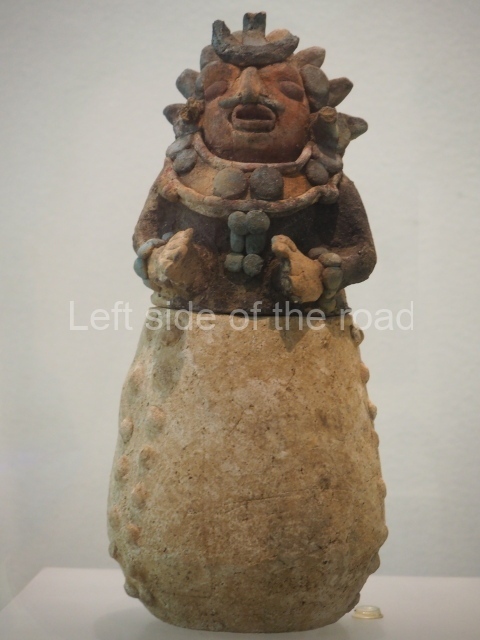
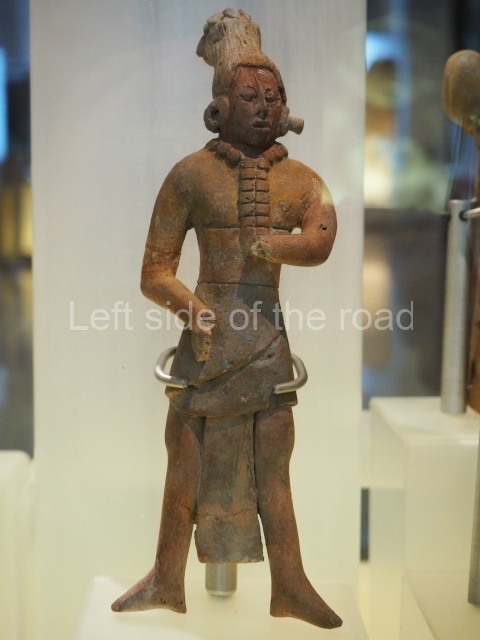
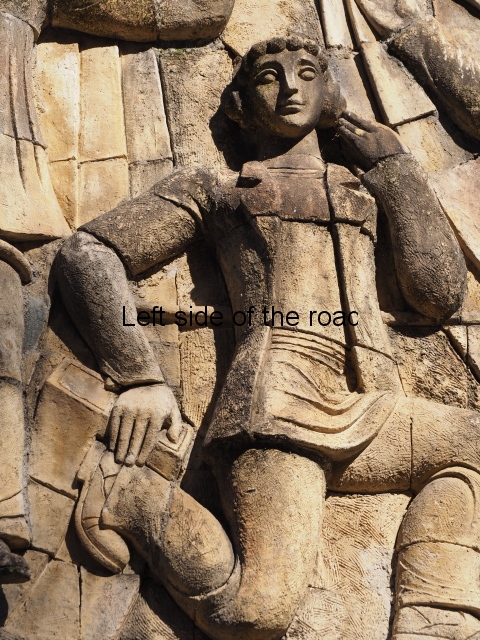
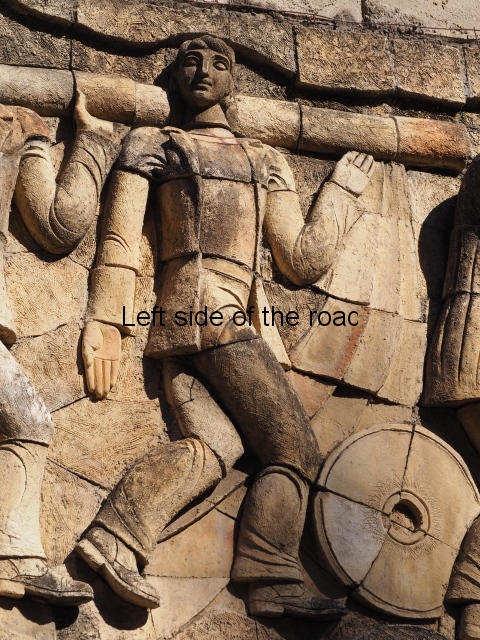
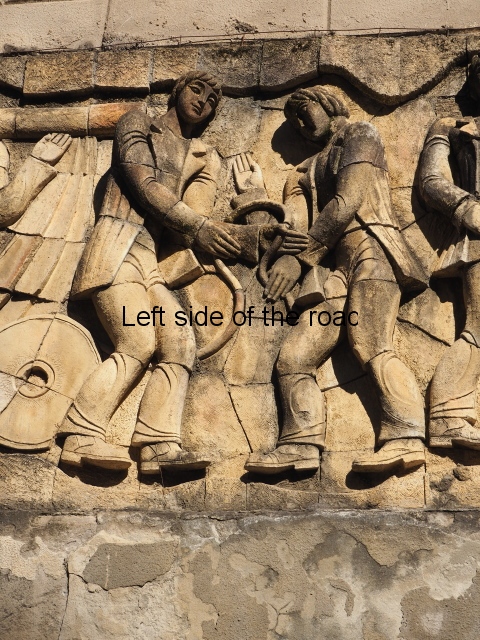
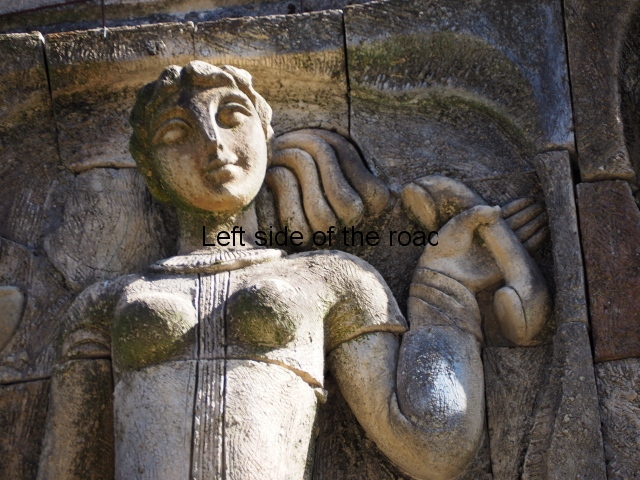
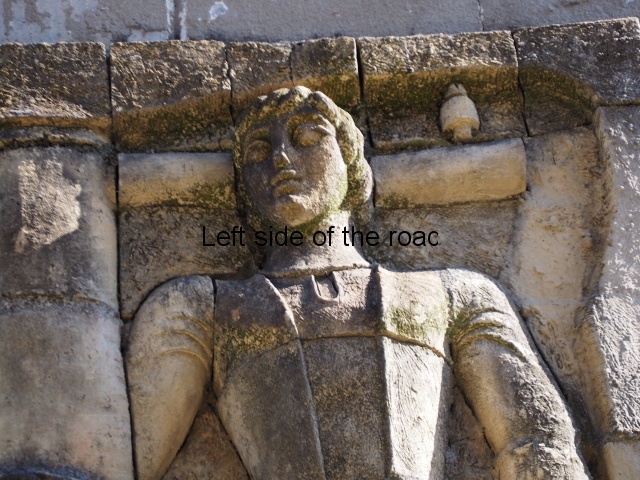
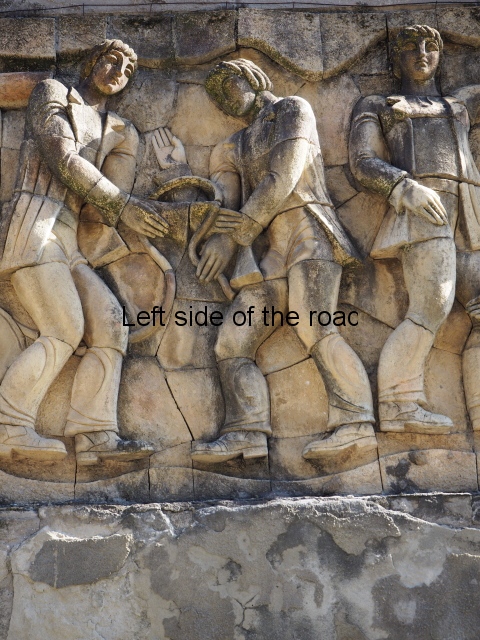
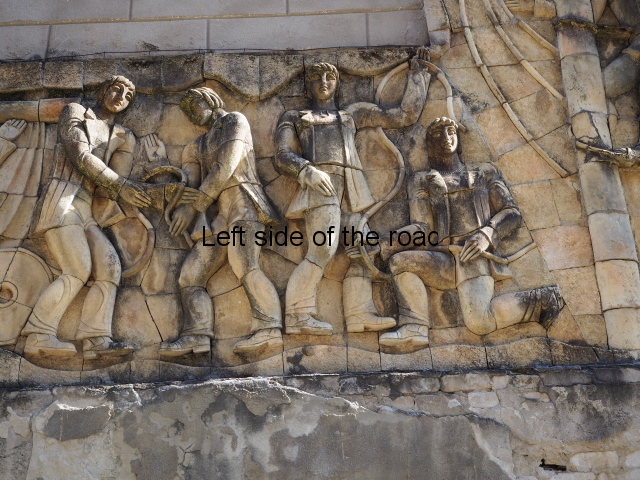
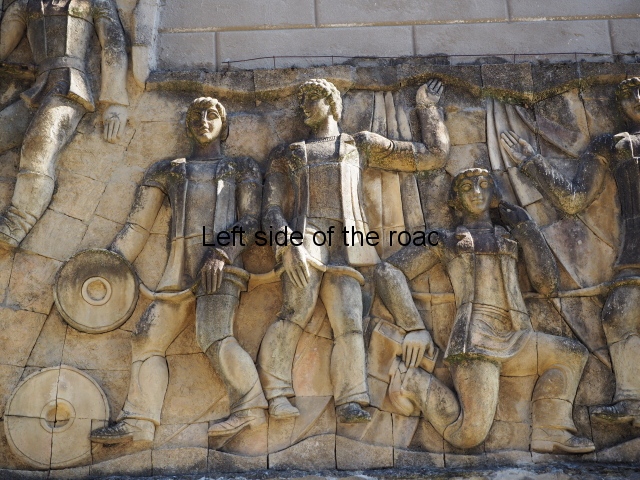
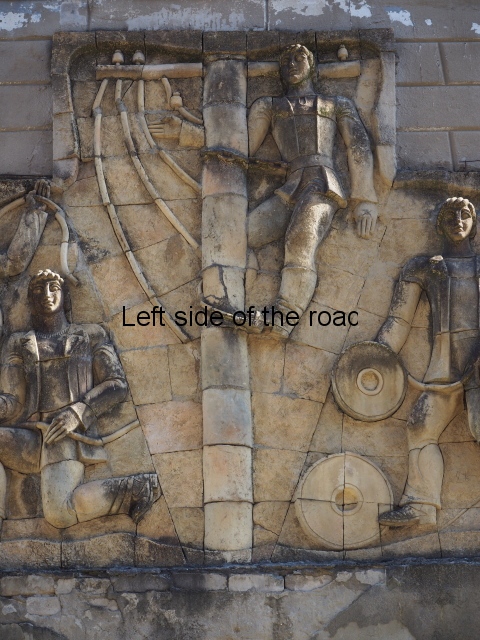
Although the main body of the mural – which stretches the width of the shortest wall of the large rectangular telephone exchange – depicts men (and they are all men) in