Dzibilnocac – Campeche
Location
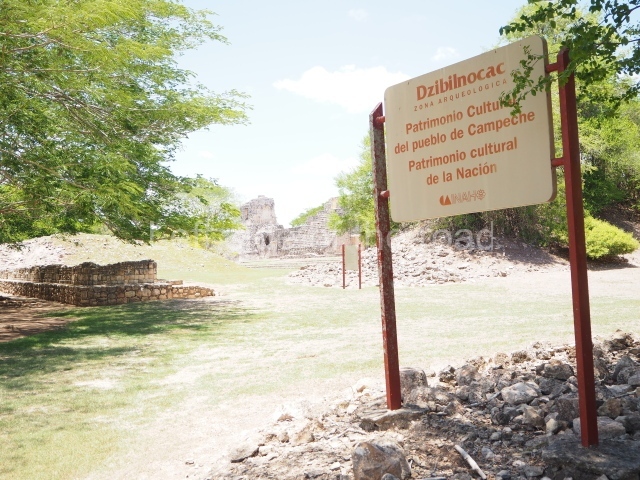
The archaeological area, and the western section in particular, has been severely affected by the modern town of Iturbide. Dzibilnocac was coined recently (20th century) and is a reference to a ‘hieroglyphic inscription on a large turtle’, possibly an allusion to a stone sculpture now lost. The site is situated 150 km south-east of Campeche City. Take the road from the latter to Hopelchen, continue to Dzibalchen and then on to Iturbide (officially, Vicente Guerrero).
Timeline, site description and monuments
A radiocarbon date and ceramic material from the Middle Preclassic confirm that the site began to develop around 400 BC. The architectural and sculptural remains show that it reached its peak during the Late Classic (AD 600-900), while the ceramics suggest that the site was abandoned around AD 1000.
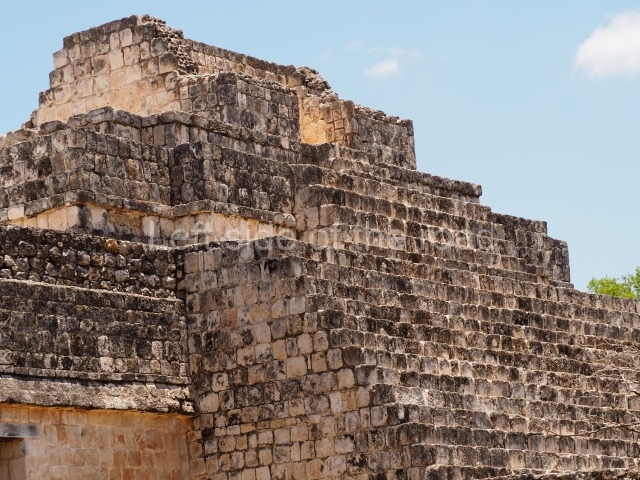
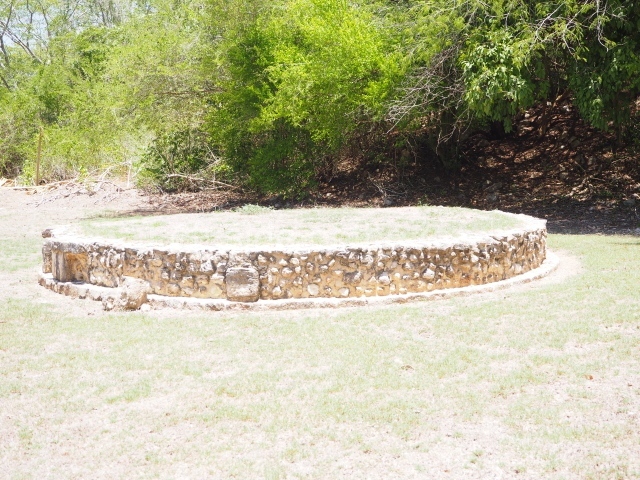
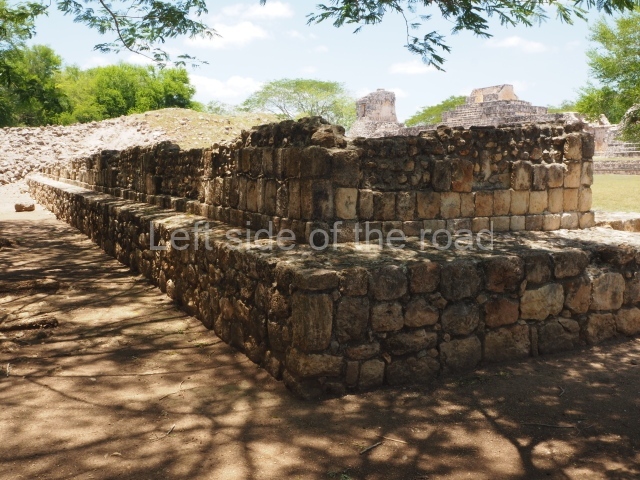
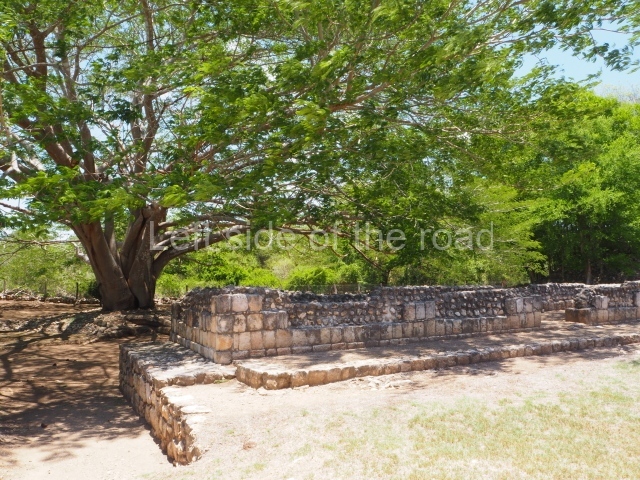
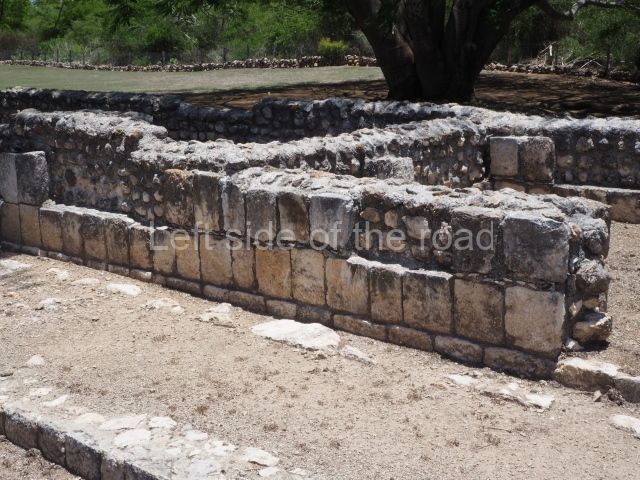
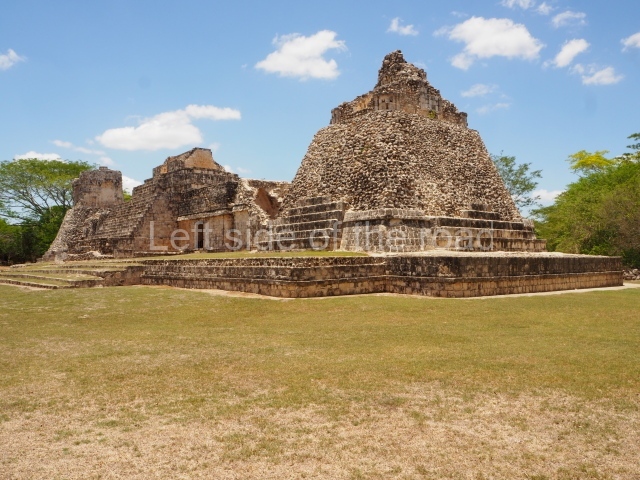
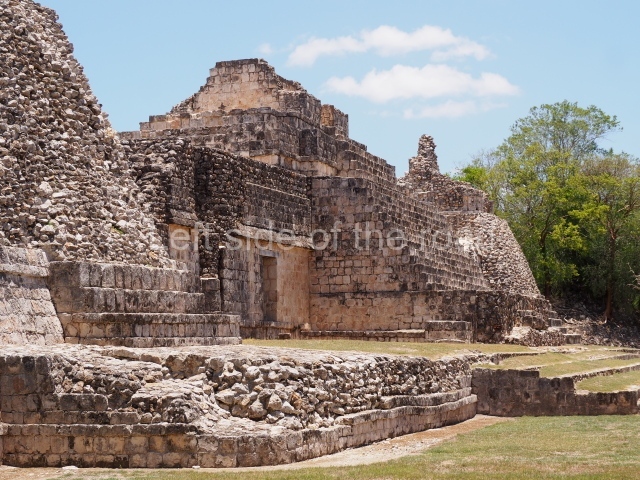
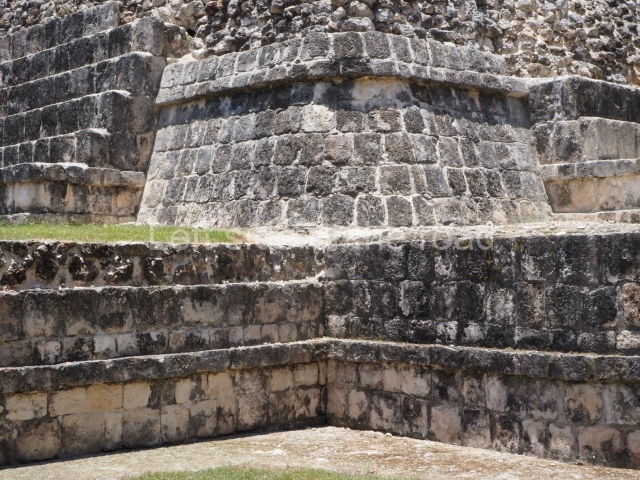
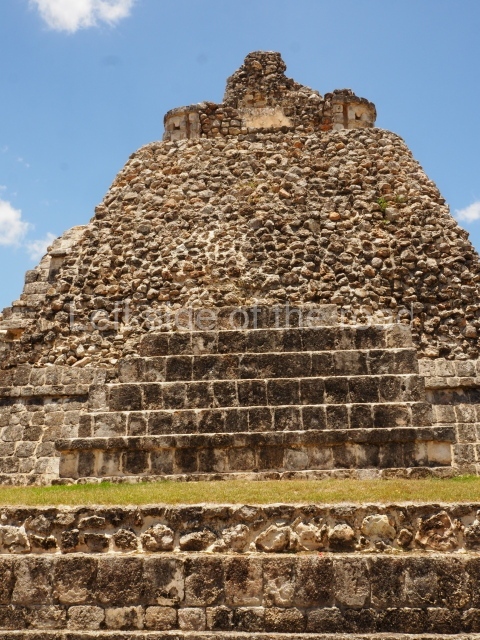
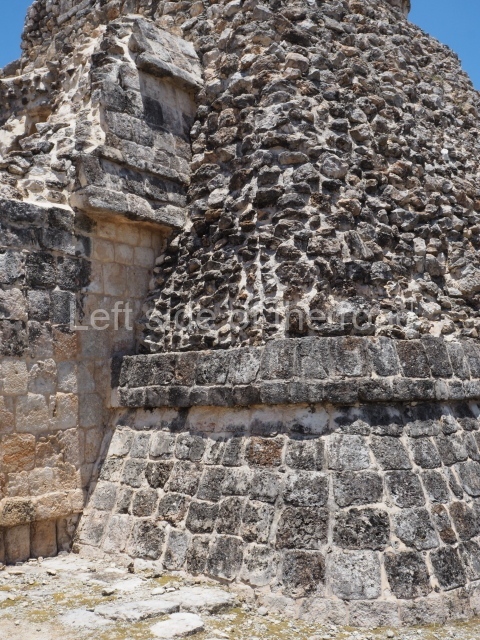
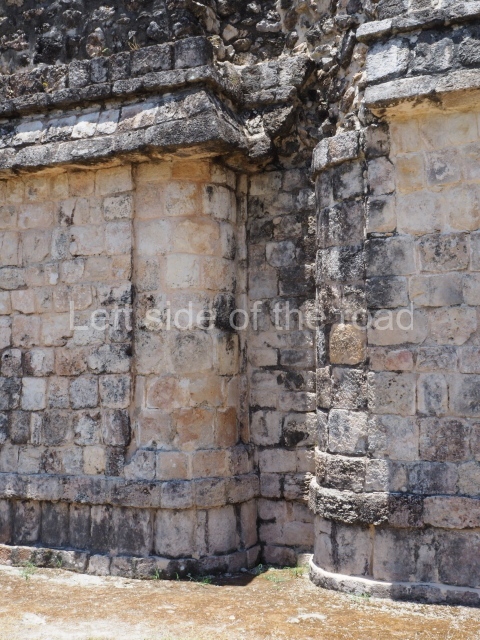
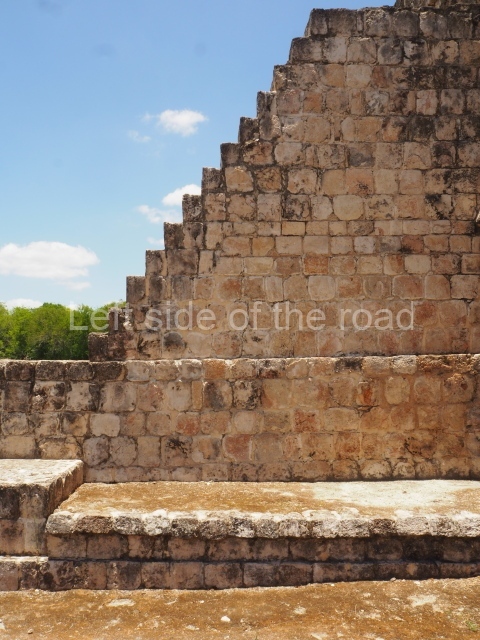
