Aurora
More on the ‘Revolutionary Year’
More on the USSR
View of the world
Ukraine – what you’re not told
Celebrate the 104th Anniversary of the Great October Socialist Revolution
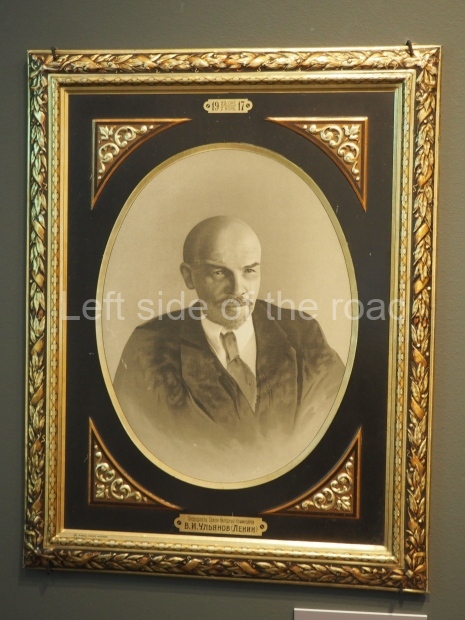
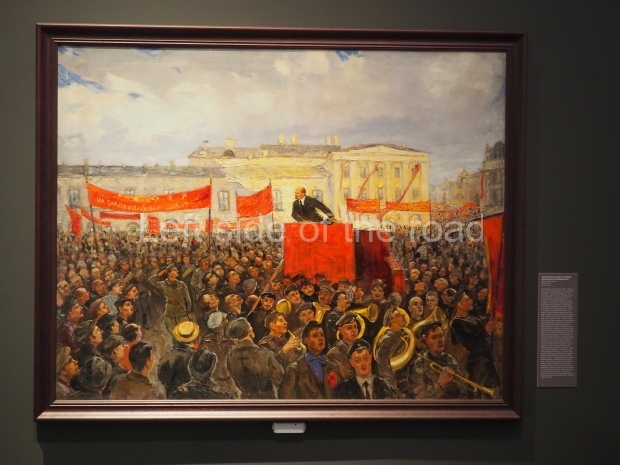
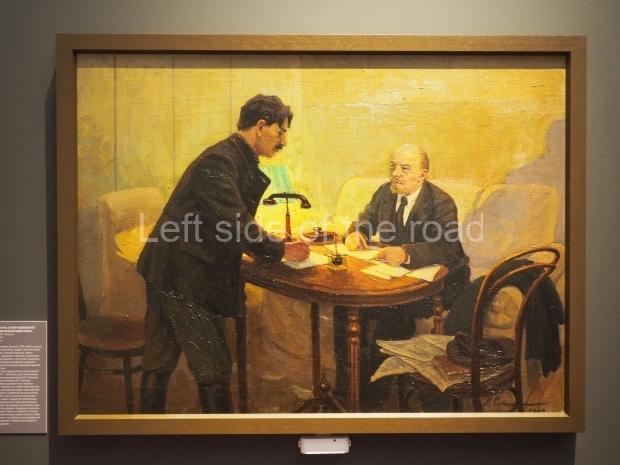
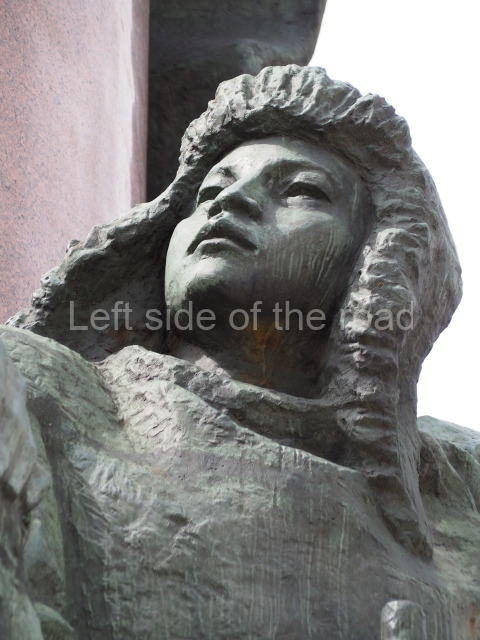
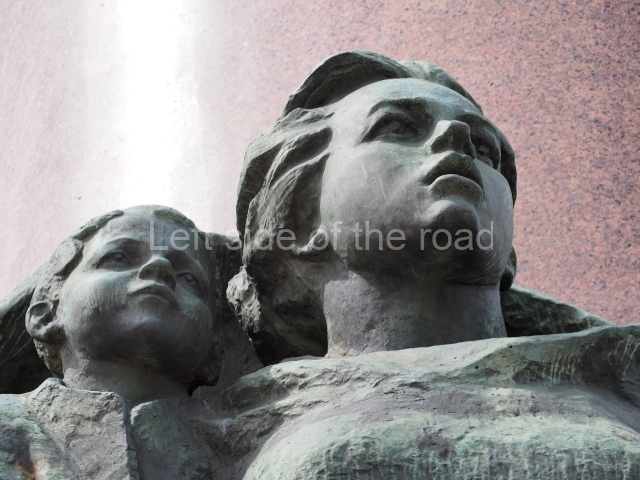
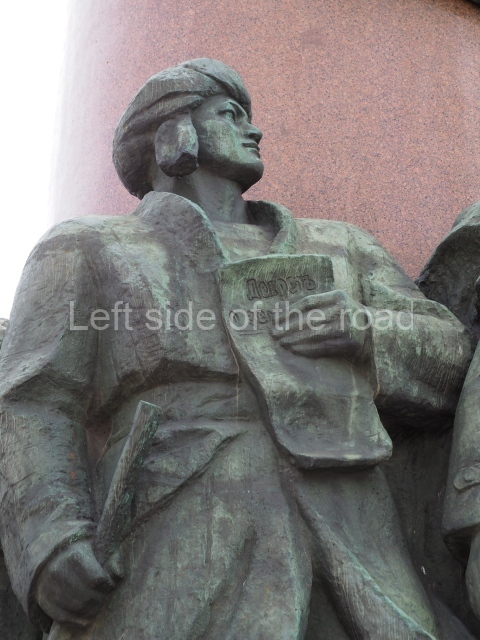
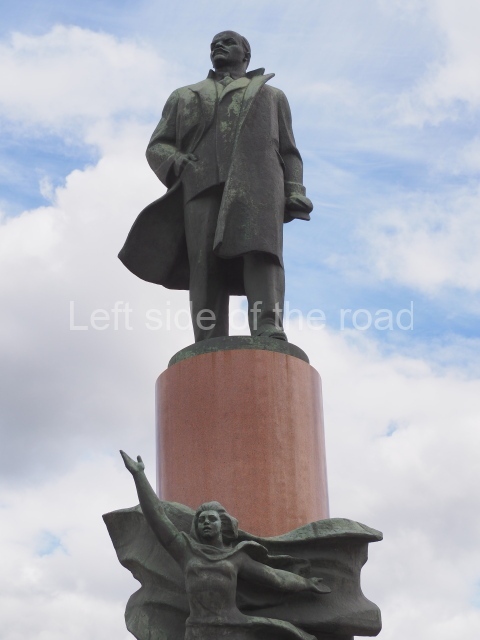