the task of erecting telegraph poles in an effort to create a means of long distance communication between the young couple at the extreme right and left of the mural. This is a 20th century activity but their look is essentially from the pre-revolutionary period.
This is especially the case if you look at the heads of all the workers. Their hairstyles are what you’d expect to see on some classical Greek sculpture and even their clothes point to an earlier era. This more ‘traditional’ dress is accentuated with the style of the clothing of the two young people at either end. It says more late 19th rather than late 20th century.
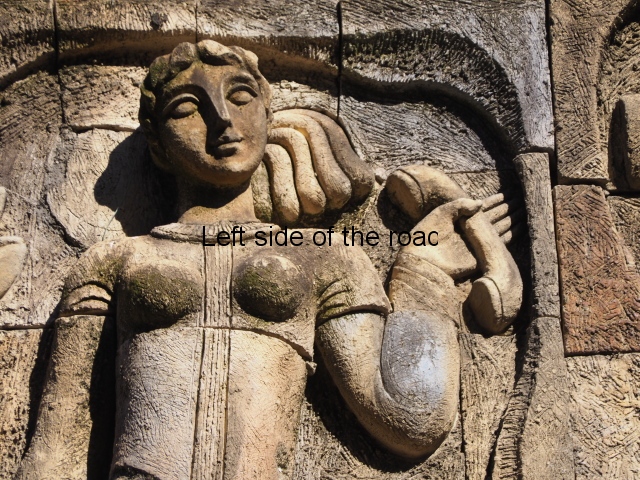
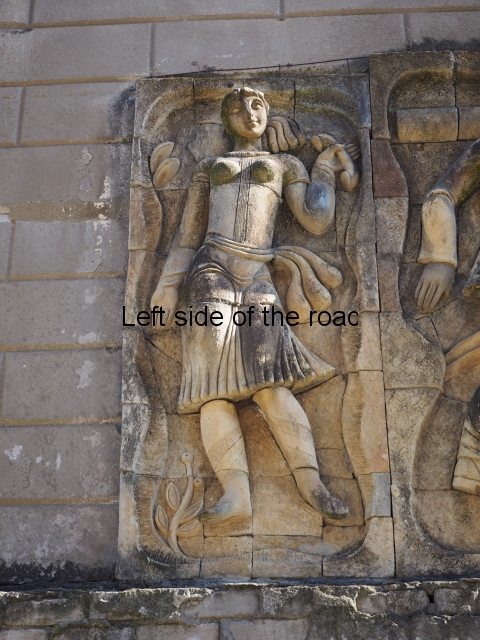
All the activity in the centre seems to be geared to uniting these two young ‘lovers’. They are in rural settings whereas the telecommunication workers indicate a city and industrial environment. The young woman is bringing a telephone receiver (the style of which you only see in museums now but which was ubiquitous for the majority of time of telephonic communication) to her left ear. Why the male doesn’t also hold a handset is confusing. He just seems as if he were walking on a cloud, not really aware of anything.