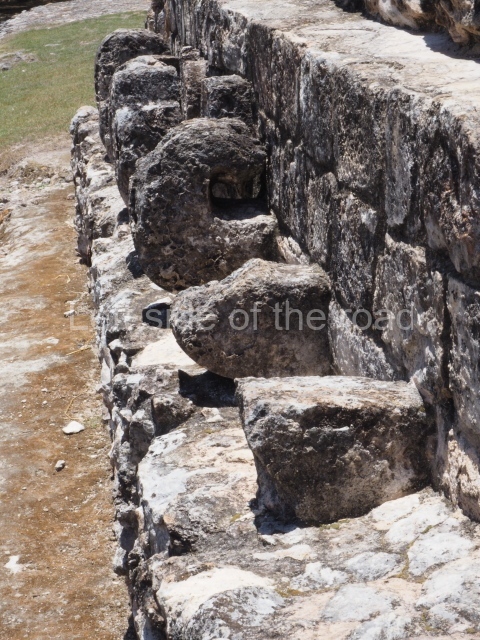
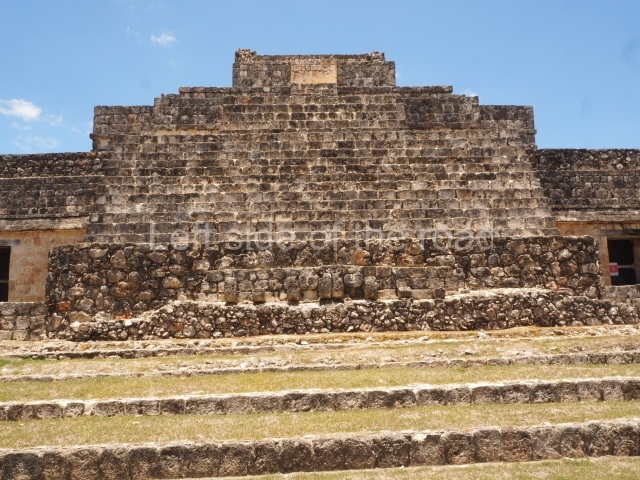
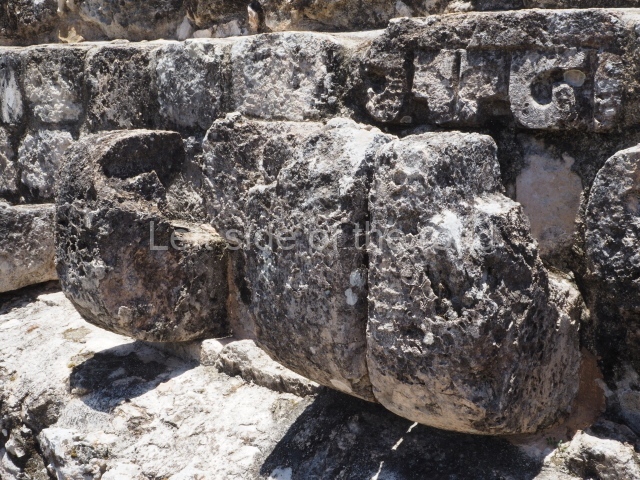
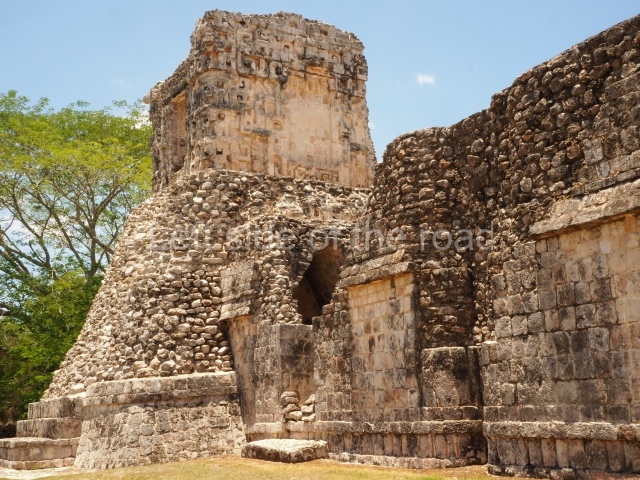
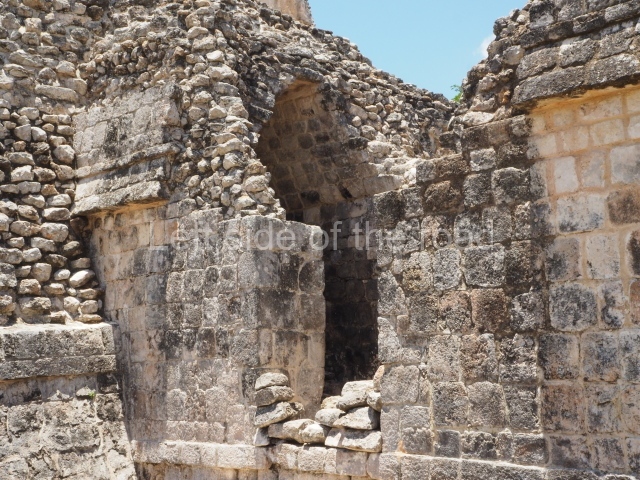
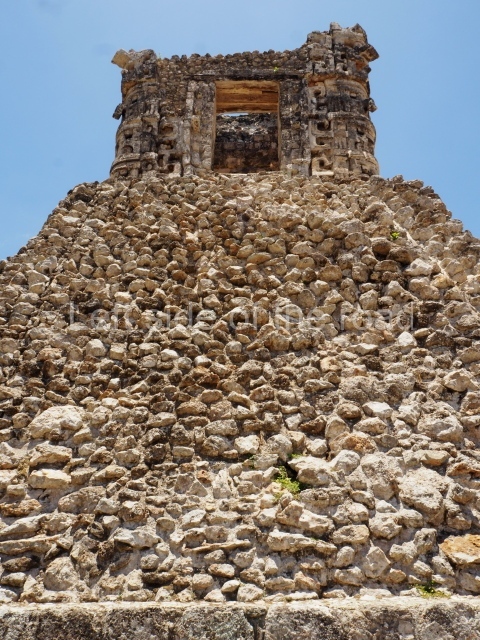
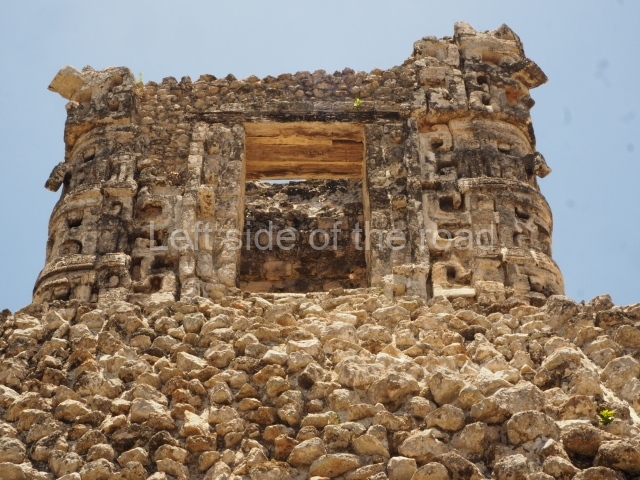
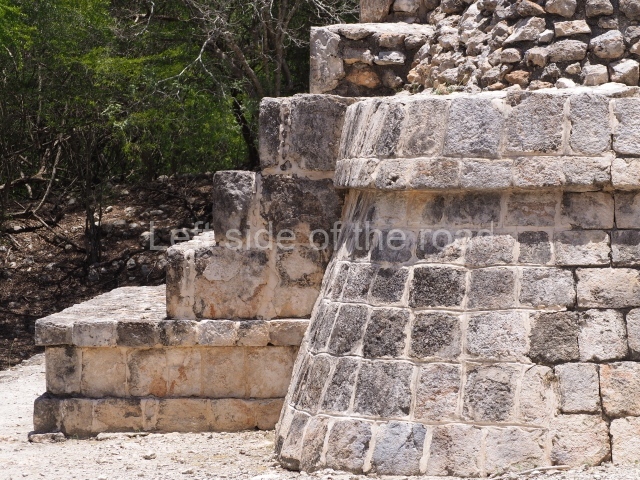
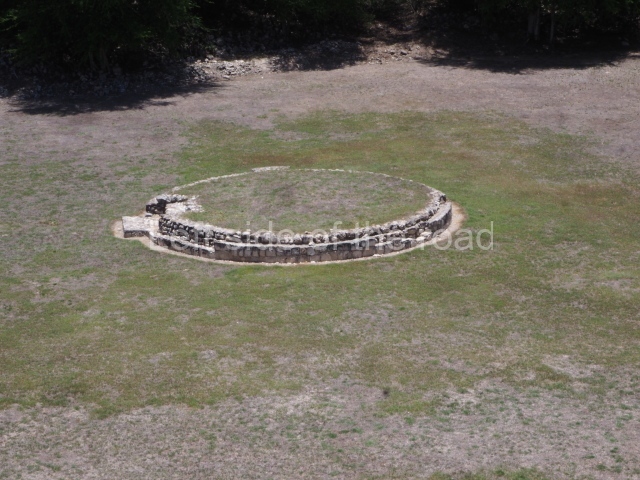
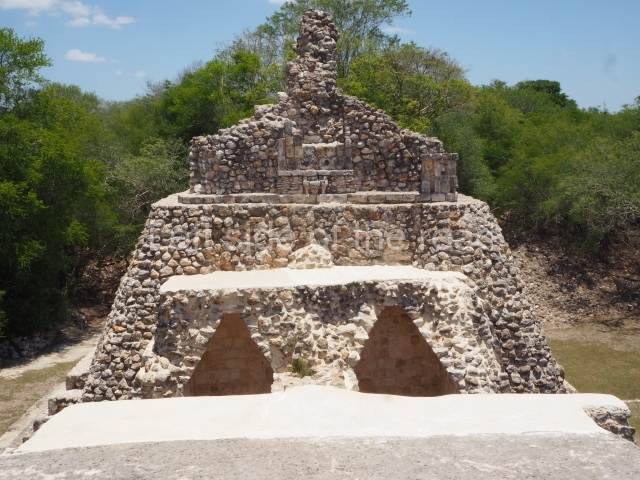
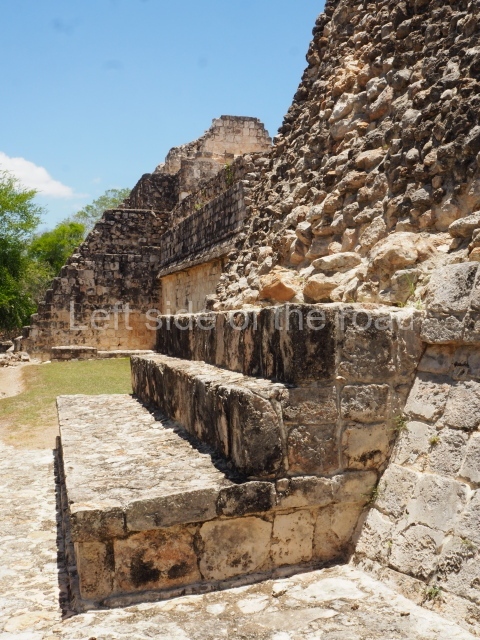
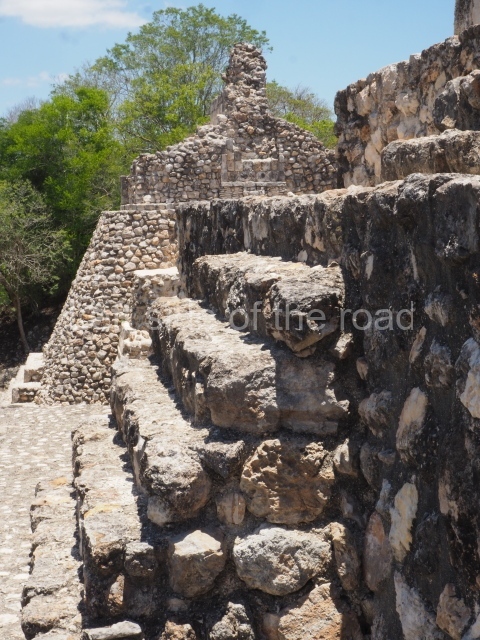
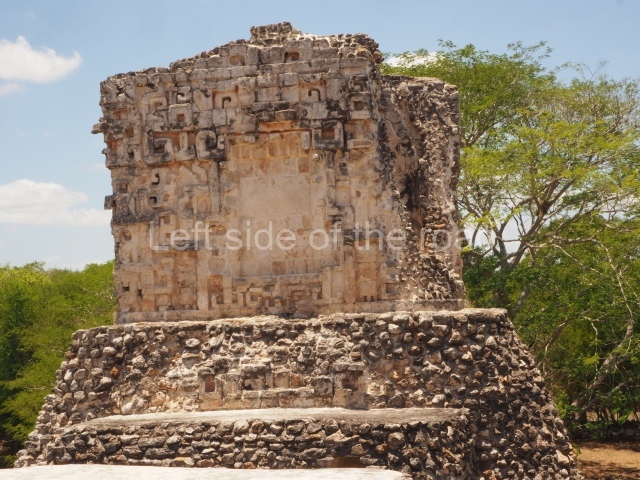
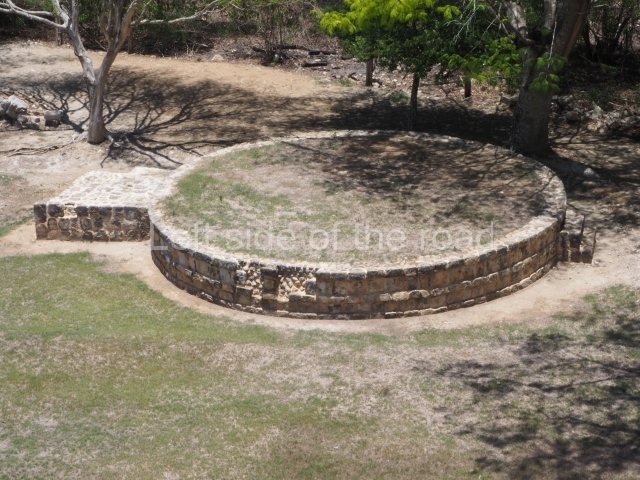
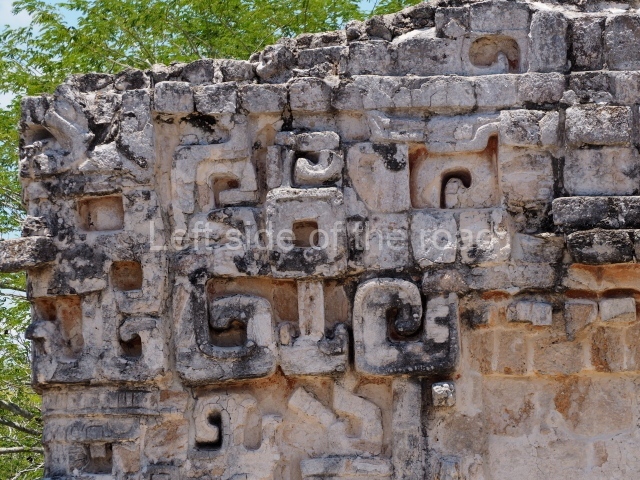
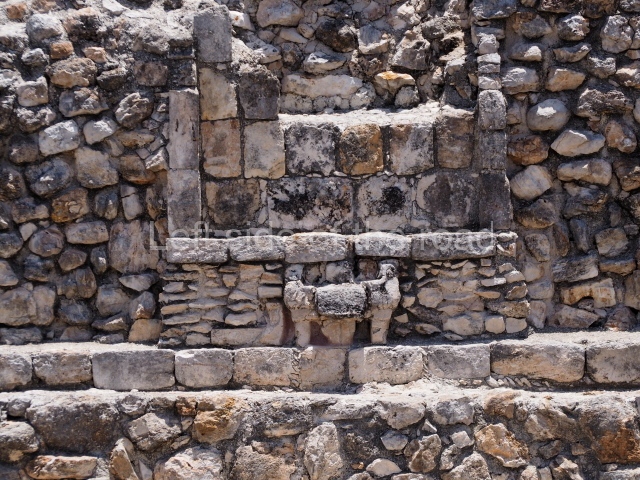
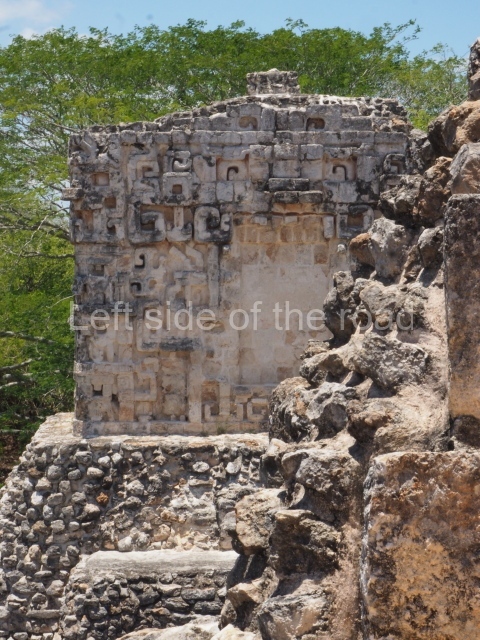
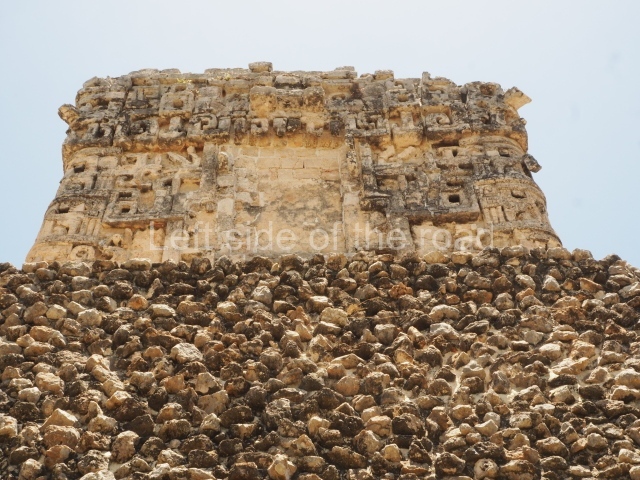
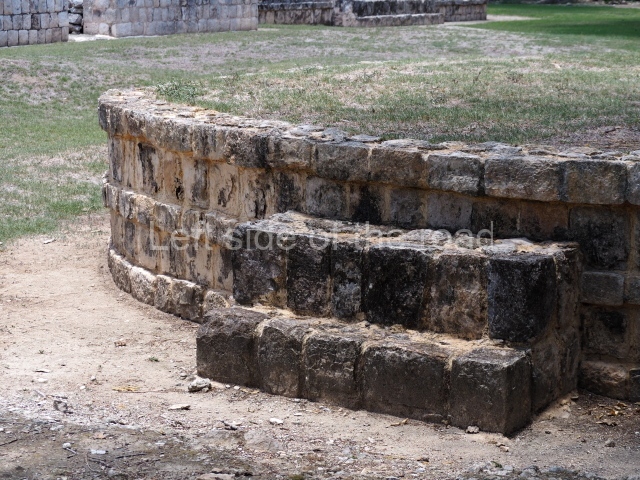
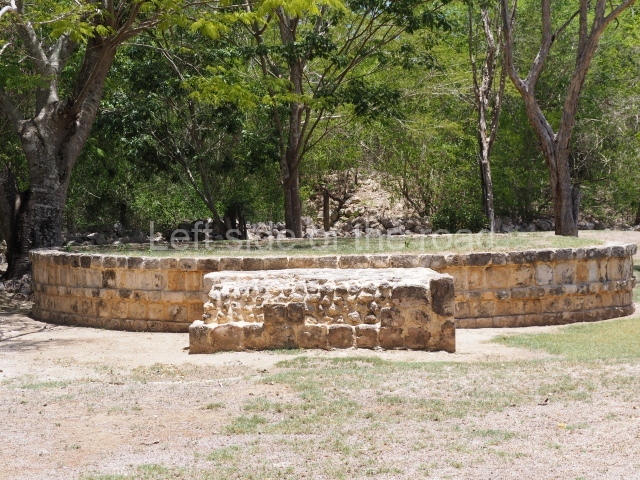
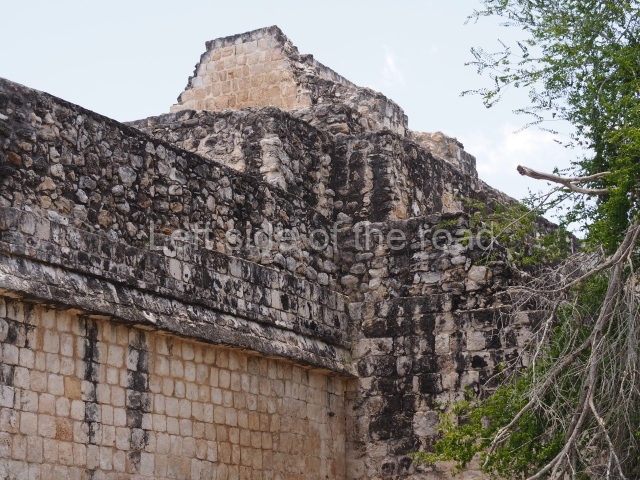
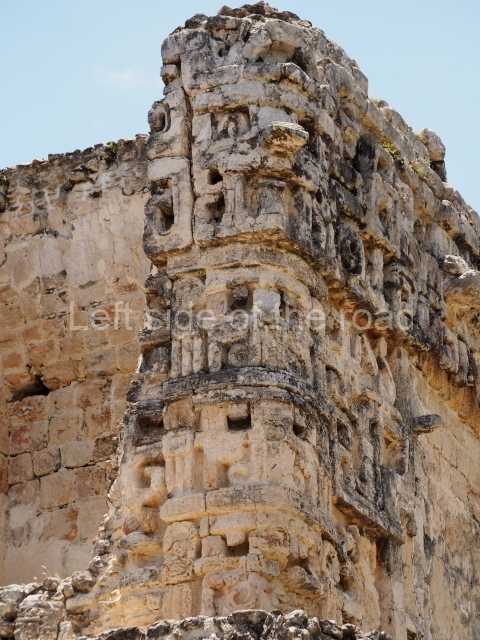
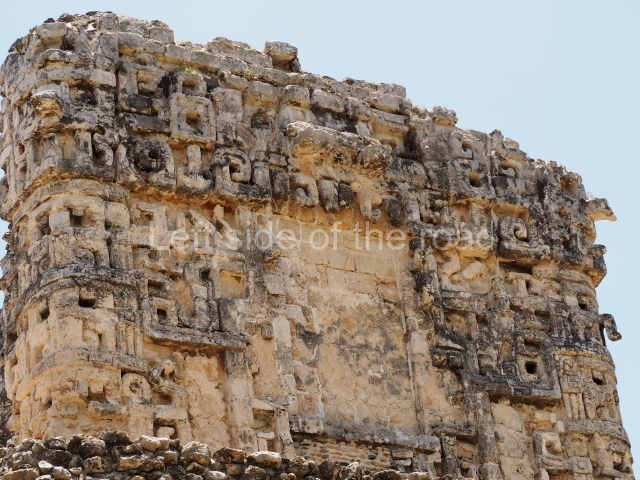
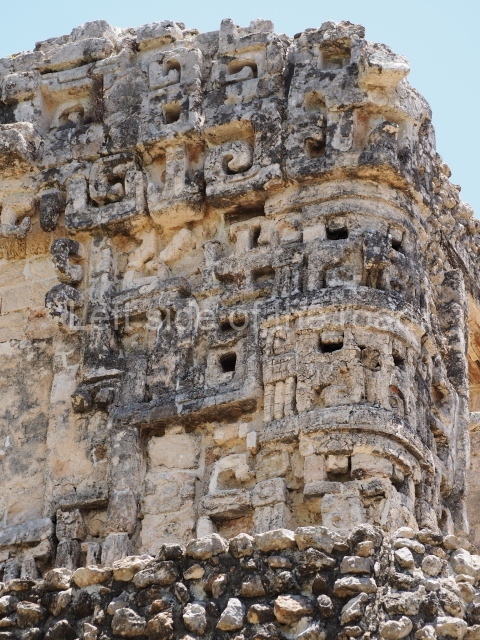
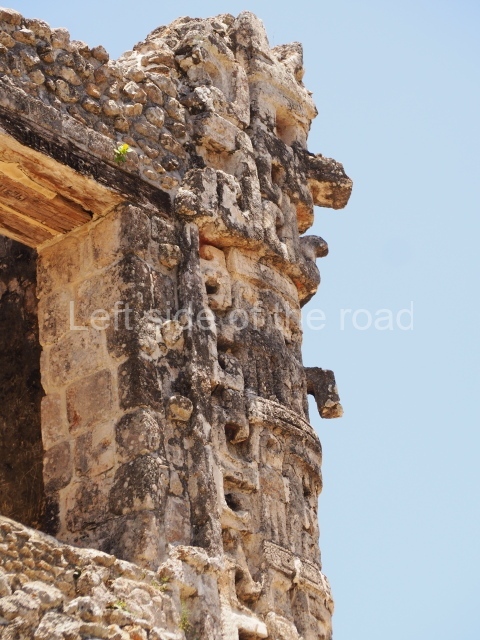
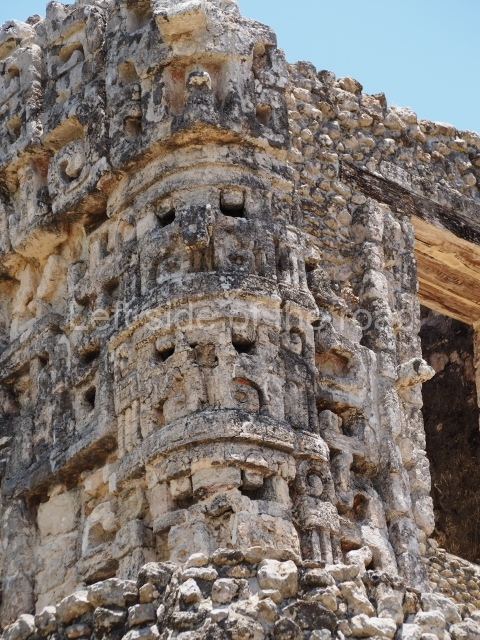
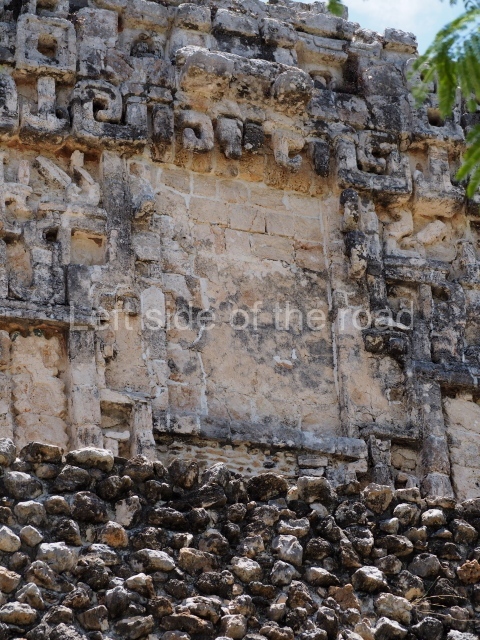
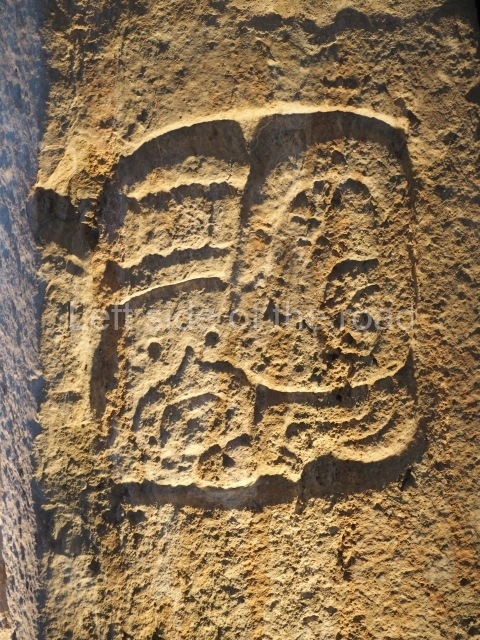
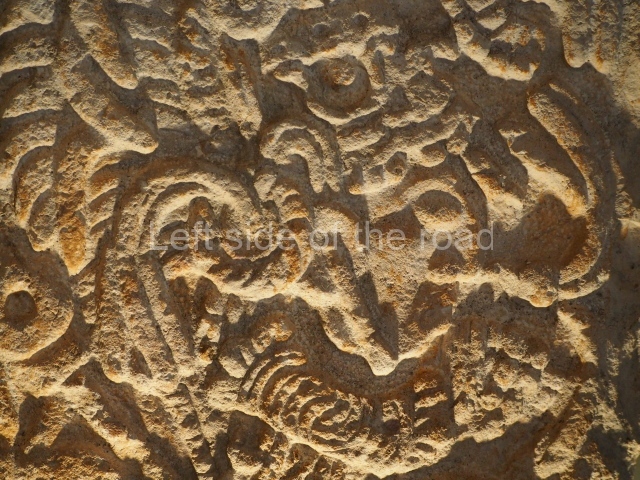
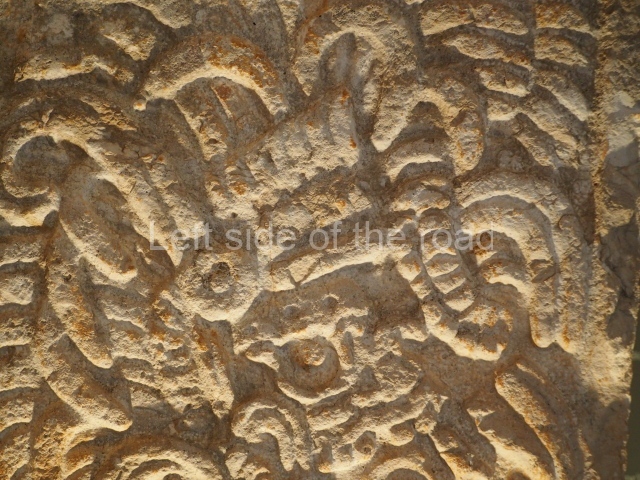
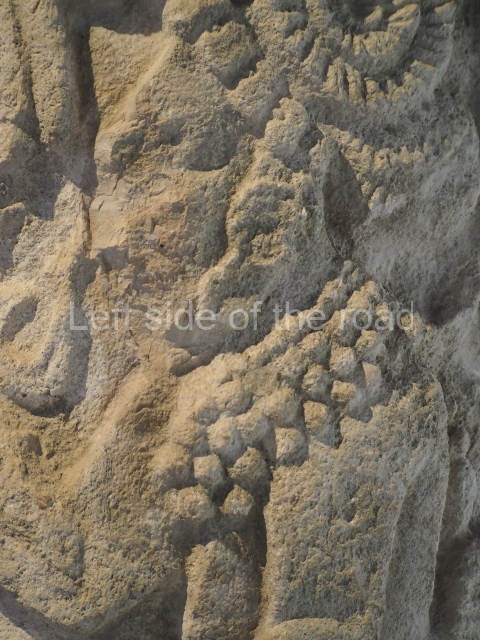
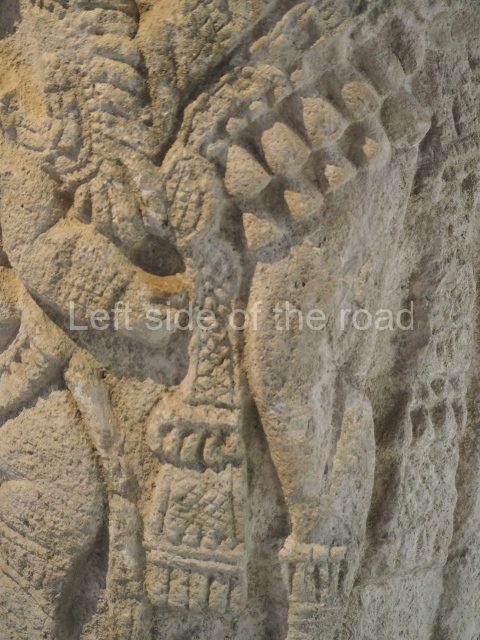
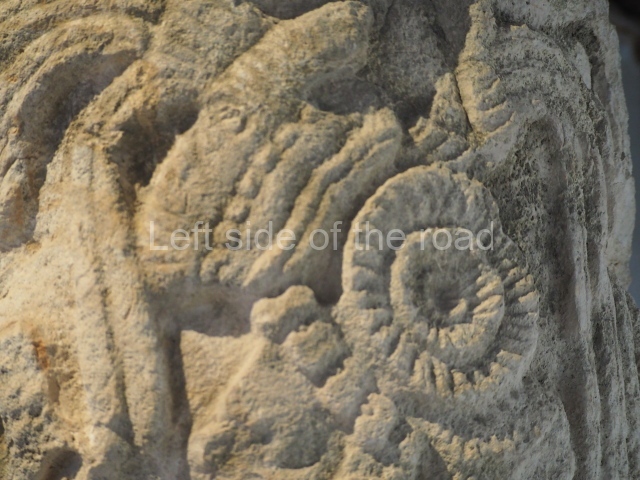
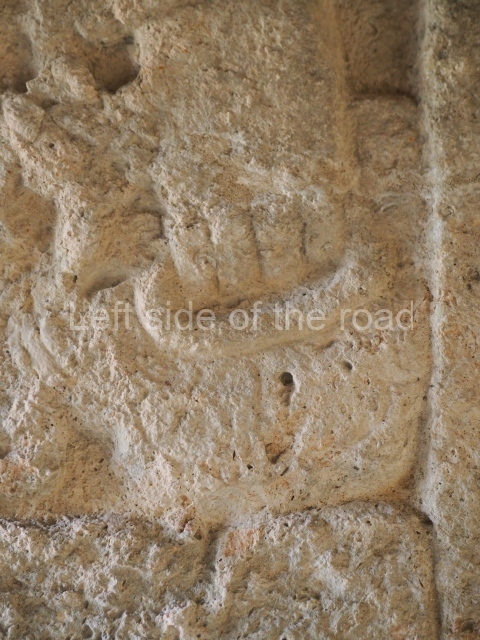