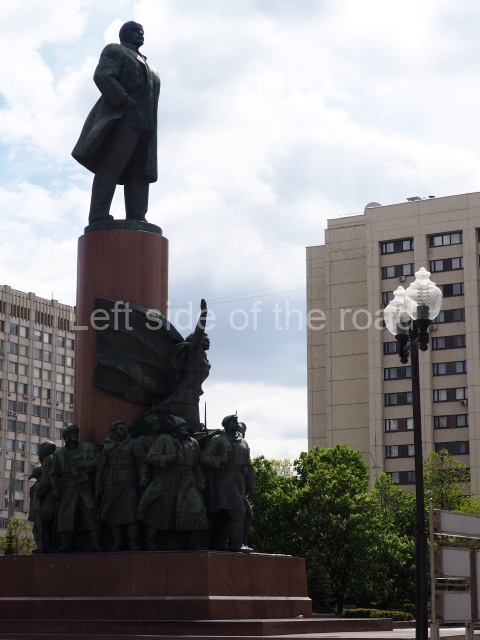
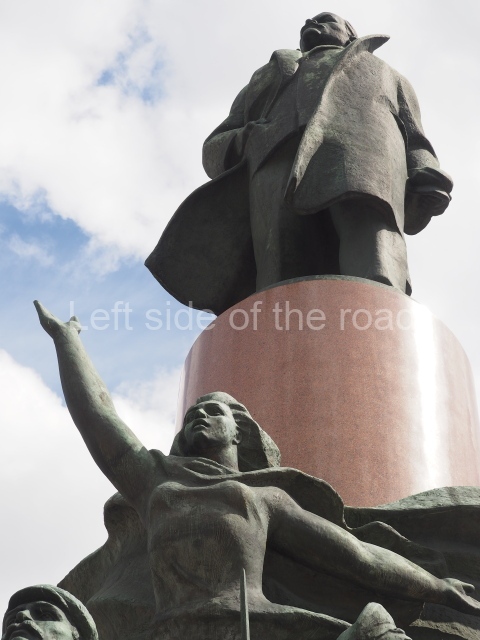
Today is the 104th Anniversary of the Great October Socialist Revolution that started in the early hours of 7th November (25th October – old style) 1917, when the battleship Aurora, anchored on the Neva River in Petrograd, fired its guns to signal the attack on the Winter Palace and to begin the destruction of the failed Tsarist State of Russia.