Georgian post-socialist depiction of women
As for the young woman I have to make reference to her breasts as the unreal depiction of the female breast is ubiquitous in Georgian sculpture of the revisionist (post Socialist) period in the country’s cultural history. The breasts seem like small bowls that have been plunked on their chests. The vast majority of sculptures of women produced during times of the construction of Socialism I wouldn’t exactly say play down the female form but in Georgia it wasn’t until the success of revisionism that the emphasis on shape, and sexuality, seems to have become the norm.
This can be seen most obviously (sic) in the large sculpture of ‘Mother Georgia’ in the hills above Tbilisi. There are other examples; on the market mural, the sculptural group in the centre of the town as well as a number of (damaged) female sculptures in the courtyard of the Kakabadze Fine Art Gallery all in Kutaisi; the facade of the magistrates court in Tskaltubo; and even on the large sculpture of ‘Victory’ which dominates the hill above the grave of the Unknown Soldier in Vake Park in Tbilisi. (Links to these locations to follow.)
Contrast all these depictions with the only two female sculptures from the Socialist period still on public show, that I’ve seen in Georgia, which are part of the façade of the Rustaveli Cinema on Rustaveli Avenue in the centre of Tbilisi.
If we refer to another country which depict women in Socialist Realist art then there are many examples in Albania. To select just a couple there’s the the statue of Liri Gero (behind the National Art Gallery) in Tirana – but contrast that with the very recent sculpture in her home town of Fier where she looks like a 21st century young woman out on the town on a Friday night – or the sculpture of the female partisan and child in the Lushnje Martyrs’ Cemetery
How the mural is made

Method of construction
The method of construction is also quite unique (at least for me) in that rather large chunks of the terracotta seem to be made and then all is revealed when the pieces are put together as in a very large, three dimensional jigsaw puzzle. This same technique is also used in the mural on the west facing wall of the market in Kutaisi – not far from the marshrutka (mini-bus) stop to Tskaltubo. More information will be provided as and when I come across it.
Location
On the left on left as you go down Tseretseli Street from the main bazaar towards Central Park.
GPS
42.3271
42.6001
How to get to Tskaltubo
Marshrutka number 30 leaves from its terminus on the western side of the Red Bridge, which crosses the Rioni River beside the main Kutaisi market. Closer to the market is the stop for a number of buses but you walk through that area (passing a cheap out door bar on the right) to cross the red painted iron bridge. The marshrutka will be on the left once on the other side. They leave roughly every 20 minutes. Cost GEL 1.20 (not the GEL 2 as in some guide books – although some of the drivers will take the GEL 2 and say nothing although others are honest). The price will be on a piece of paper somewhere, normally at the front of the vehicle.
Journey takes about 30 minutes to get to the centre of Tskaltubo. Once you cross the railway track (after 20 or so minutes) you are at the bottom end of Central Park. The marshrutka then follows Rustaveli Street on the eastern edge of the park passing the railway station and information office, the Municipality, Court and Police buildings, and then the entrance to the huge (now luxury 5 star) Tskaltubo Spa Resort all on the right. (The marshrutka takes the same route when going back to Kutaisi and can just be flagged down anywhere along this road.)
When you get to the northern edge of the park the road widens out and after passing the Sports Palace on the left and the now being renovated (although seemed stalled to me) huge Shakhtar Sanatorium on the right the marshrutka heads up to the main market. Get off when the bus turns right at the corner by the ugly, modern Sataplia Hotel. This is where you would look for another marshrutka if you wanted to go to the Prometheus Cave.
To get to the telephone exchange and the Central Park go back along Tseretseli Street (not the road you came up) and the mural is on the left just as the road heads slightly down hill – the park spread out in front of you.
More on the Republic of Georgia