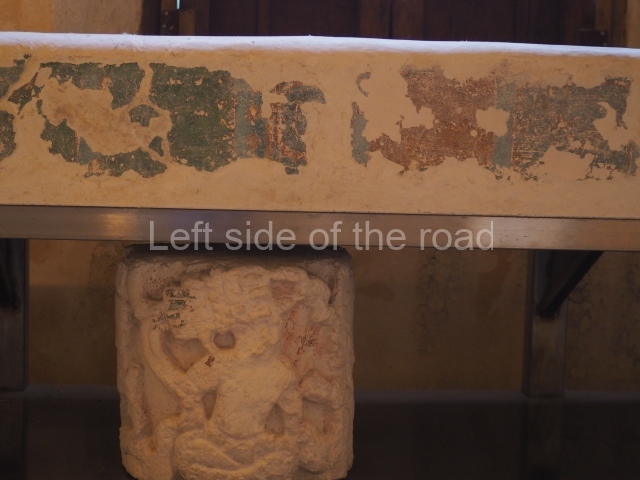
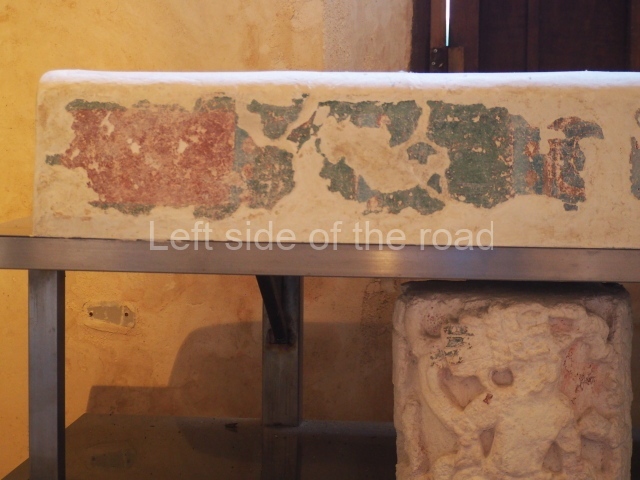
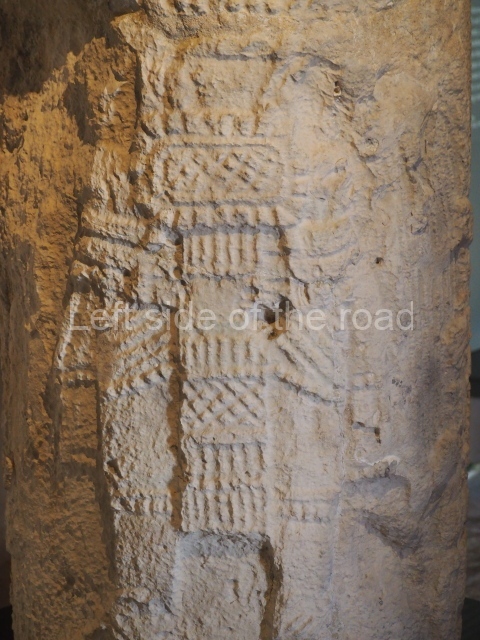
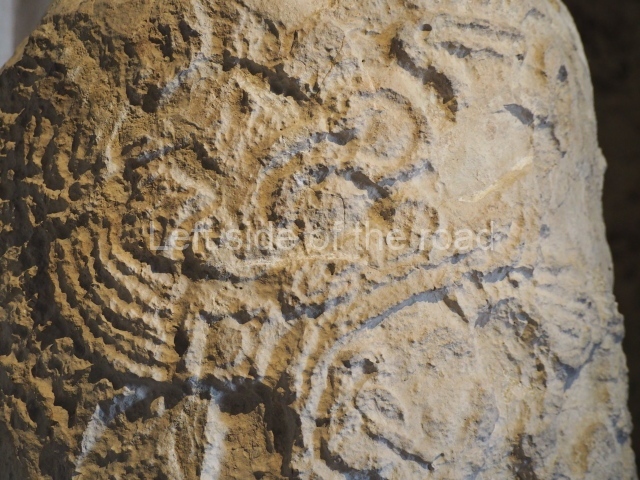
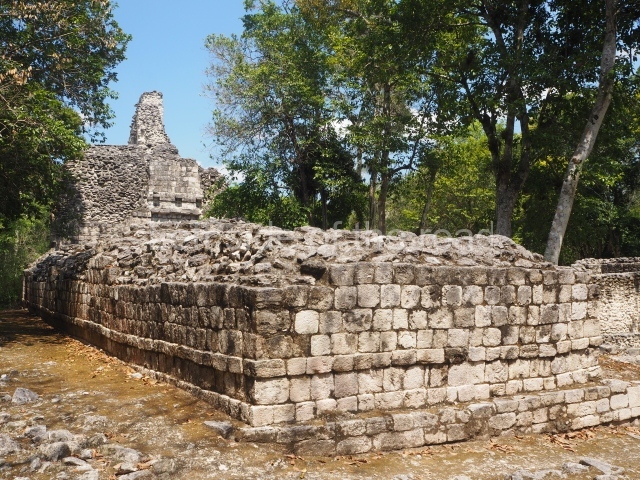
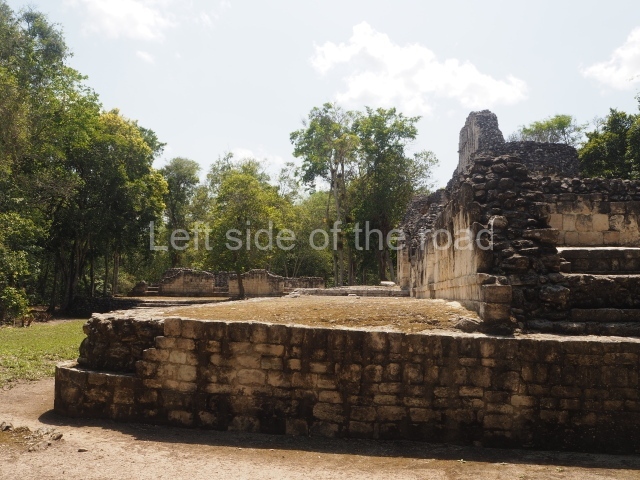
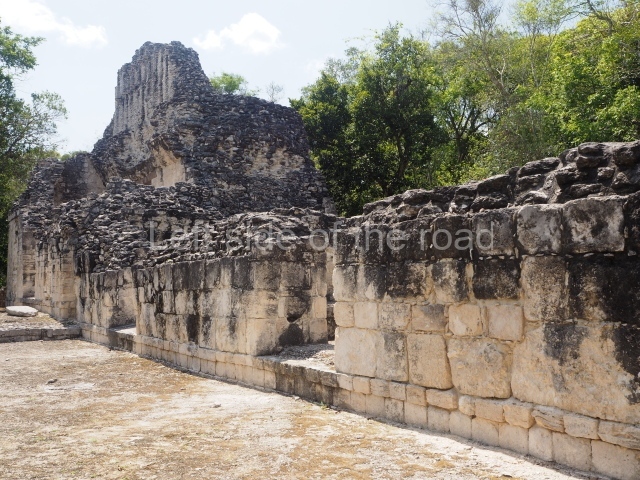
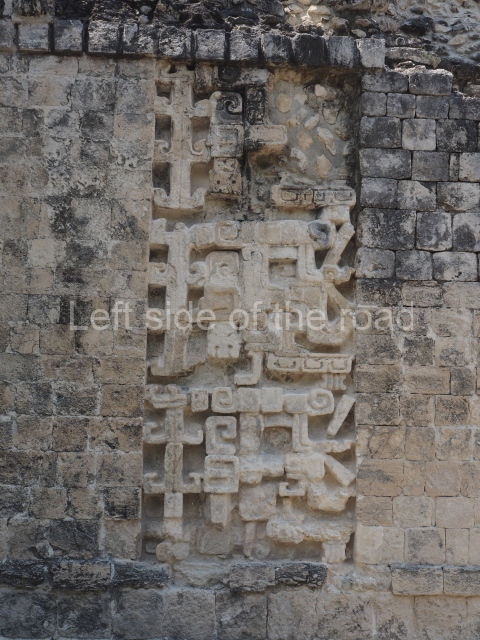
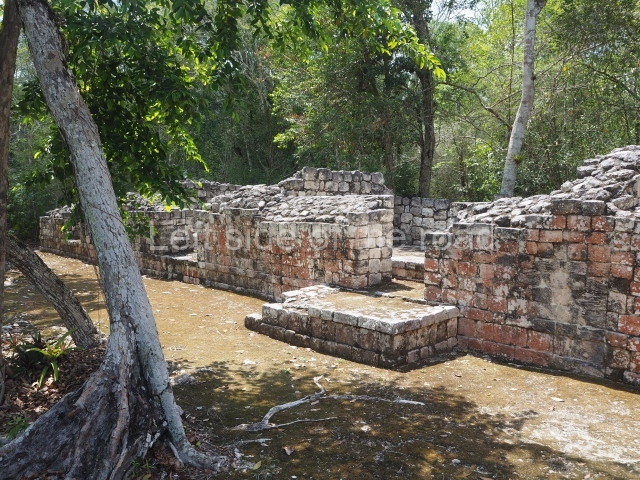
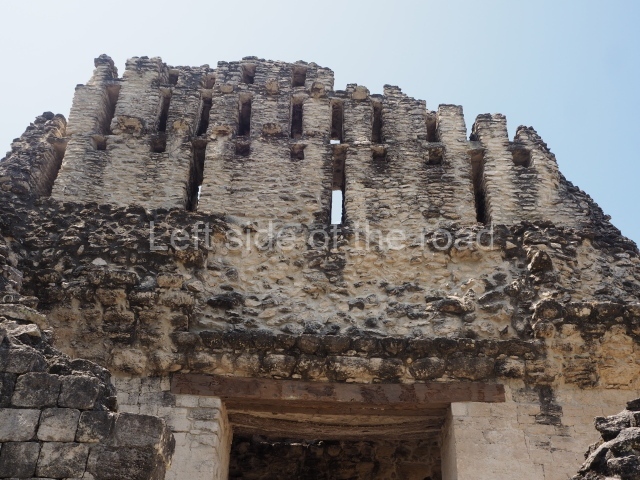
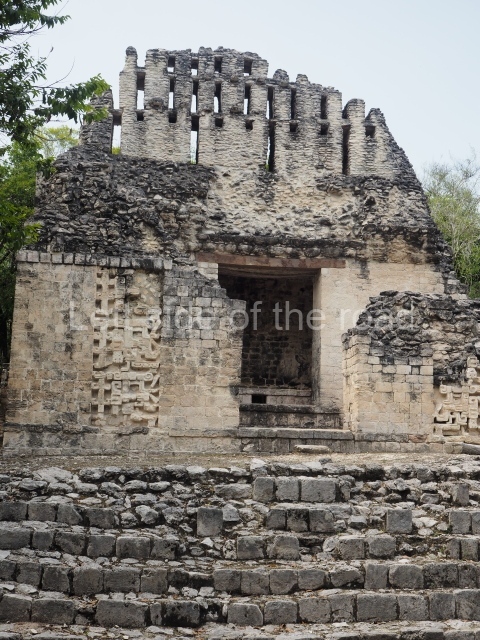
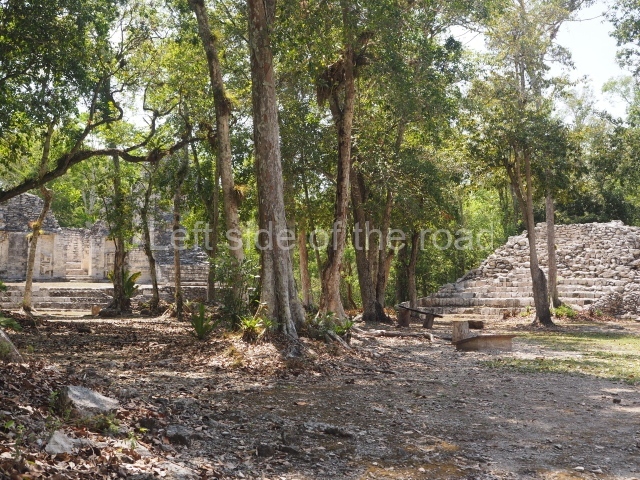
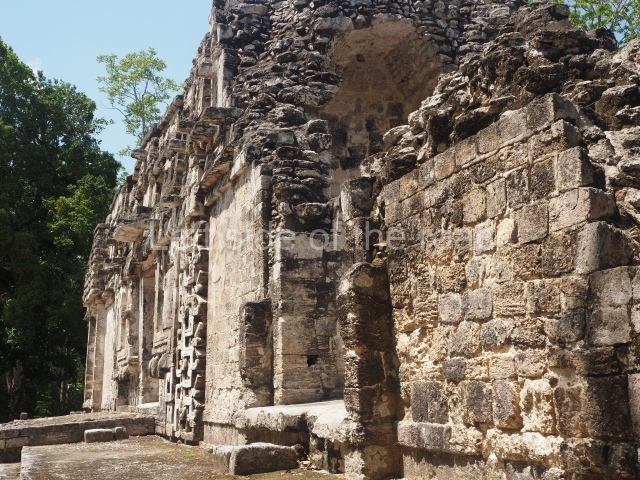
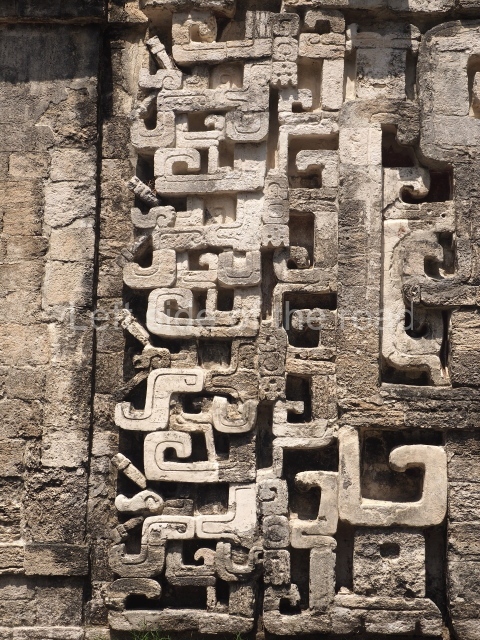
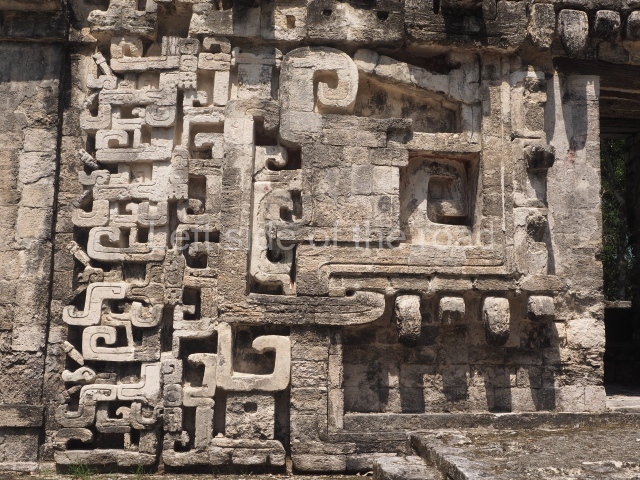
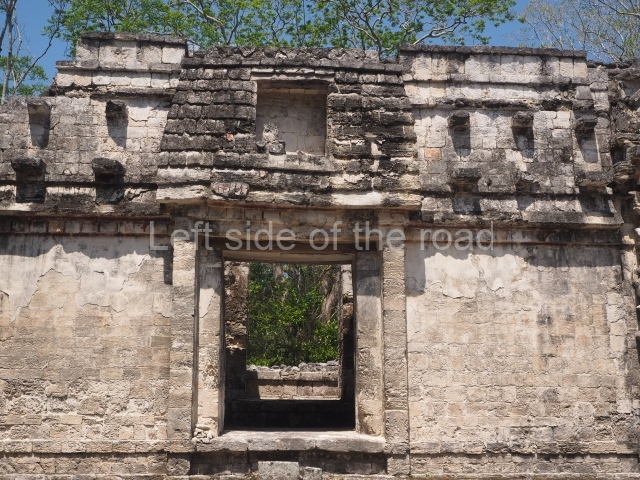
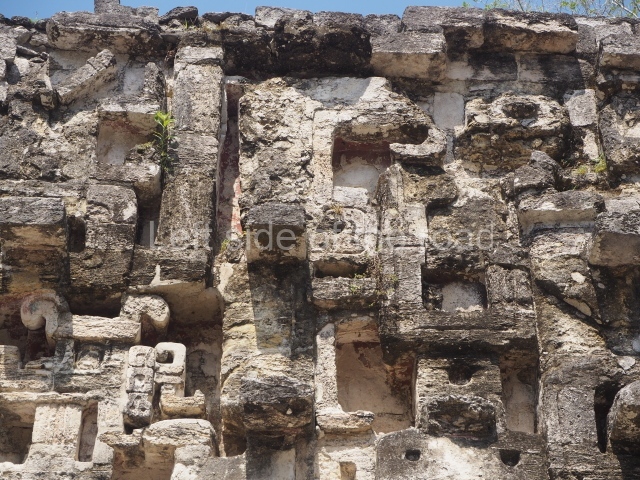
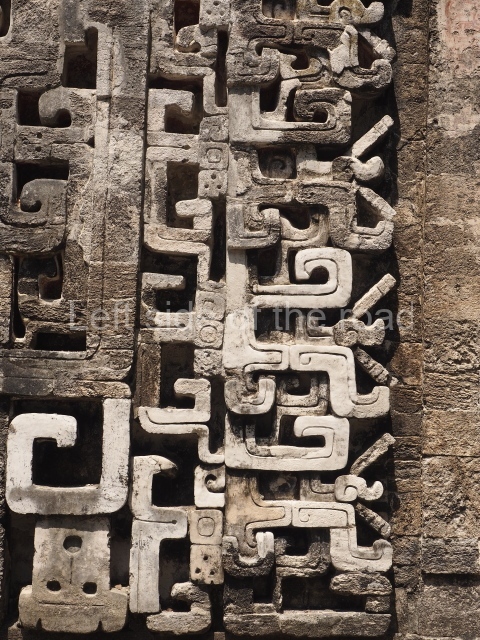
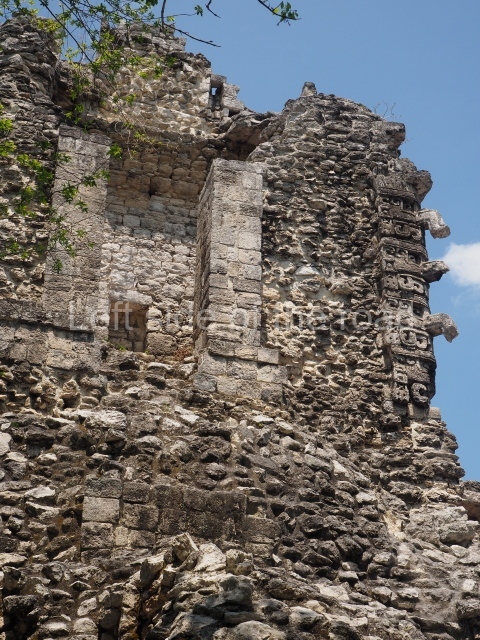
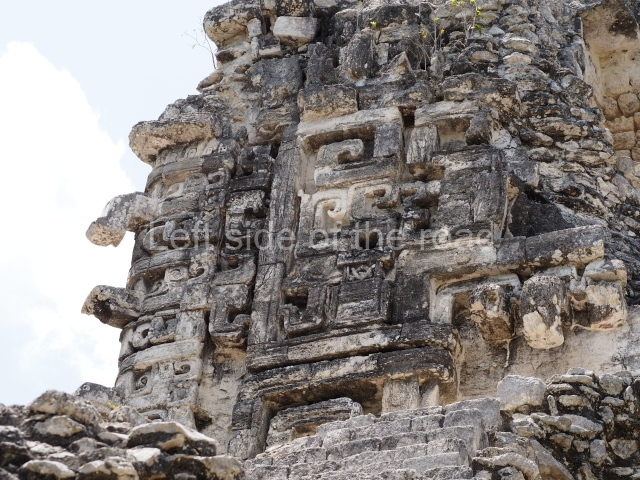
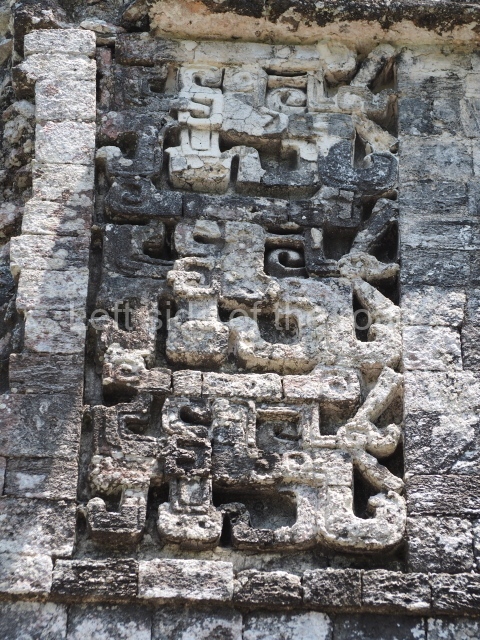
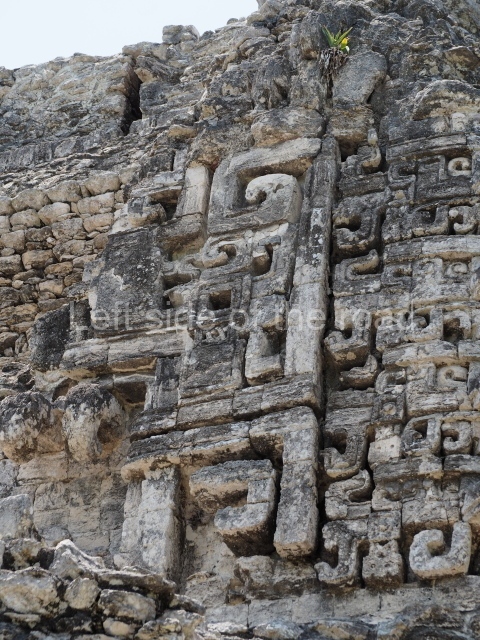
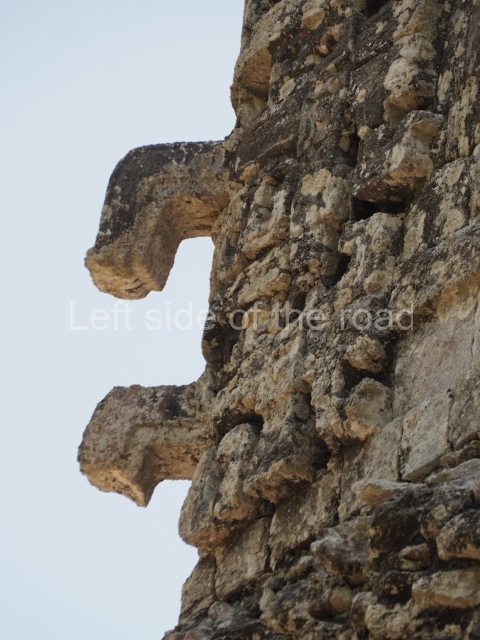
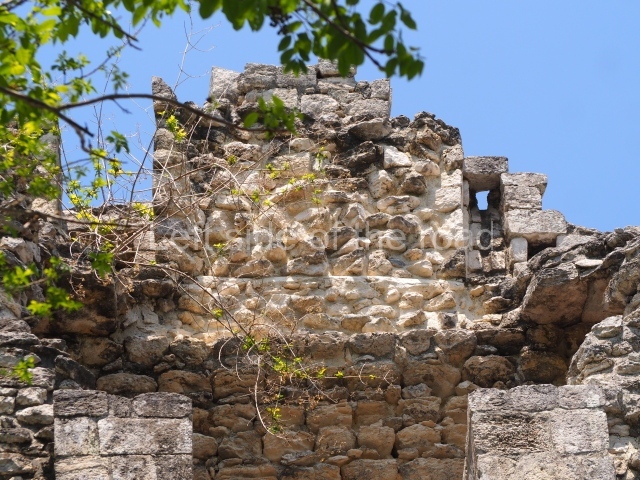
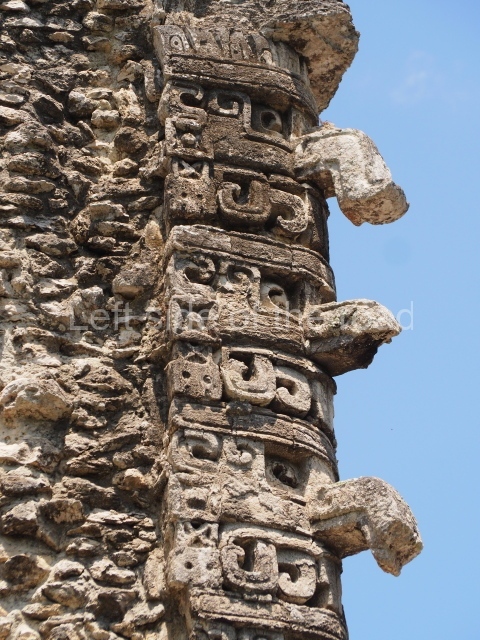
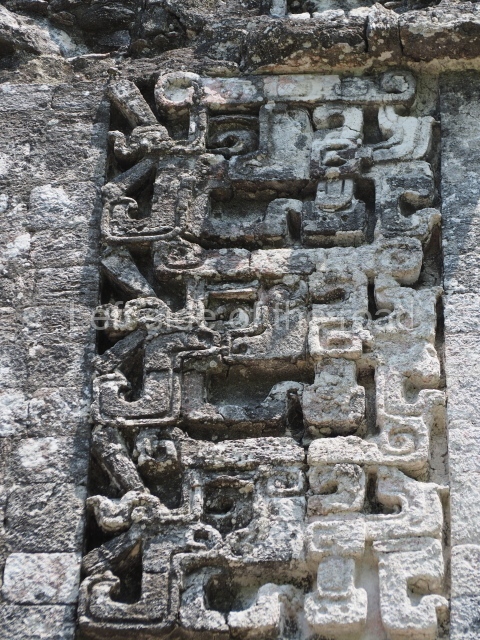
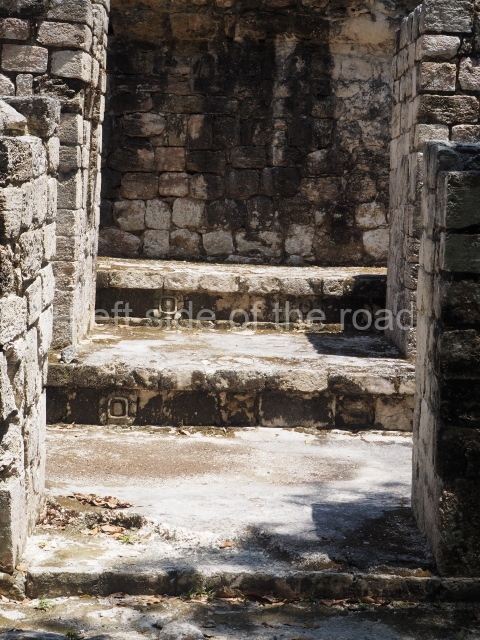
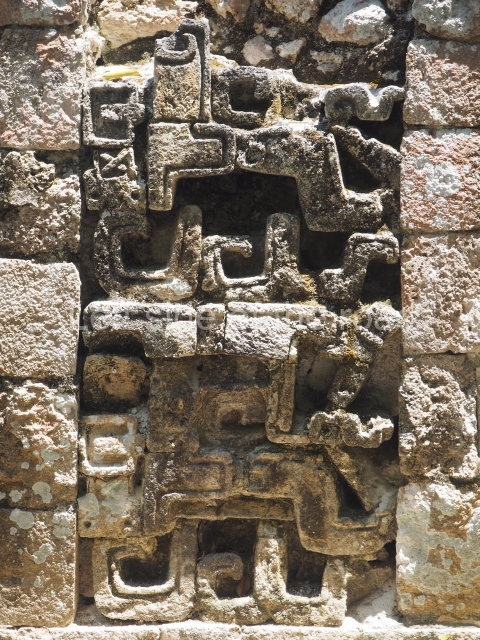
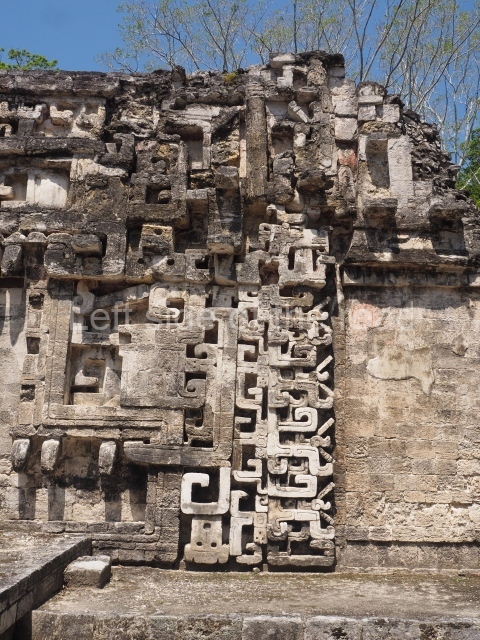
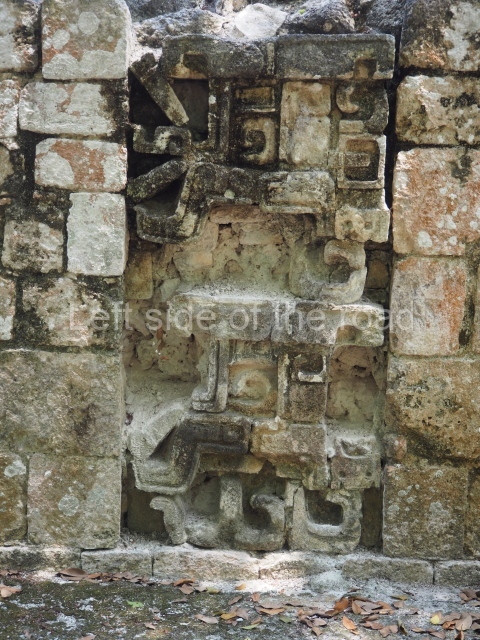
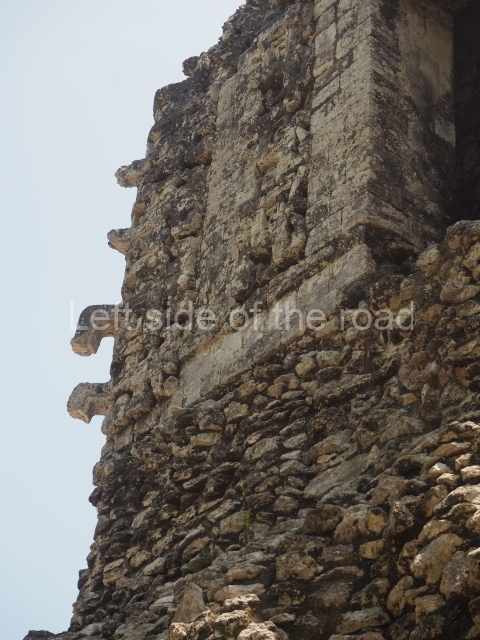
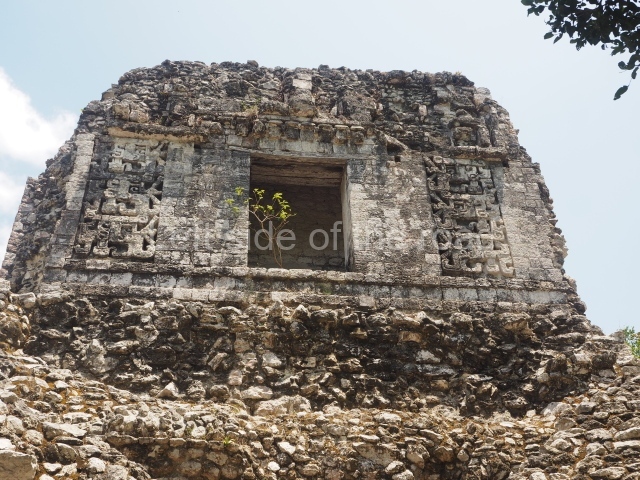
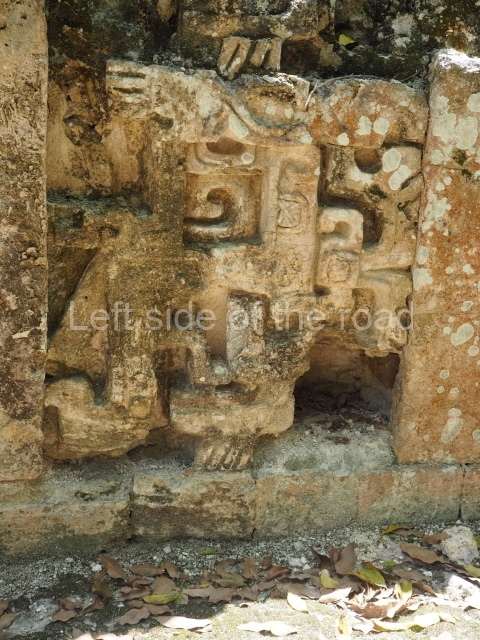
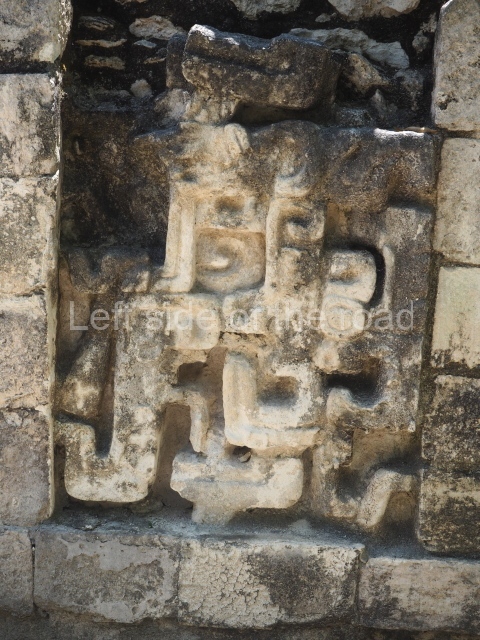