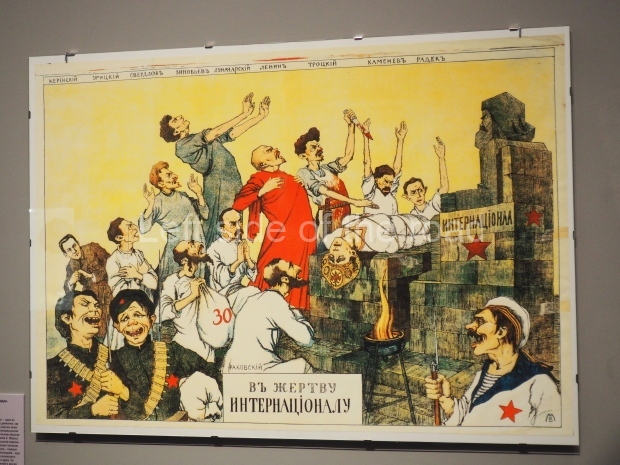
The actual revolution was relatively painless and easy – maintaining it in the early days and then the years from 1918 to 1922 when White reaction tried to turn back the tide of history was much more difficult. Even with the full and active support of the world’s imperialist and capitalist powers (who had spent the previous 4 years trying to physically destroy each other) they failed. The glorious Red Army of the workers and peasants, of what was to become the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (the Soviet Union), displayed their mettle, courage and determination against all comers in order to attempt – for the first time in the world – the momentous and glorious task of the construction of Socialism (leading to Communism) the only way for the oppressed and exploited of the world to finally liberate themselves from the shackles of thousands of years.
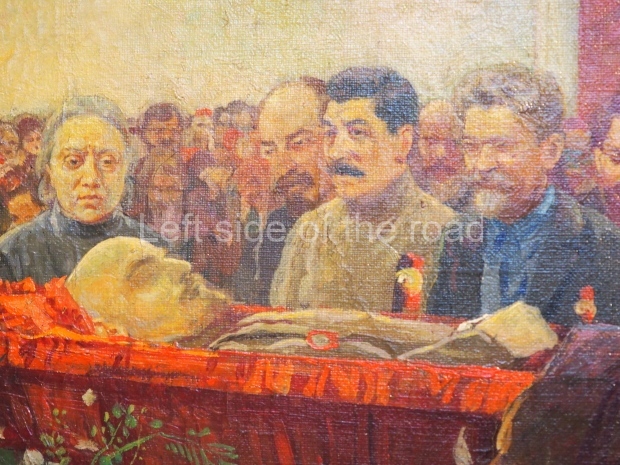
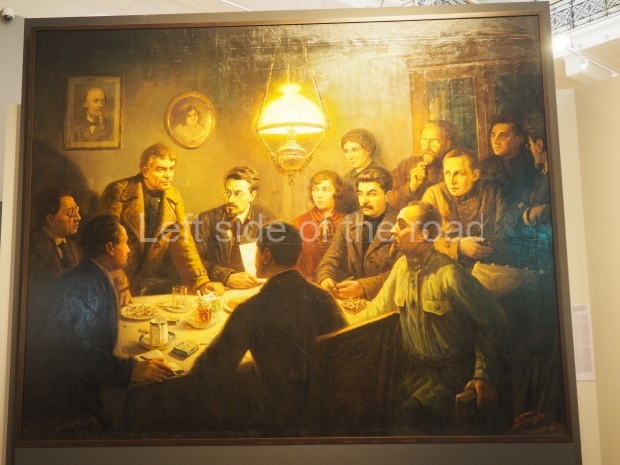
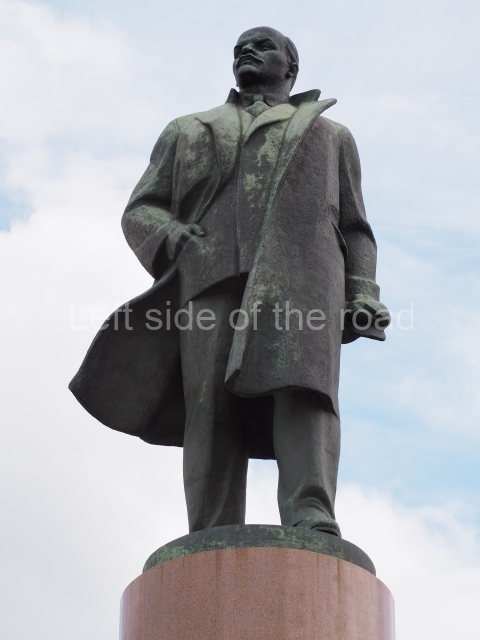
Through the trials and tribulations of the 1920s and 1930s the young Socialist state was able to achieve many successes and as well as making mistakes (although this doesn’t include the purging of the Party of opportunist elements) – both from which future generations will have to learn. Mistakes are to be expected. The first to make their way to their goal along an uncharted course will always face difficulties that for the weak are insurmountable. The Soviet people, under the leadership of the Marxist-Leninist Communist Party of the Soviet Union (Bolshevik) (CPSU(B)) of Comrades Vladimir Ilyich Lenin and Joseph Stalin, showed themselves up for the task.