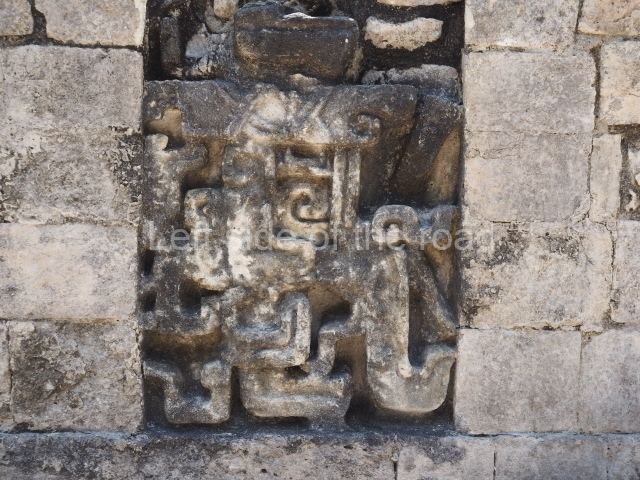
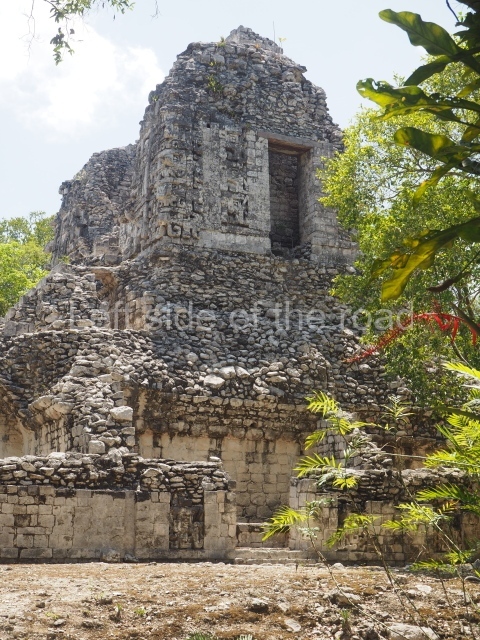
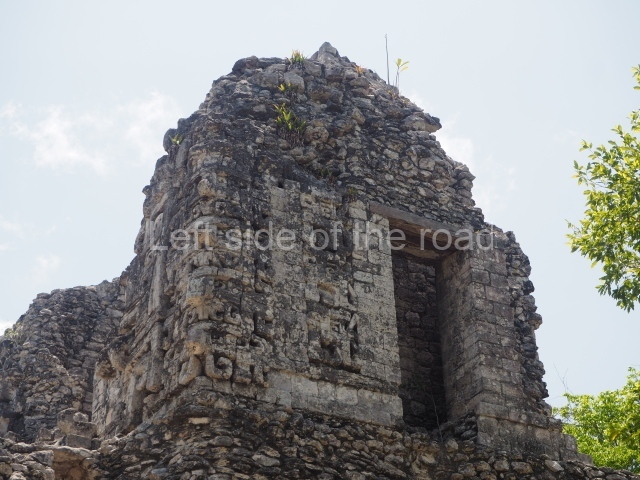
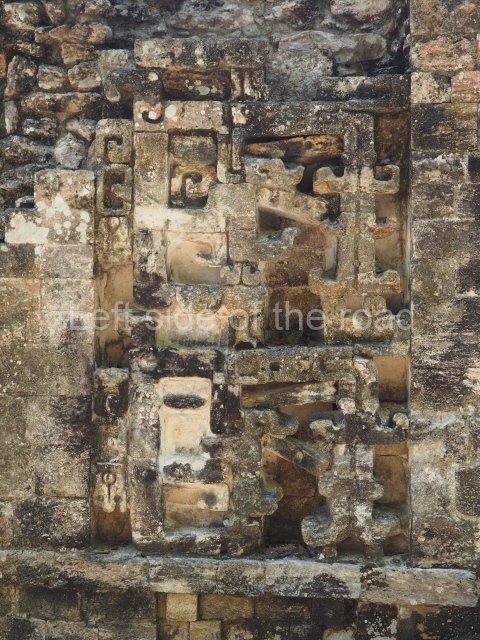
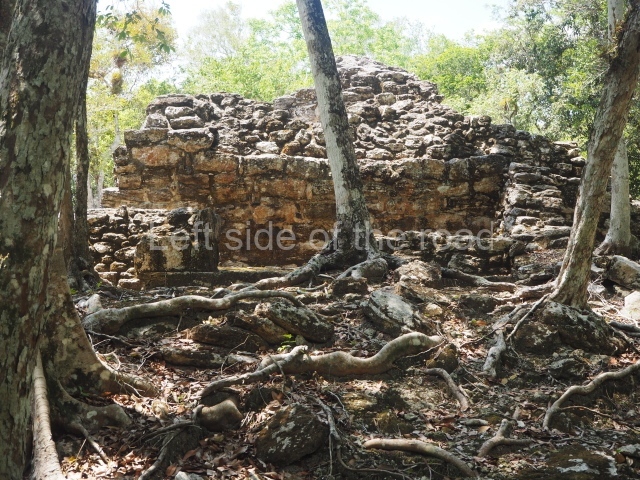
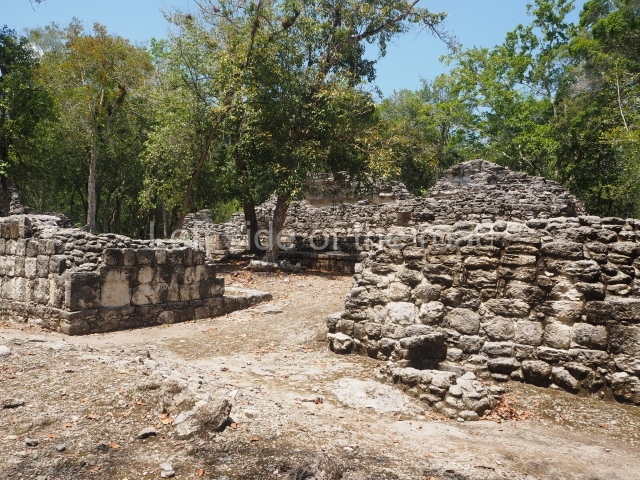
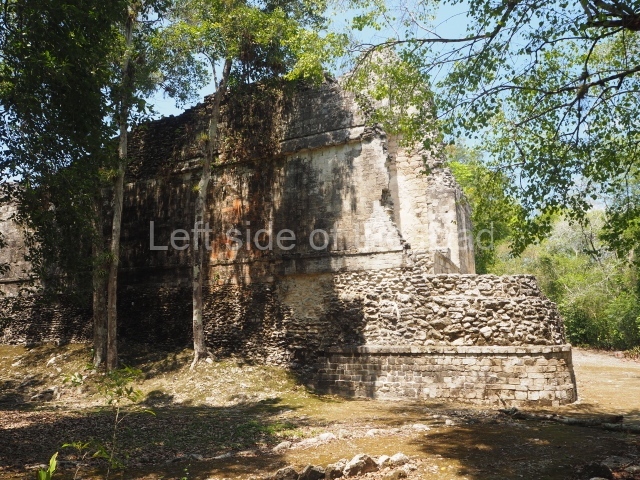
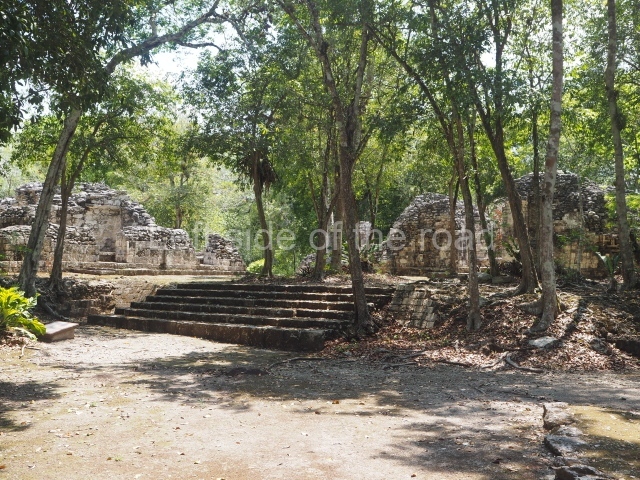
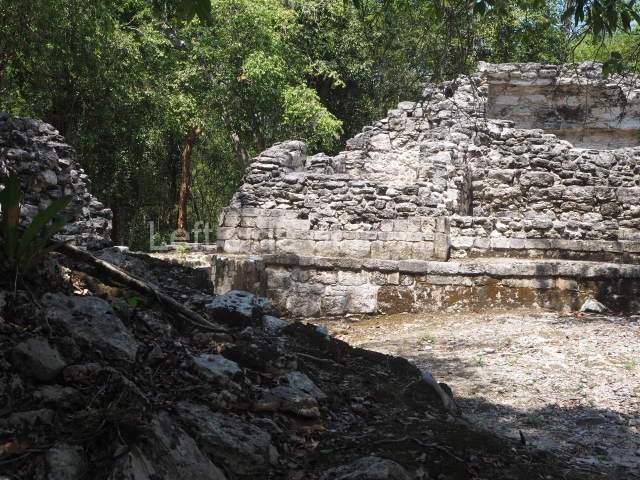
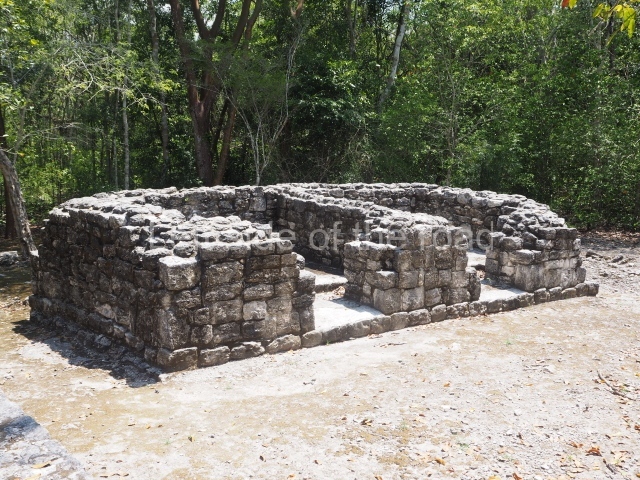
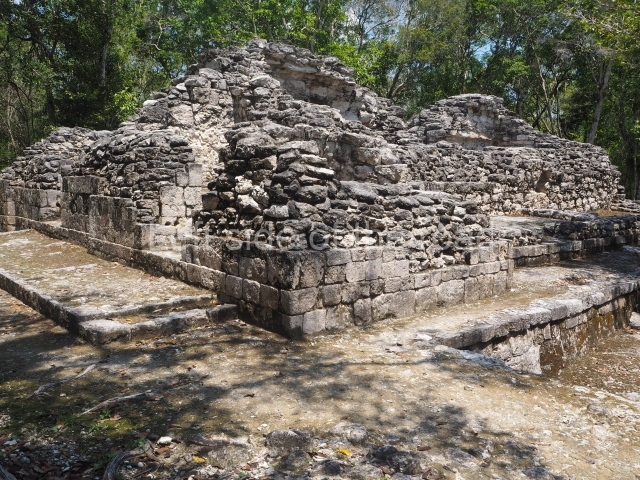
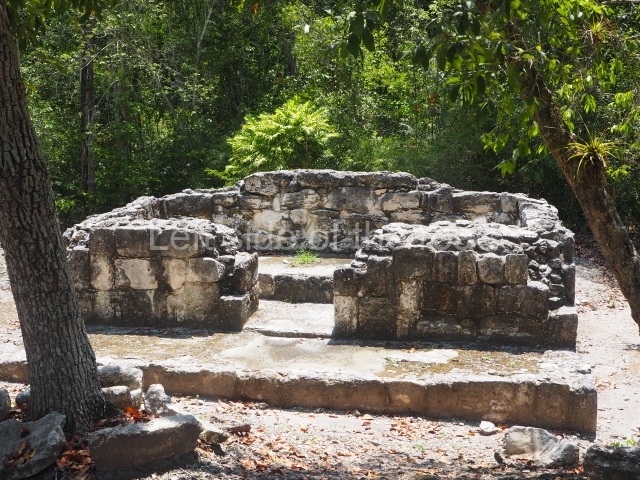
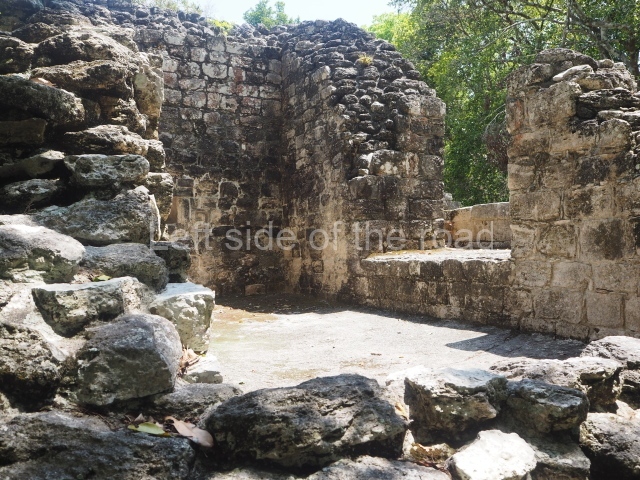
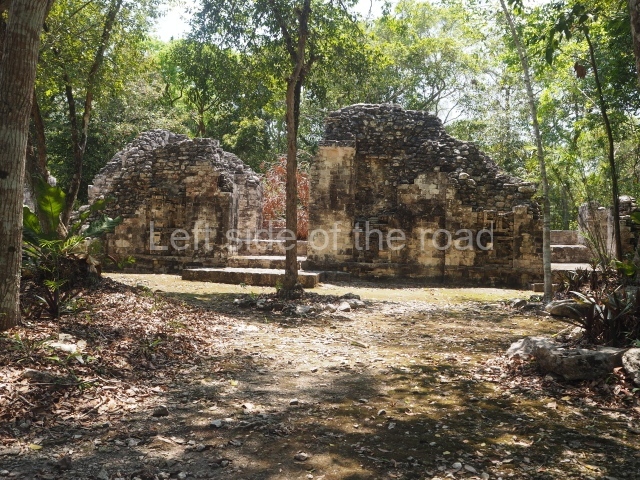
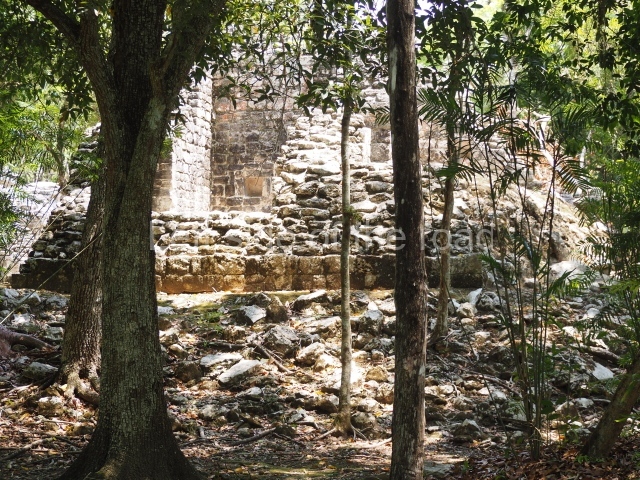
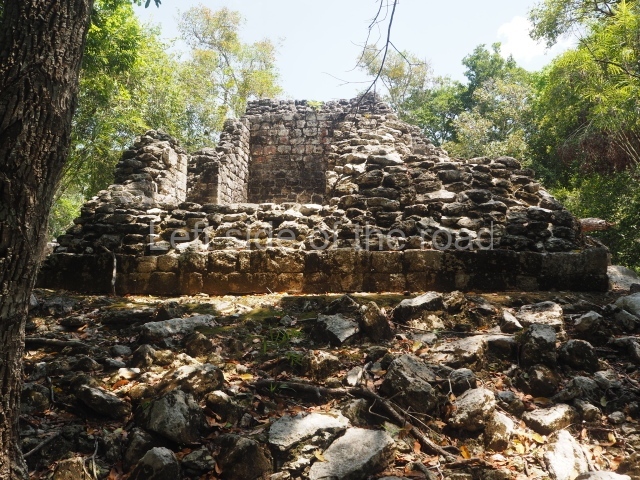
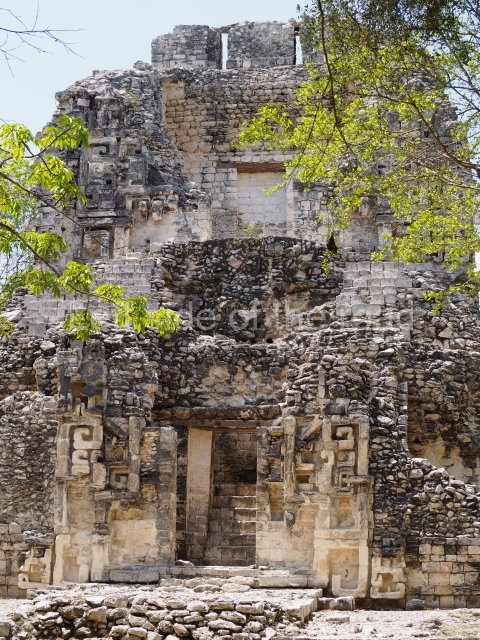
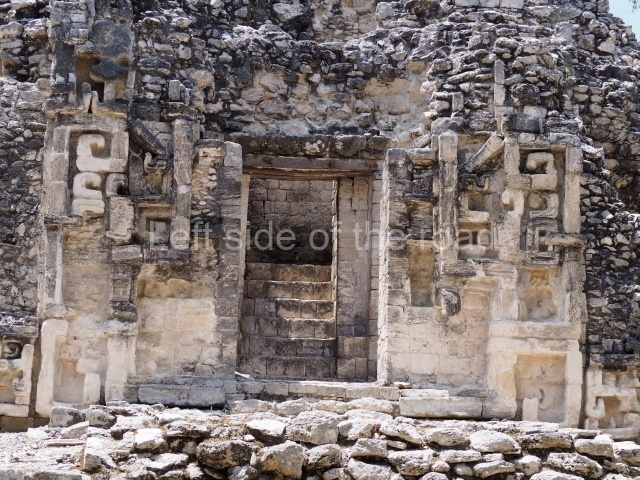
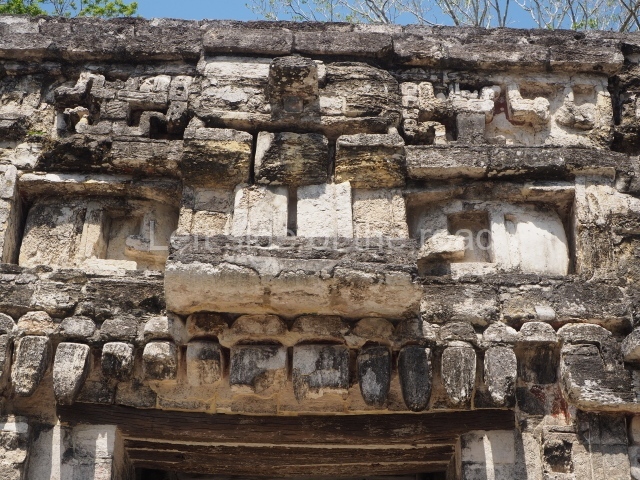
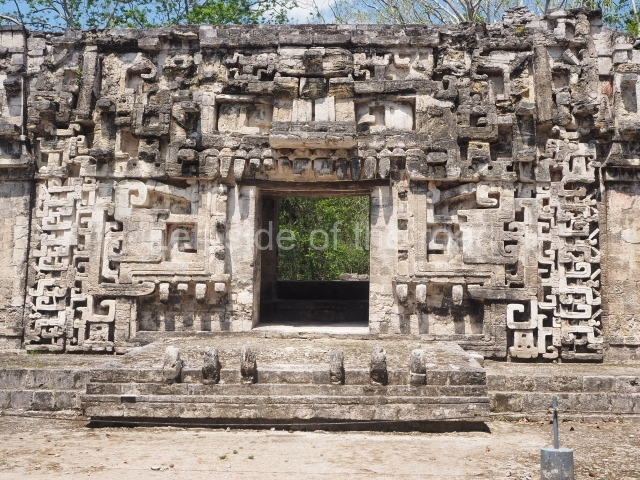
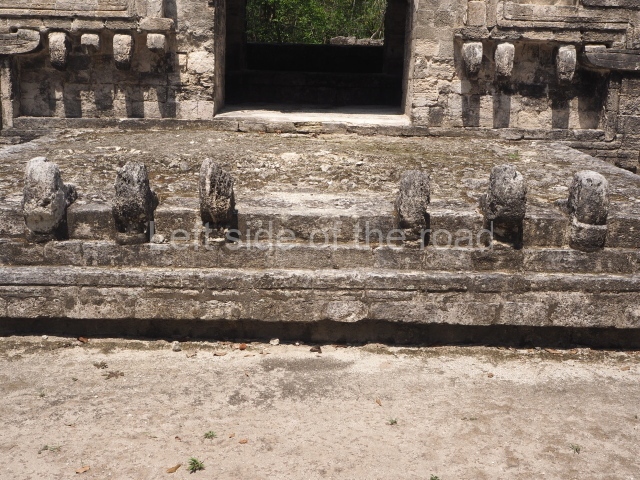
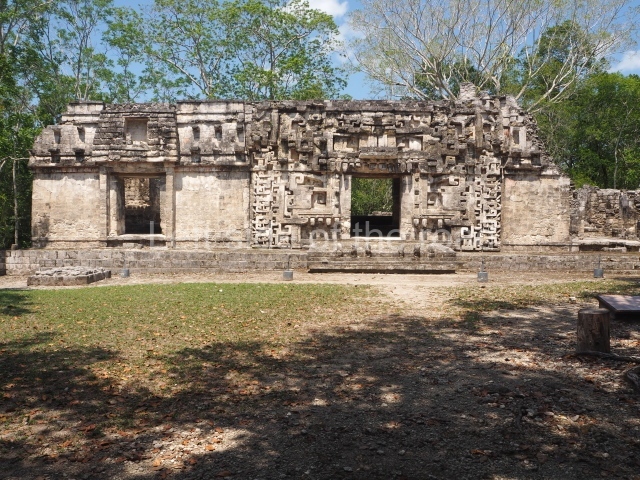
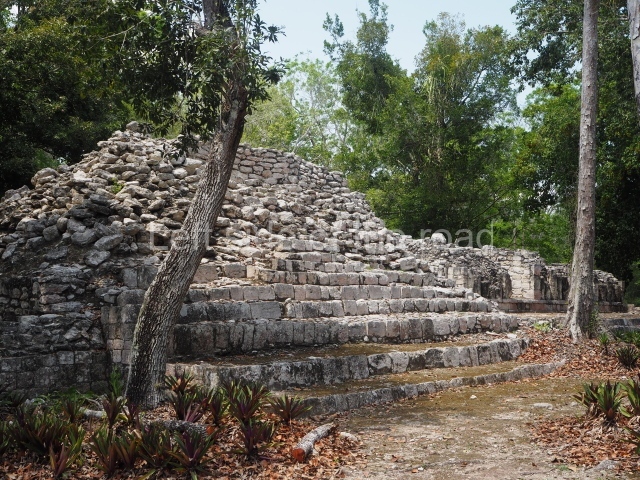
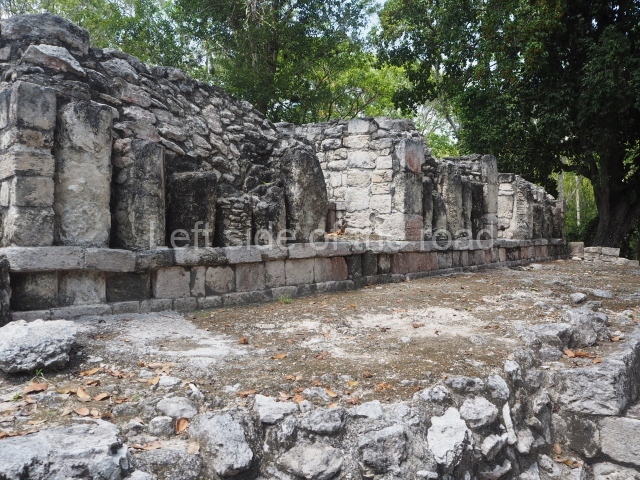
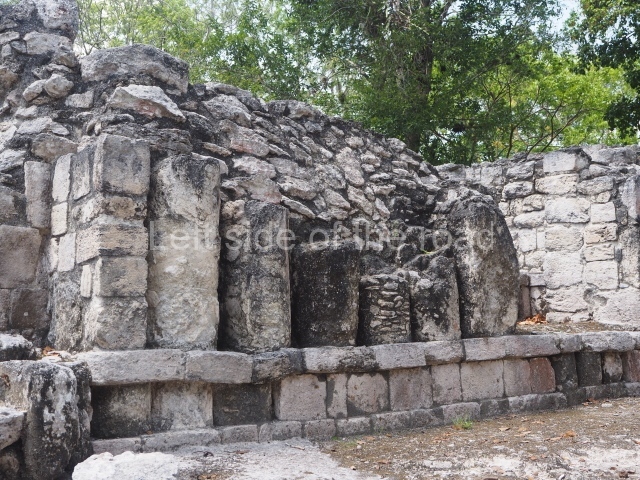
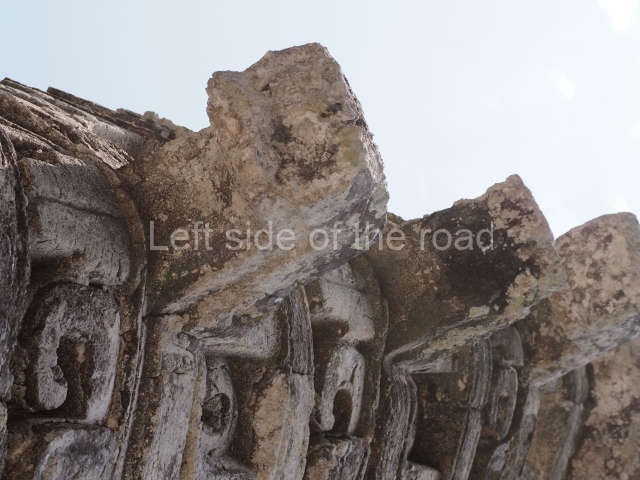
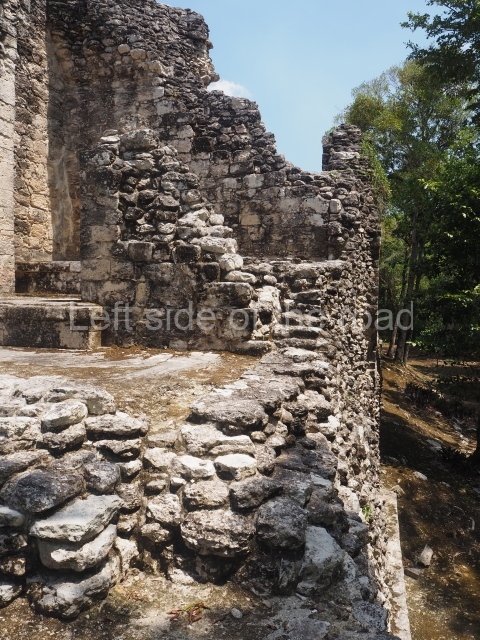
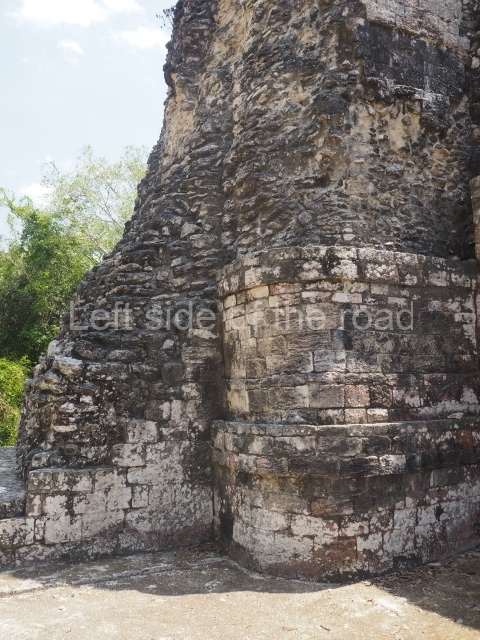
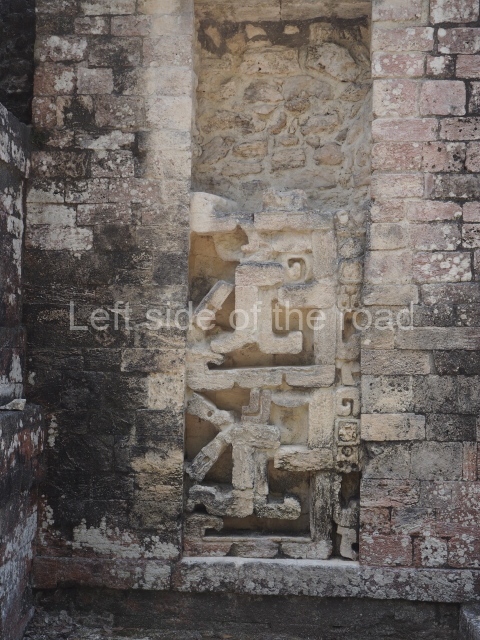
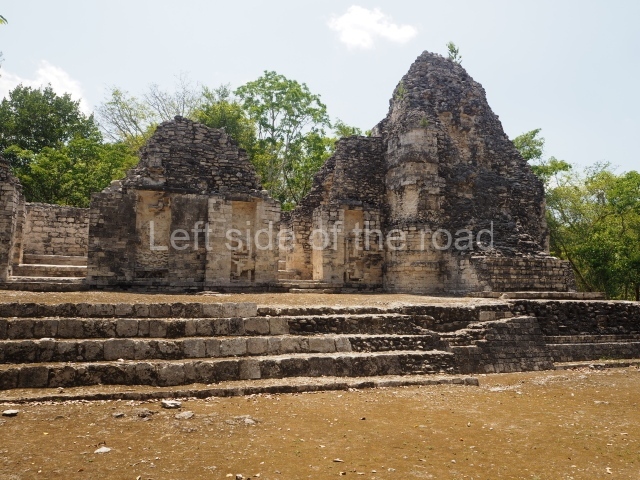
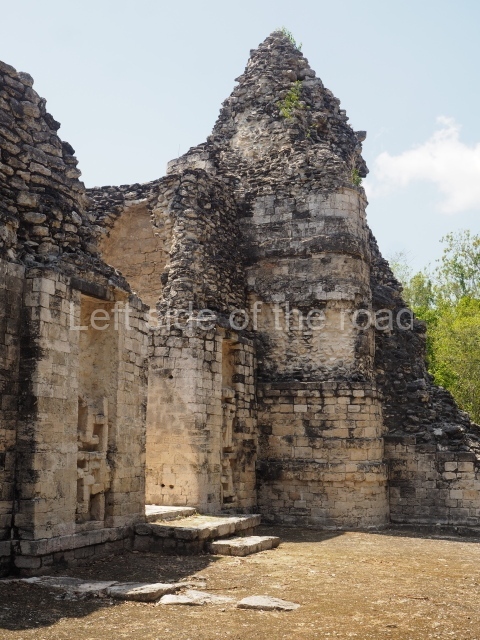
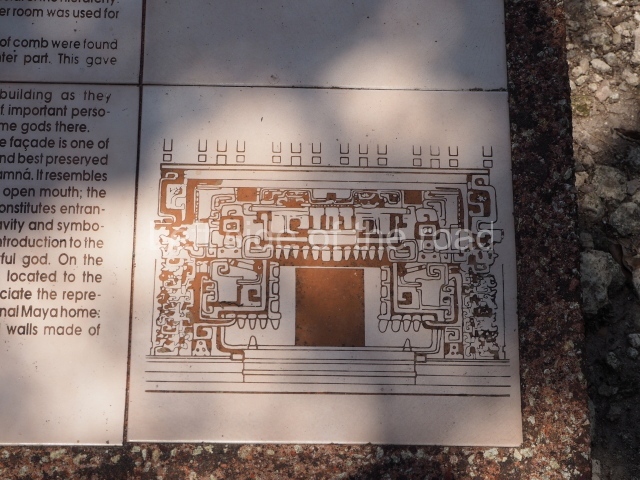
Dzibilnocac was a large settlement comprising several groups of monumental constructions arranged in a regular pattern. Devoured by the rainforest for centuries, it was repopulated in 1822, when it was christened Iturbide after Agustin de Iturbide y Aramburu (1783-1824), the self-proclaimed Augustine I, Emperor of Mexico. The pre-Columbian site lies beneath several urban and rural layers, and can still be seen to occupy a surface area of approximately 1 sq km. There are numerous mounds of rubble and platforms, pyramids, buildings with several rooms that once had masonry corbel-vault ceilings and exterior decorative elements composed of stone mosaic masks. The only construction that has been restored – and only partially at that – is Structure A-1, which comprises several rooms arranged longitudinally to which three towers were abutted: one at each end and one in the centre. Various features denote the Chenes style, which is characterised by profuse decoration and long-nosed masks in particular. Rounded corners are another frequent feature of this style. Visible in the central section of both of the long sides are the jaws of the great Earth Monster, on which the central tower rests. The representation is made of stone mosaic and in addition to the curved veneer stones or teeth the allegory was adorned with cartouches showing stucco symbols of water and the scales of one of the Maya gods, painted in different colours.
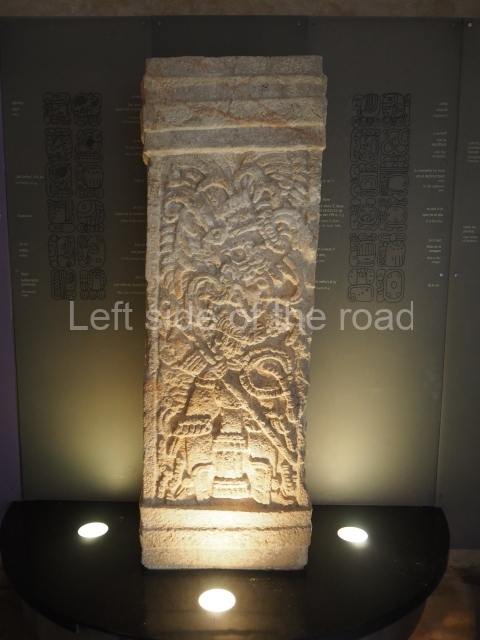
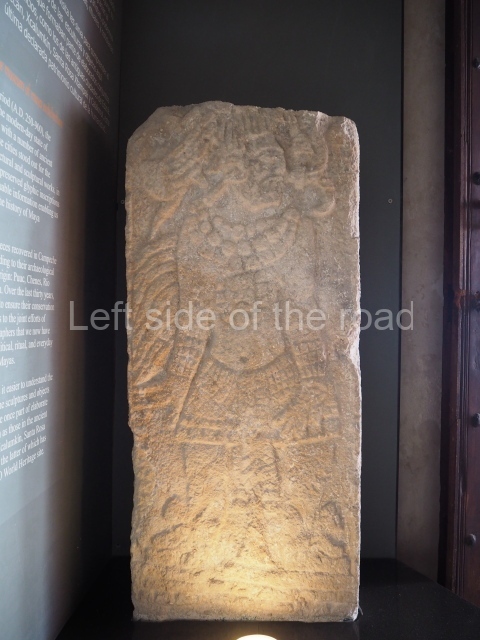
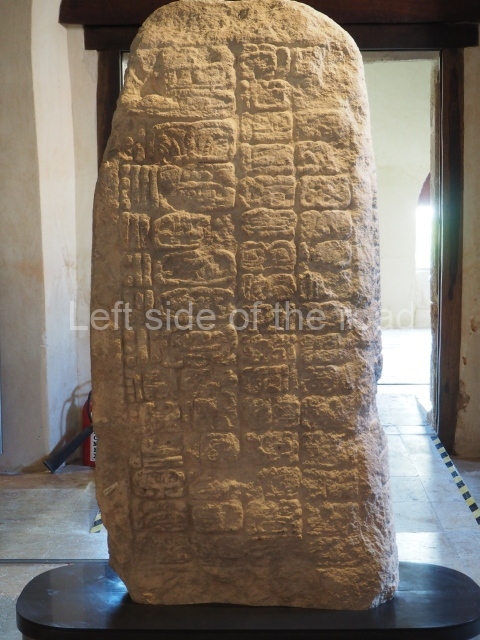
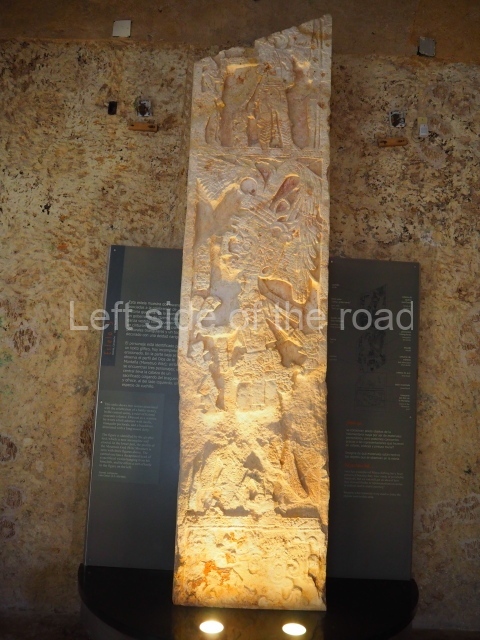
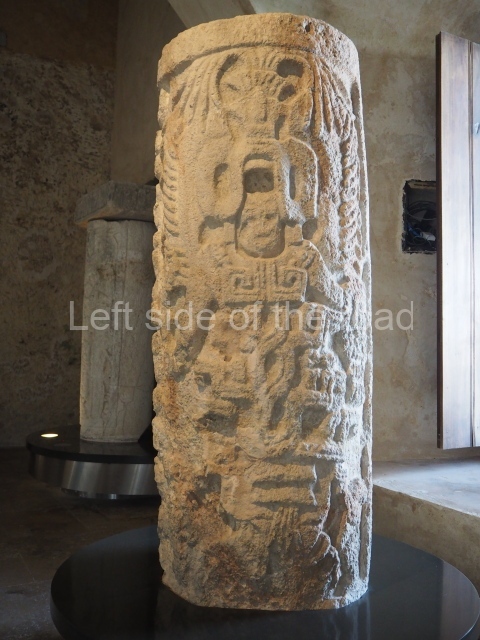
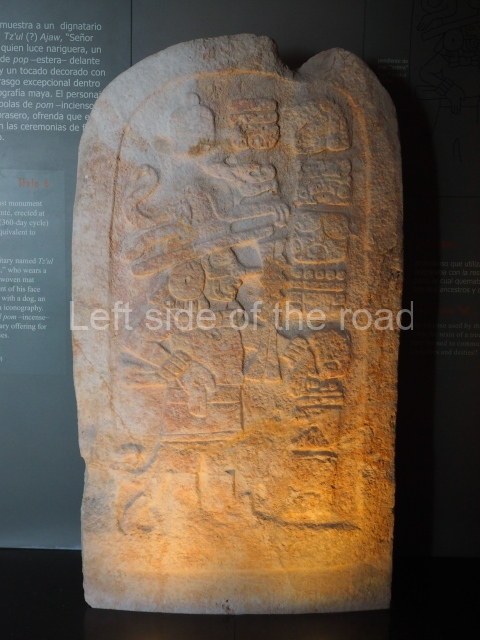
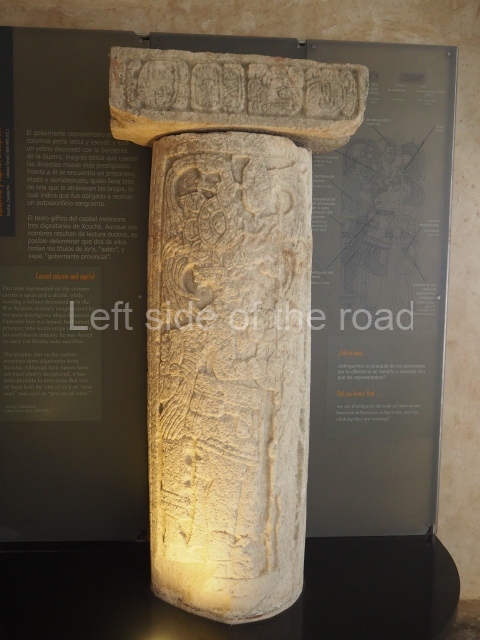
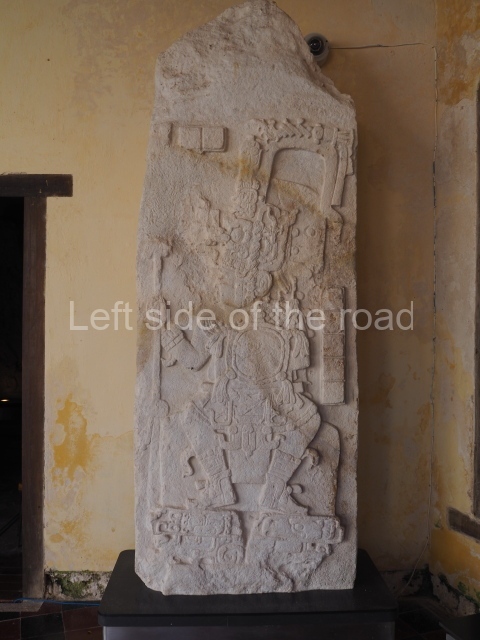
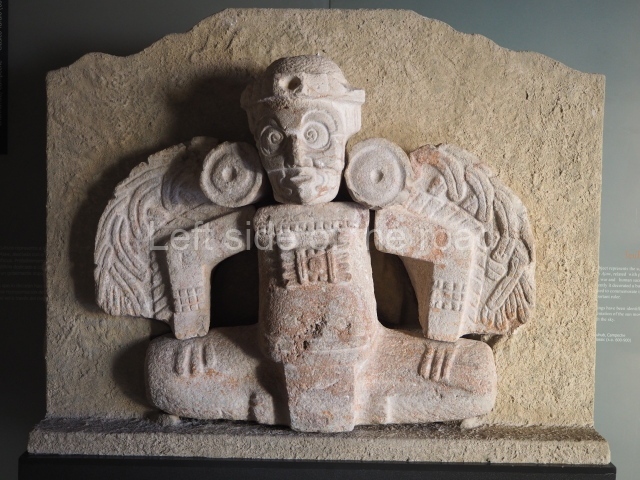
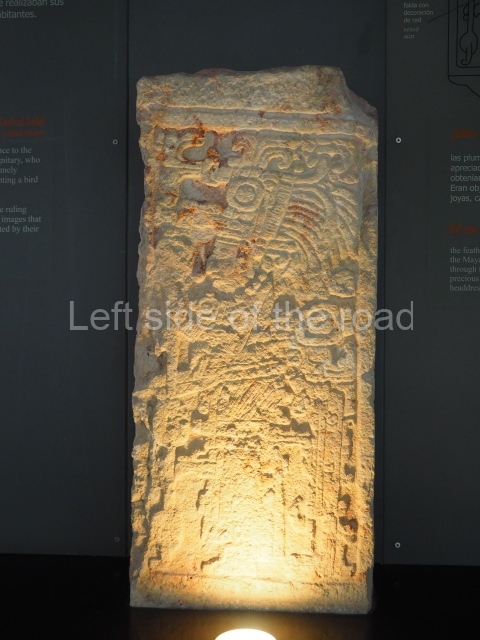
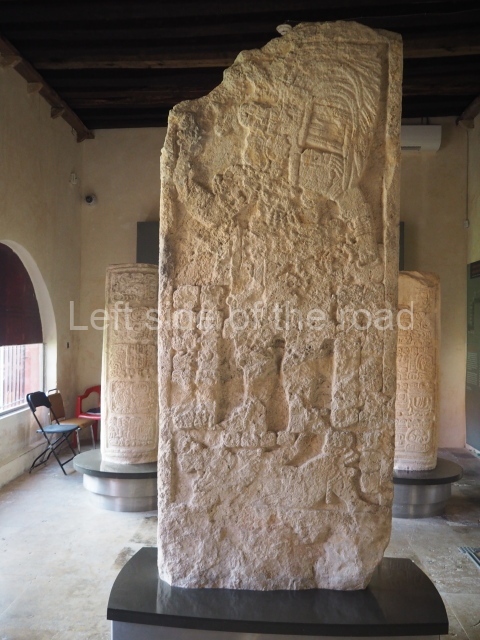
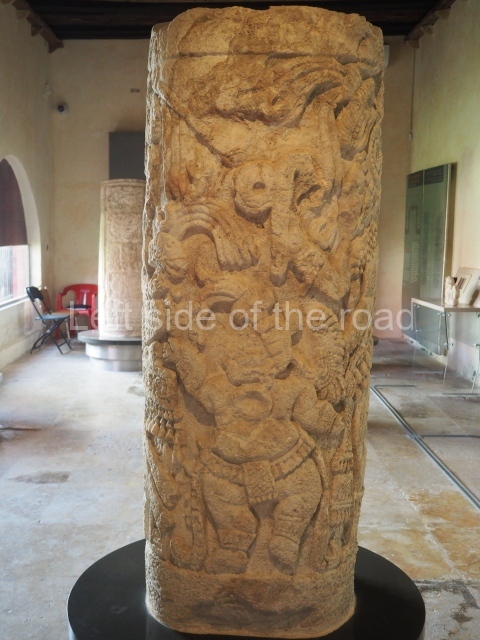
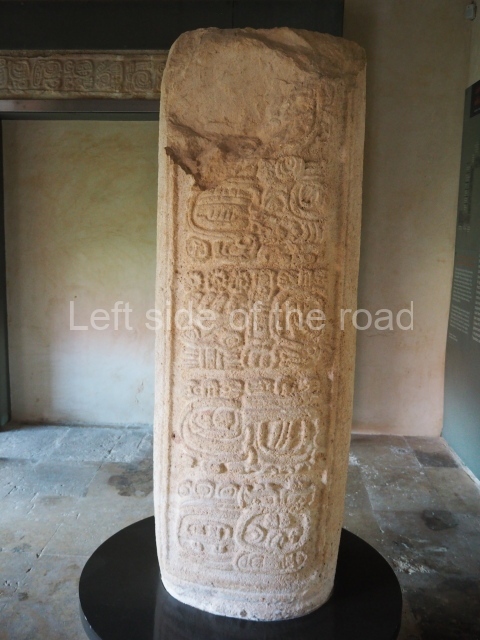
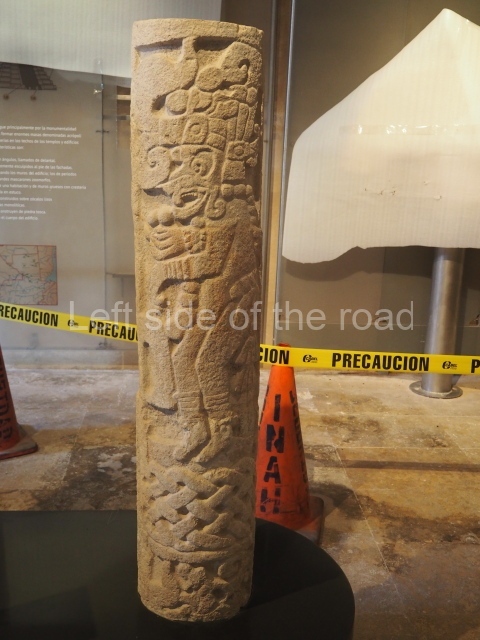
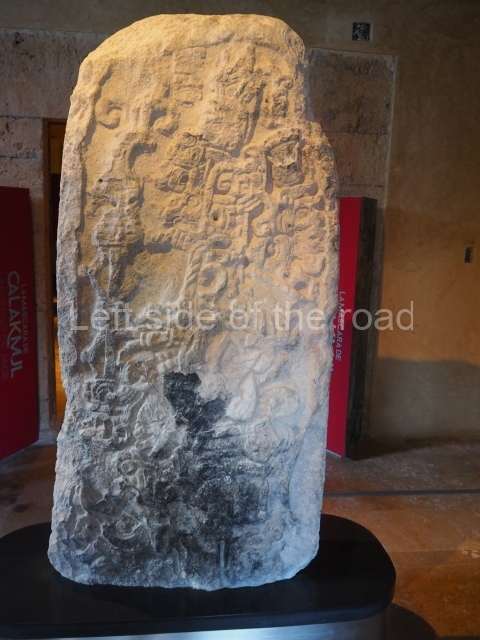
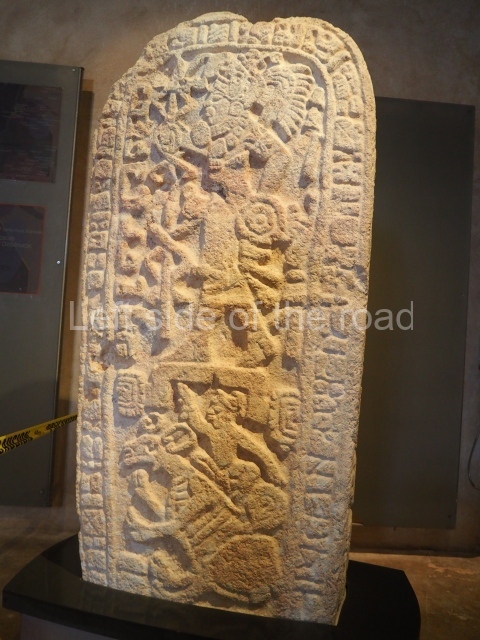
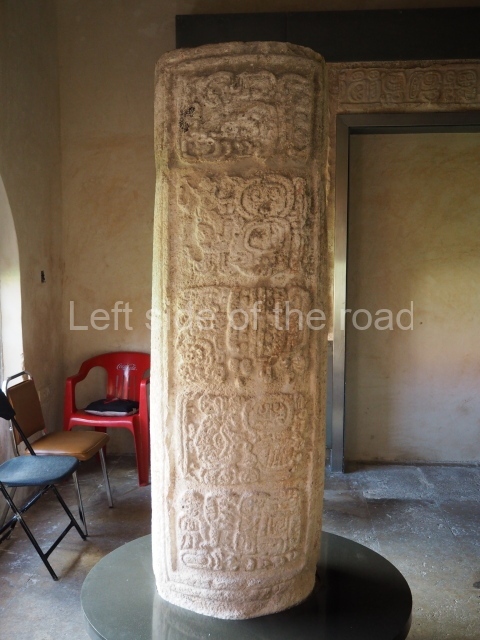
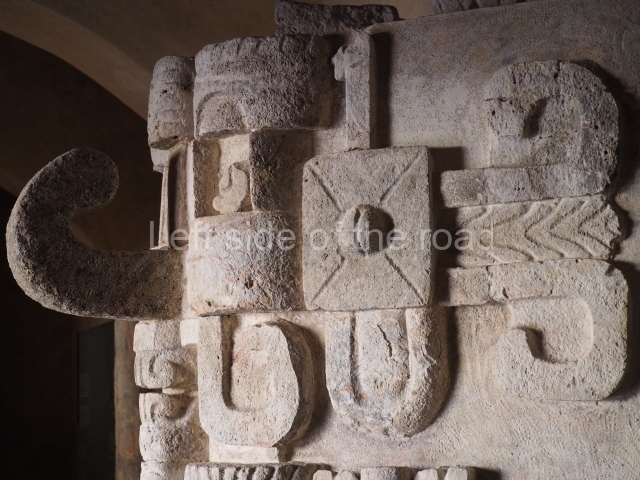
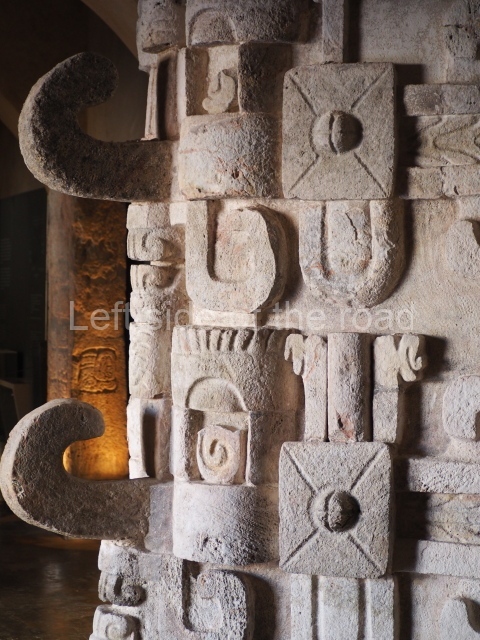
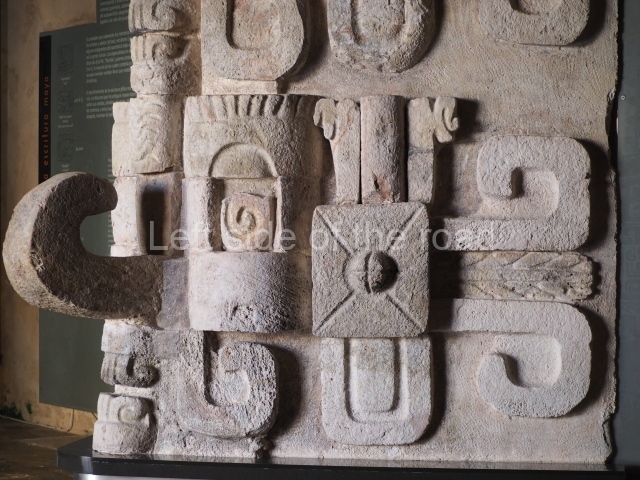
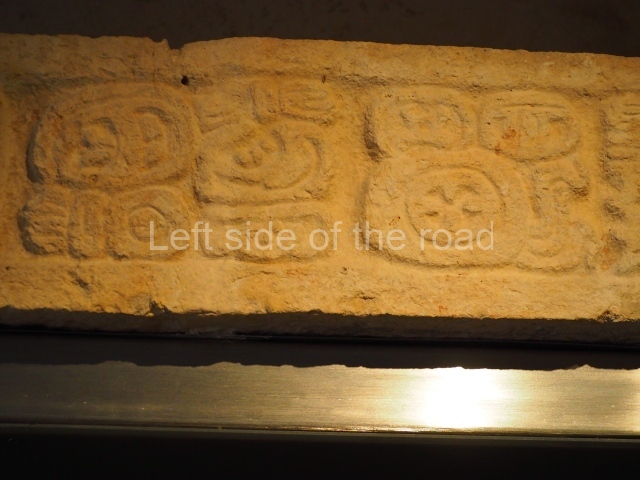
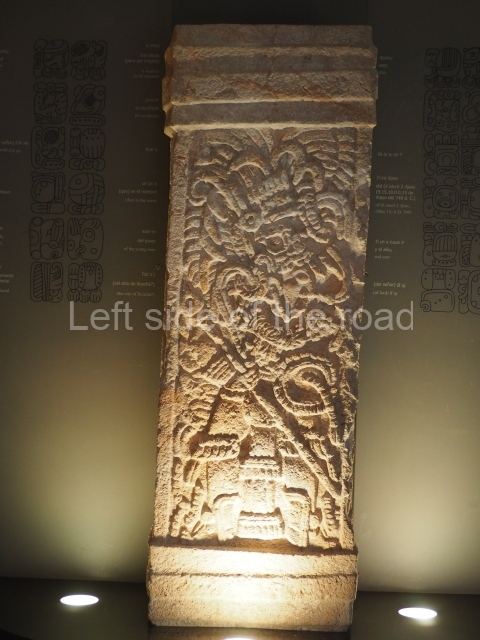
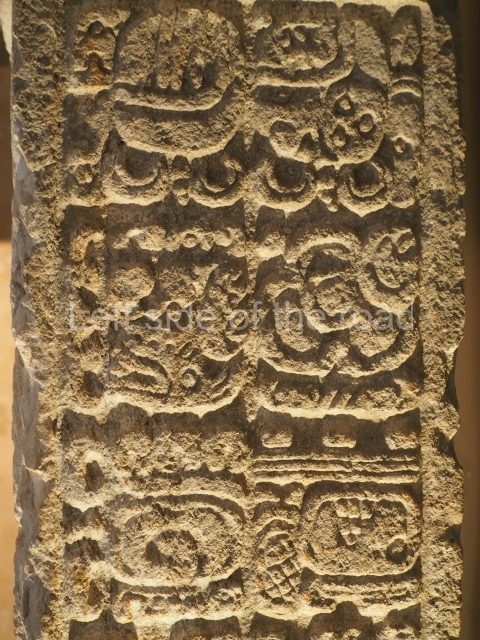
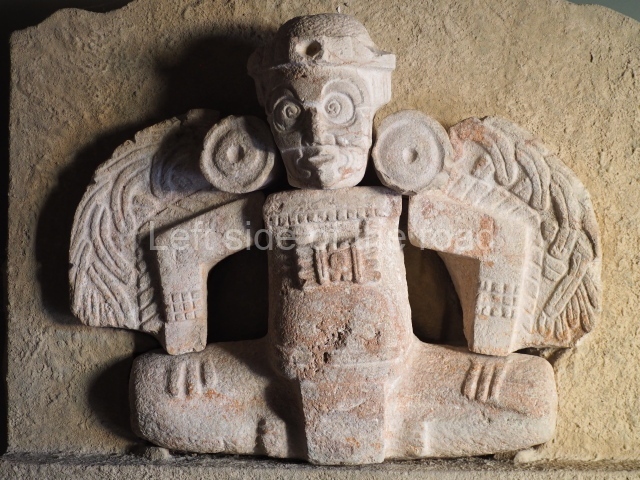
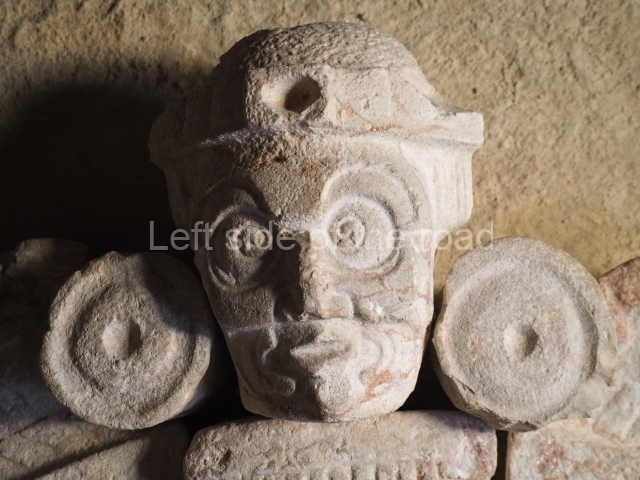
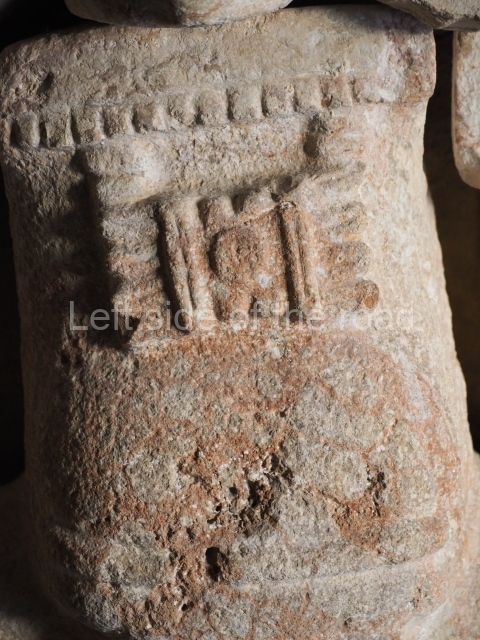
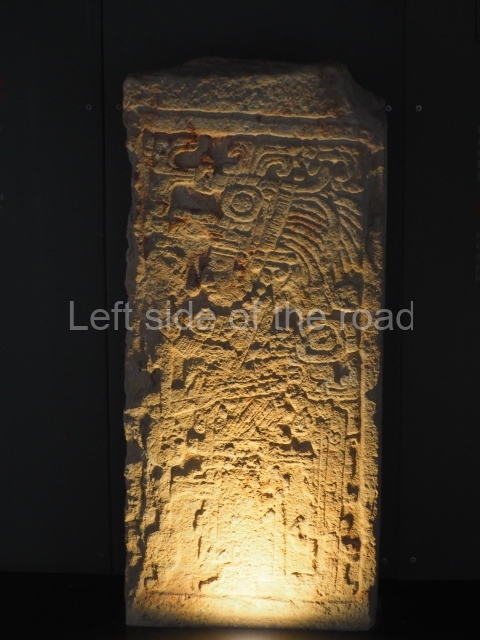
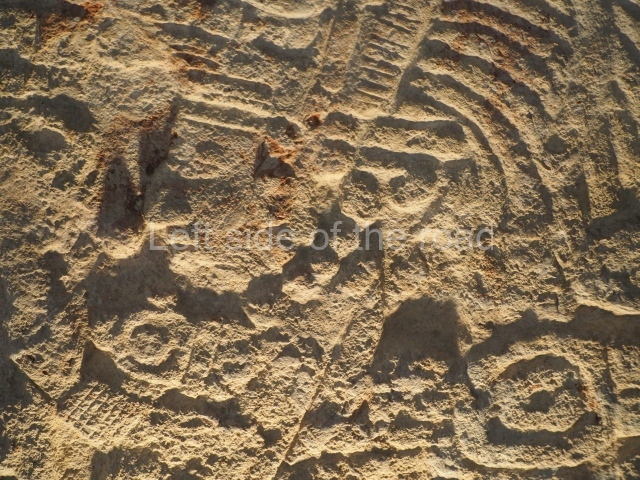
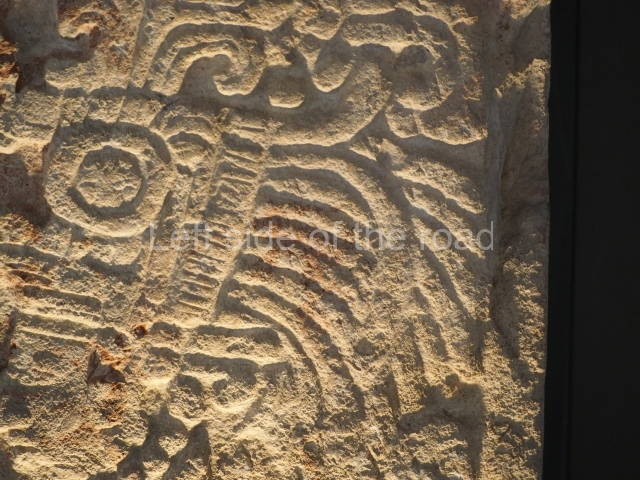
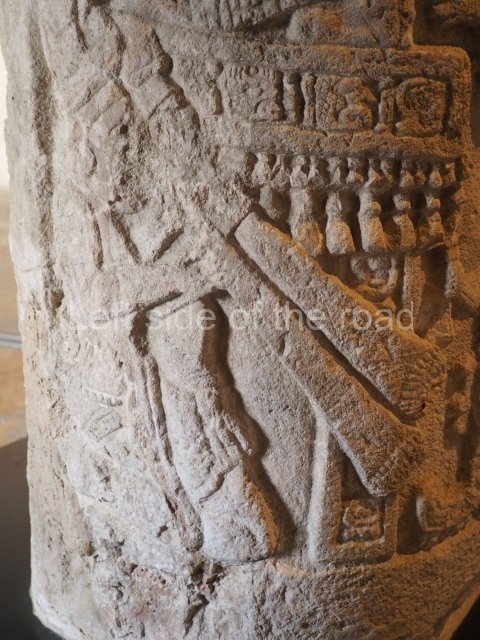
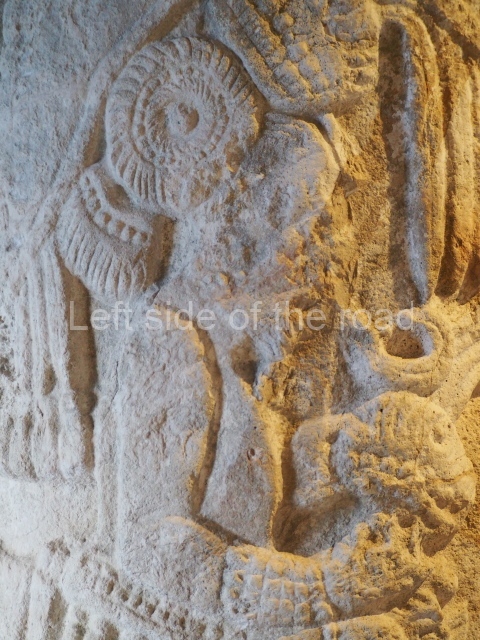
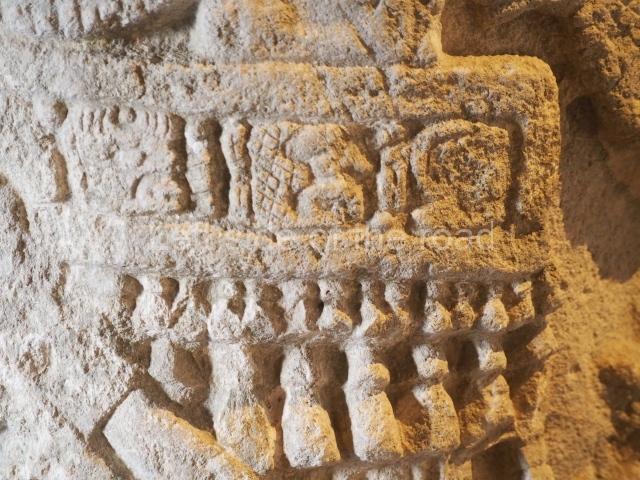
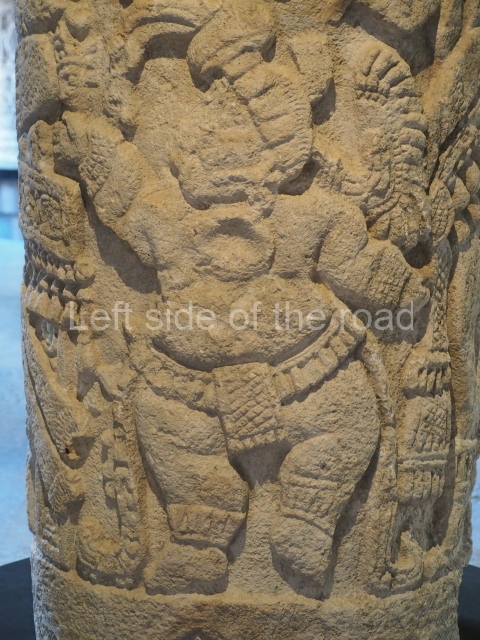
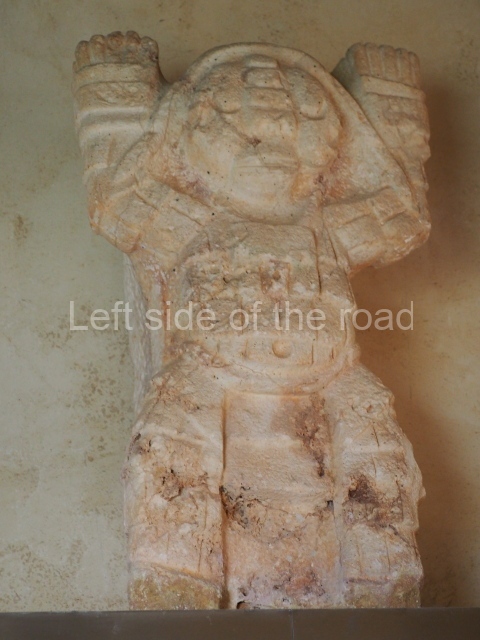
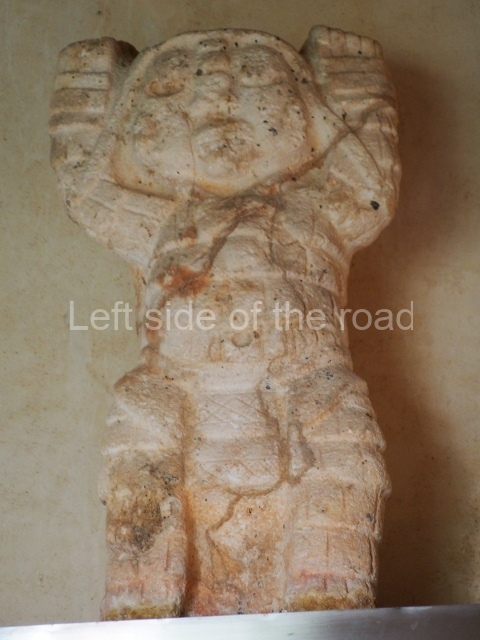