This was never more so than during some of the darkest days in Europe where it was the Red Army of the Socialist Republic which defeated the Nazi Beast and chased it down to its lair to make the victory final. The debt that the people of Europe, and the world, owe to those courageous Soviet men and women is incalculable.
But the road to a new future is tortuous and difficult. Traitors within ally with the forces of reaction without and undermine the achievements of the past with false promises of plenty in the world of capitalist dominance. In these times of the victory of reaction, ignorance and opportunism there are some (a very few) who benefit from the theft of the public wealth but for the majority of the population such changes are a disaster, in economic, political and cultural terms.
Capitalism never has, doesn’t now and never will offer any long term future for the benefit of the majority of the population of the world.
The victory of Revisionism (and ultimately capitalism) in the Soviet Union in the 1950s was later followed by the collapse of the Socialist systems in the other major revolutionary societies of the People’s Republic of China, the People’s Socialist Republic of Albania and the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. Other societies in Eastern Europe which also attempted to build a new society were to later fall lacking the substance to remain independent (for reasons that are too complex to go into here).
This means that 104 years after the momentous events in what was to become (and still is) Leningrad the world is yet again totally dominated by the moribund system of capitalism and imperialism.
People continue to fight – they always will – but without the leadership, the strategy and the perspective that can lead them to a bright future. Issue politics dominate and even in those national liberation movements that are nascent in certain countries the movement is fractured, divided and weak.
Comrade Mao Tse-tung, said that ‘either revolution will prevent a world war or a world war will lead to revolution’. That insightful analysis is as pertinent now as it was many years ago – at a time when the tide of revolution was on the rise.
For the world is becoming a dangerous place once more – with various capitalist/imperialist states jockeying for position of dominance.
The leaders of the erstwhile Socialist states of China and Russia no longer have the social conscience of the revisionists of the past. Even the arch-renegade Khrushchev recognised that when faced with the belligerent and bellicose attitude of the warmonger Kennedy in 1961 in Cuba. The American imperialists were prepared to destroy the world in order to determine what should happen in ‘their back yard’ but it was Khrushchev who made the moral decision to withdraw and prevent a potential nuclear holocaust – even against the wishes of the Cuban people themselves.
Now the contending forces no longer have that social conscience ‘brake’ on their ambitions.
However, the future does not belong to the old order. It constantly demonstrates, even in its homelands, that the sufferings of working people are of no concern and that their lives are expendable if they produce no profit for their system.
Yes, the weapons at the disposal of these warmongers are vastly superior and more destructive than those available just a few decades ago. If the world falls into another international conflict (different from the surrogate wars that have dominated the last 70 or more years) then the destruction will be immense and there are doubts whether society would be able to recover from such devastation.
That makes learning the lessons of the Great October Socialist Revolution, the strategy and tactics, the importance of leadership, the embedding of the Party amongst the population even more of an urgent task.
The people will win, ultimately. What they have to do is to decide if they want to build a new society free from exploitation when conditions are more or less stable or whether they want to do so from the ashes and in a poisonous atmosphere of a world destroyed at the whim of capitalism, whether it be through the destruction of the ecosystem due to the constant thirst for profit or the result of a nuclear or biological holocaust.
Long live the Great October Socialist Revolution!
Long live Marxism-Leninism-Maoism!
Forward to a future free of exploitation and oppression!
More on the ‘Revolutionary Year’
More on the USSR
View of the world
Ukraine – what you’re not told