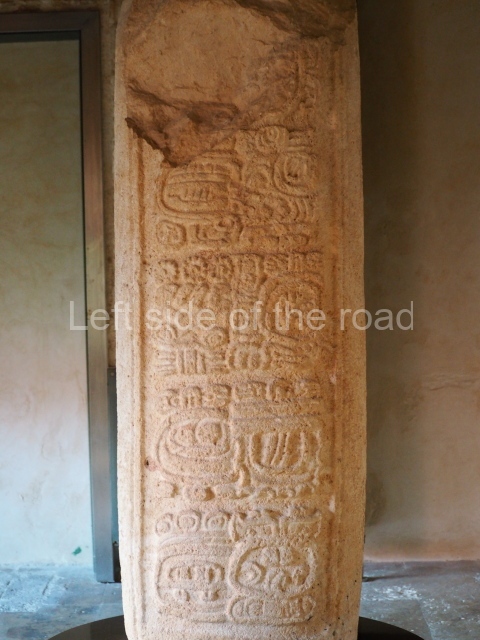
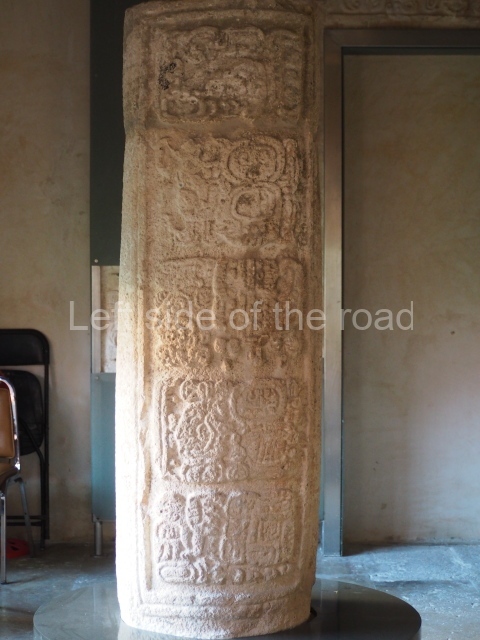
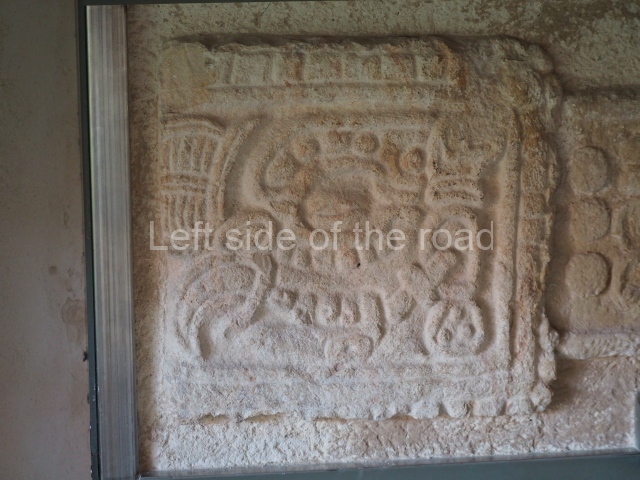
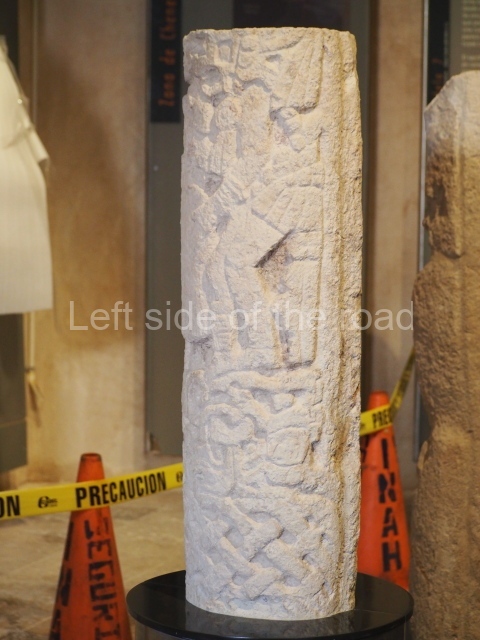
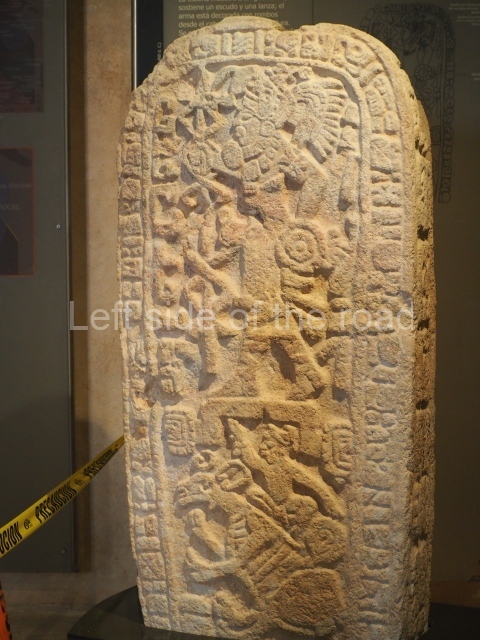
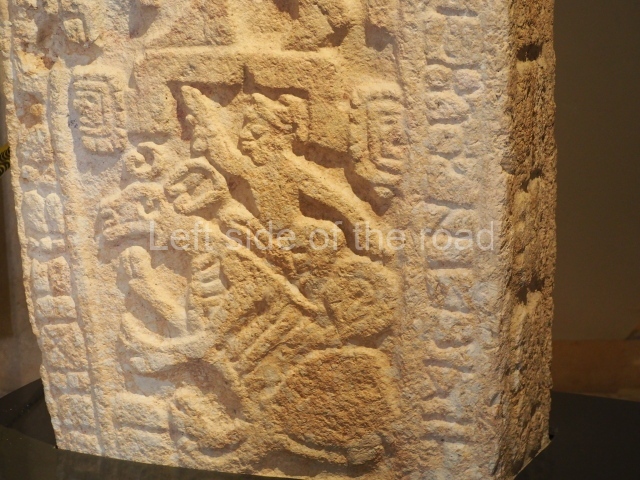
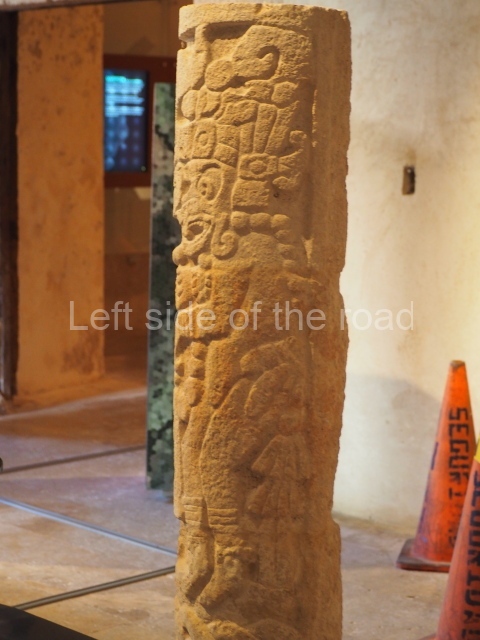
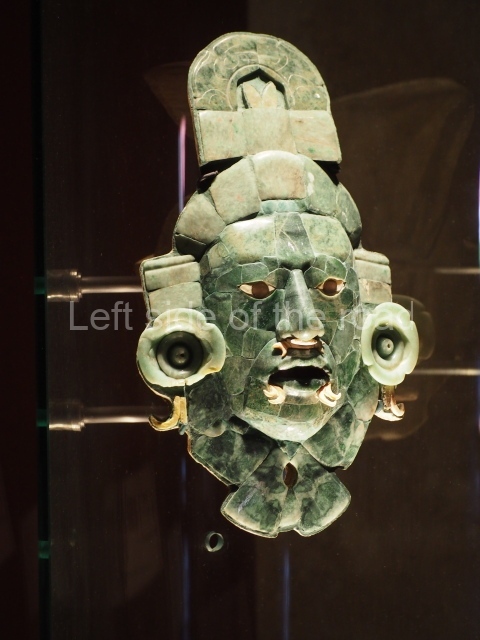
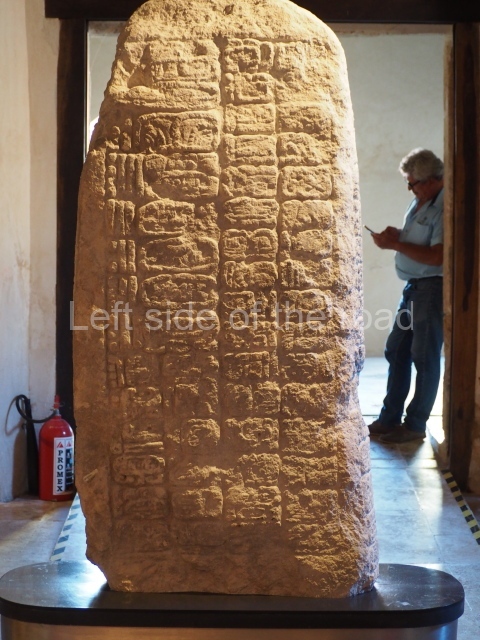
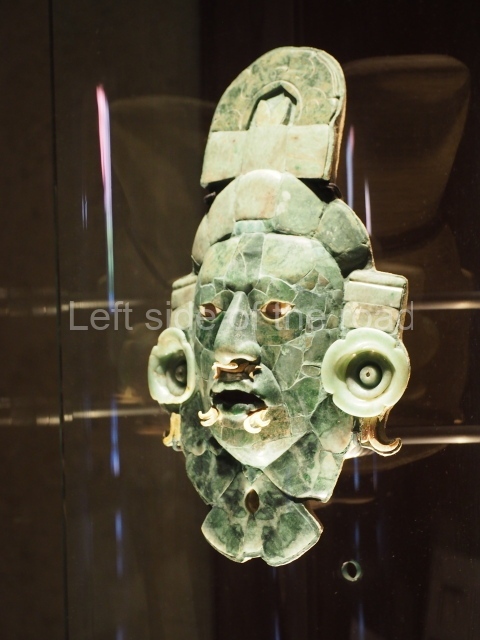
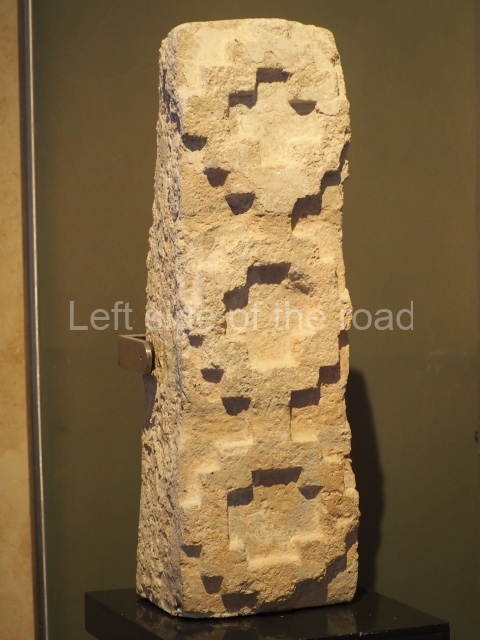
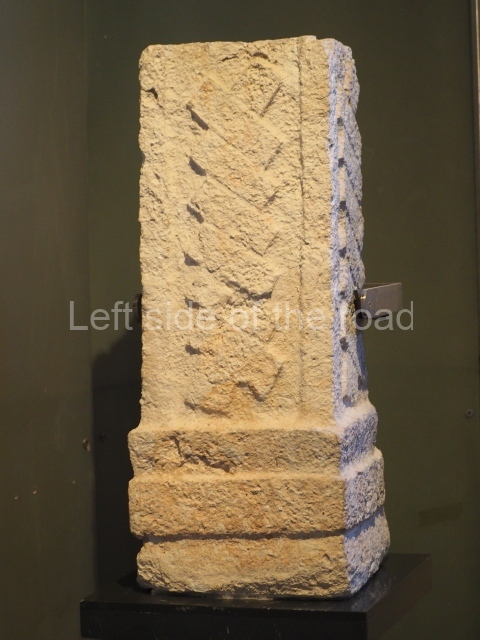
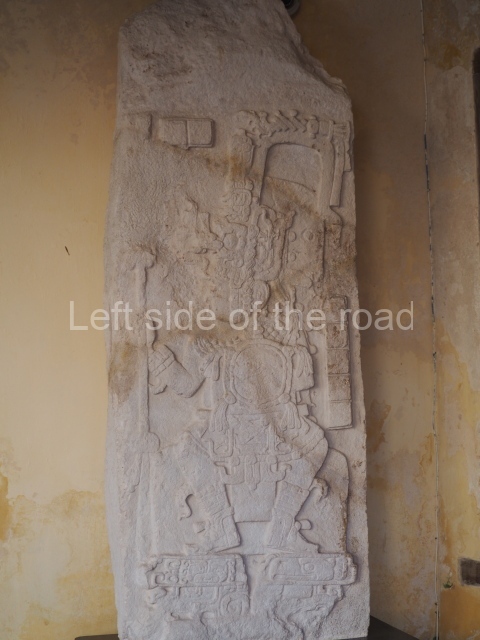
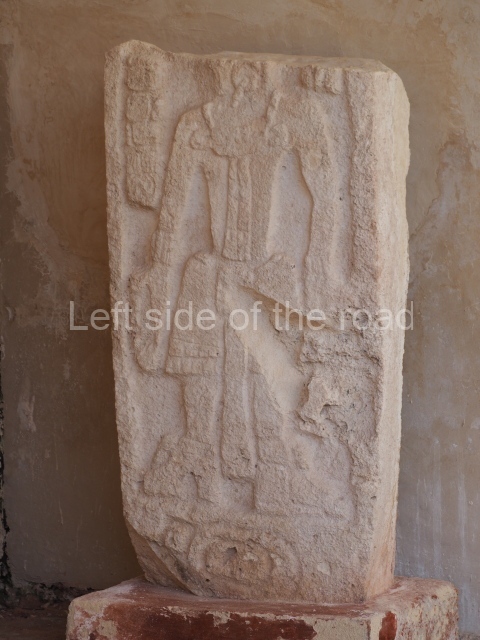
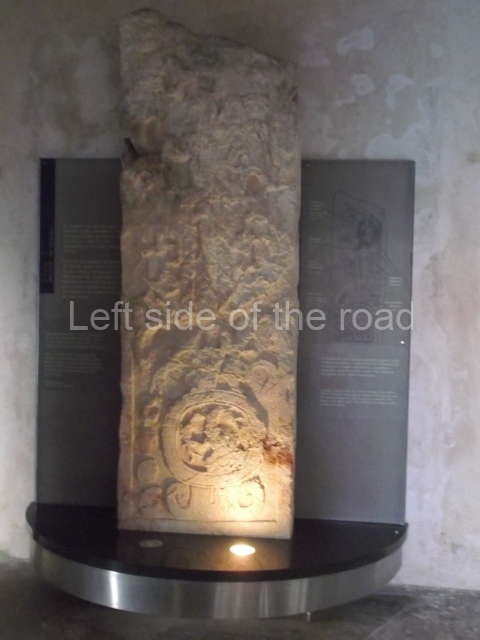
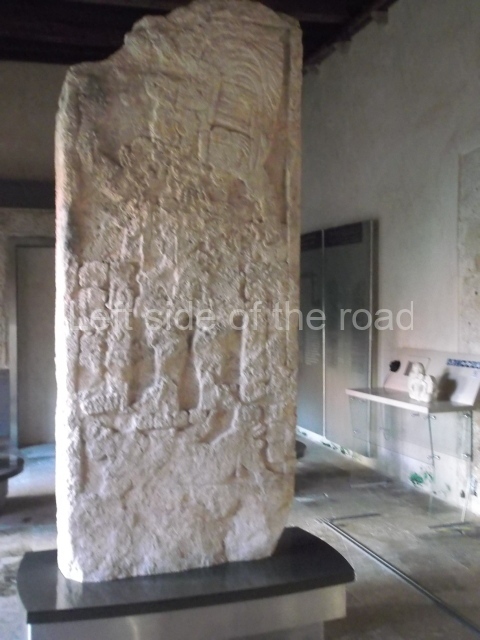
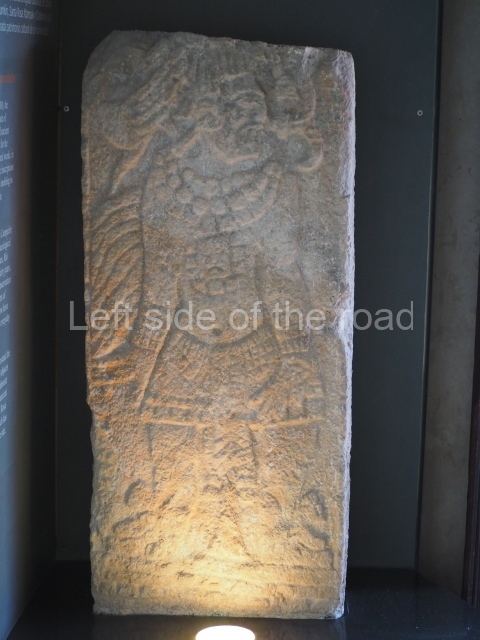
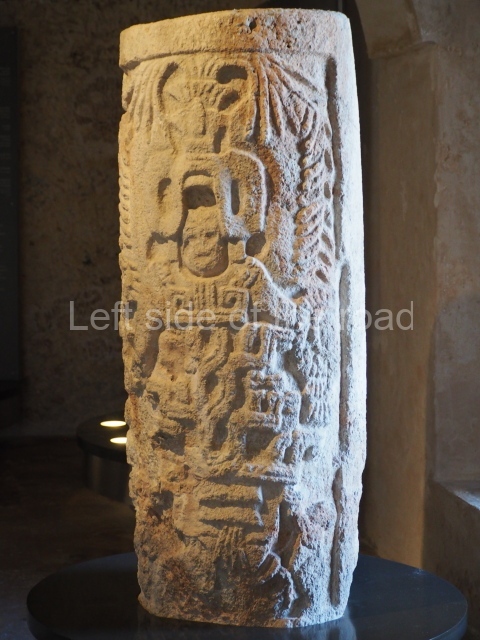
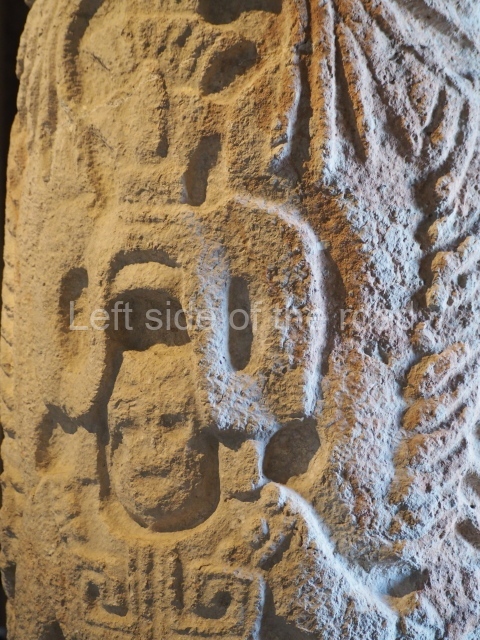
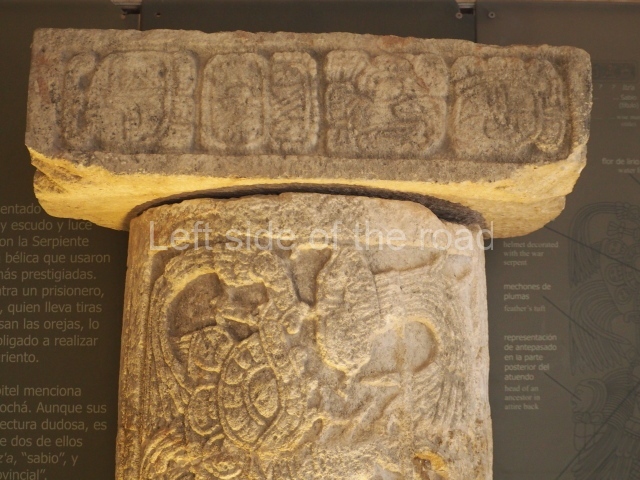
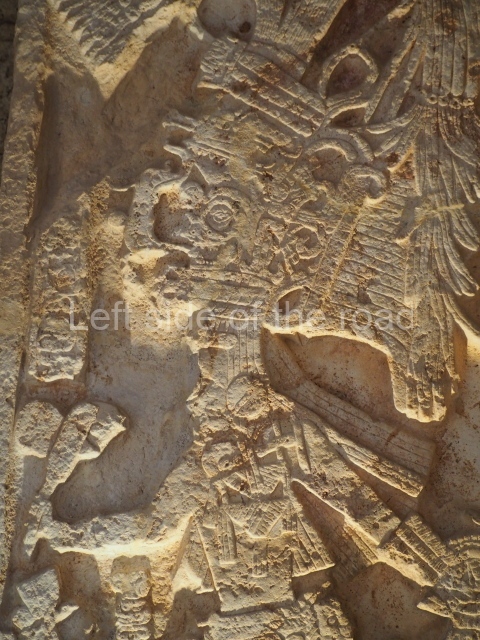
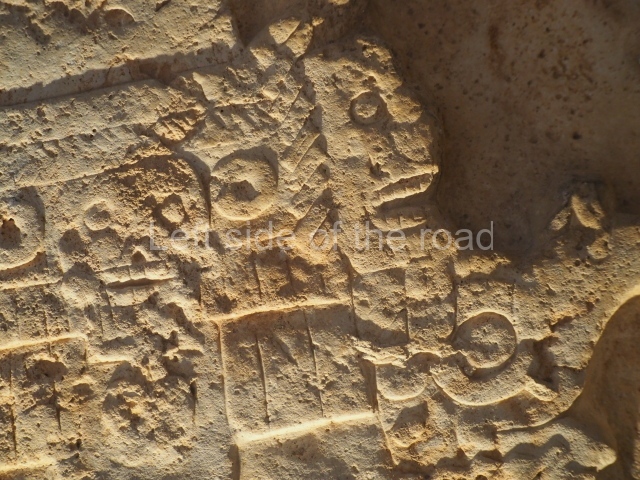
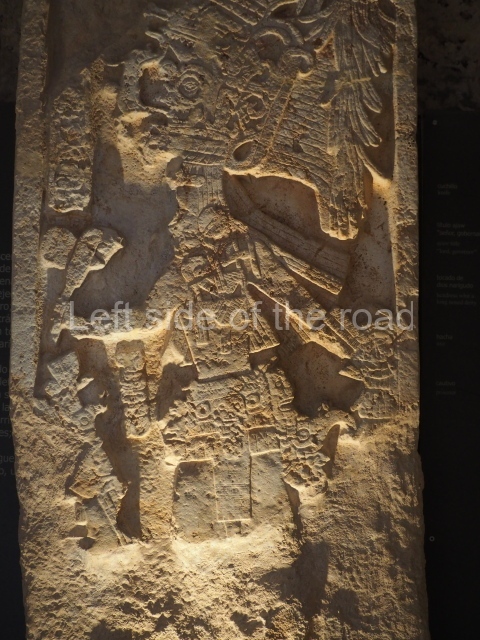
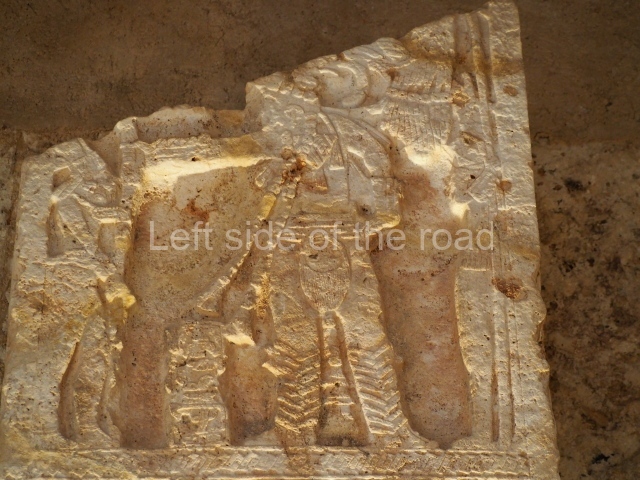
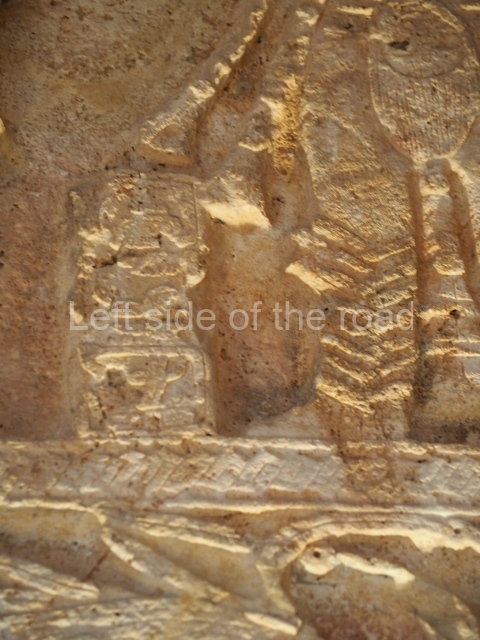
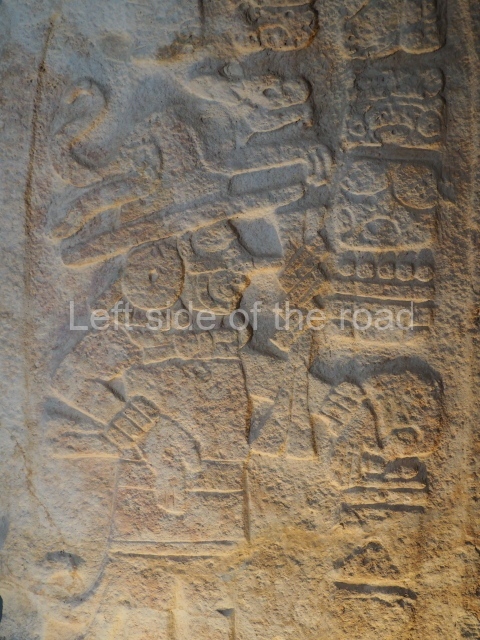
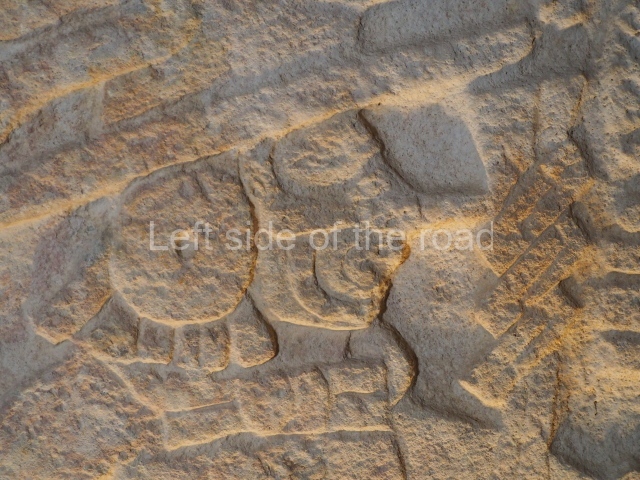
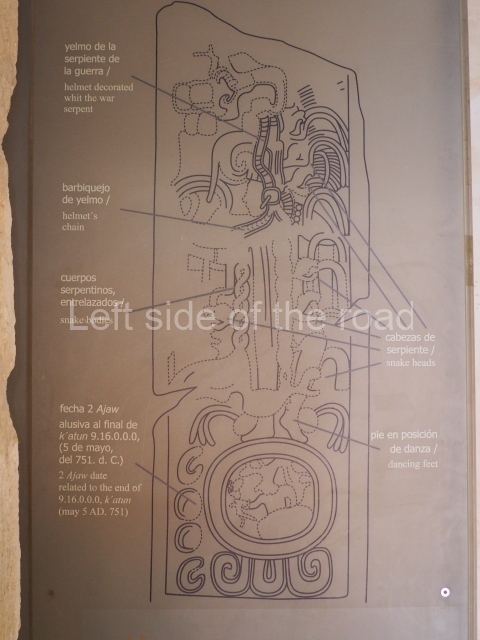
Several pieces from Dzibilnocac are on display in the museums in Campeche City: a stela, various capstones and an anthropomorphic sculpture. The stela has bands of hieroglyphs. The capstones represent the deity Kauil in red on a white background, and the sculpture shows the head of a figure with an unusual headdress, the ends of which hang down on both sides of the face.
Importance and relations
Although Dzibilnocac is situated in the Chenes stylistic region, characterised by the use of profusely decorated facades, the presence of non-functional towers at Structure A-l is associated with architectural features of the Rio Bec region, some 100 km further south but still in the Campeche region. The numerous monumental remains at the ancient city and several of the hieroglyphic inscriptions – as yet only briefly studied – confirm a regional hegemony lasting several centuries, especially during the 8th century AD. Stelae 1 and 2 are inscribed with the year 731, while a fragment from another piece shows the year 764.
From: ‘The Maya: an architectural and landscape guide’, produced jointly by the Junta de Andulacia and the Universidad Autonoma de Mexico, 2010, pp303-304.
1. The Palace at Chunhuhub.
Getting there:
From Hopelchén. There are reasonably regular buses from the Sur ‘bus station’ in Hopelchén, where you’ll also find a written timetable of departures from the town. Iturbide (Vicente Guerrero – never got to know why the place had two names) is the end of the line heading south-east. Get off at the terminus and take the road below the sports area, heading east. The site is signed to your right in less than 10 minutes walking.
GPS:
19d 34’ 41” N
89d 35’ 41” W
Entrance:
Free