Becan
More on the Maya
Becan – Campeche
Location
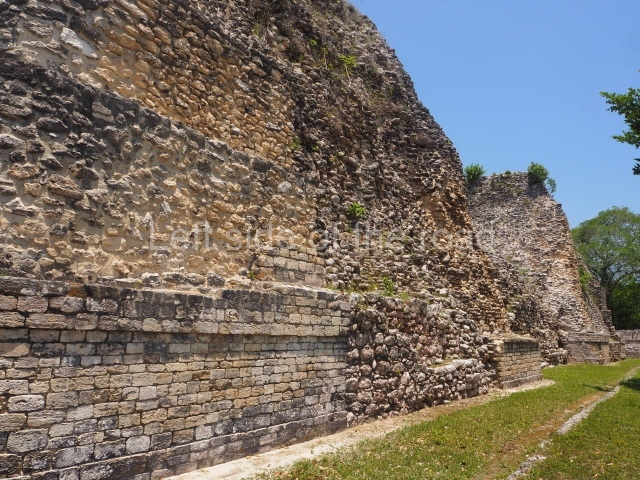
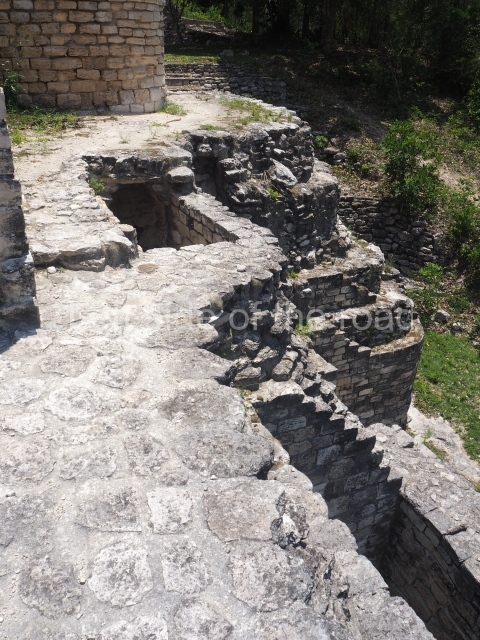
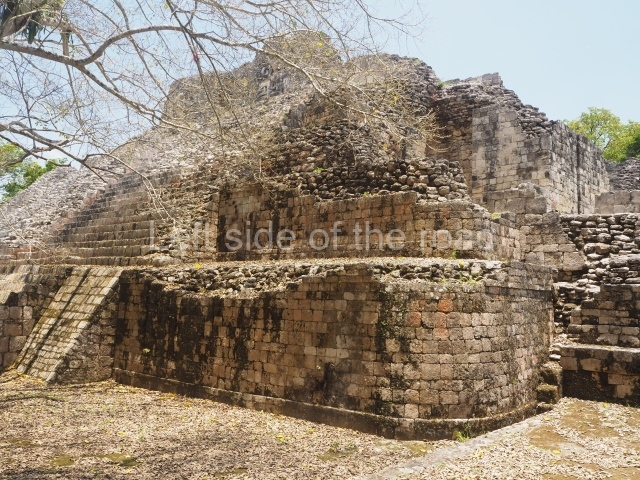
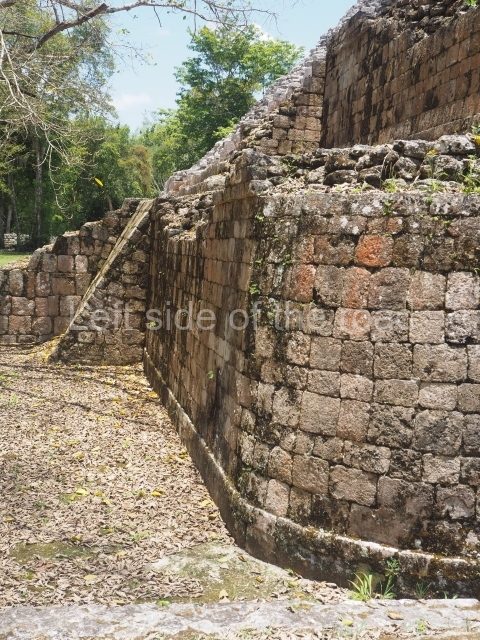
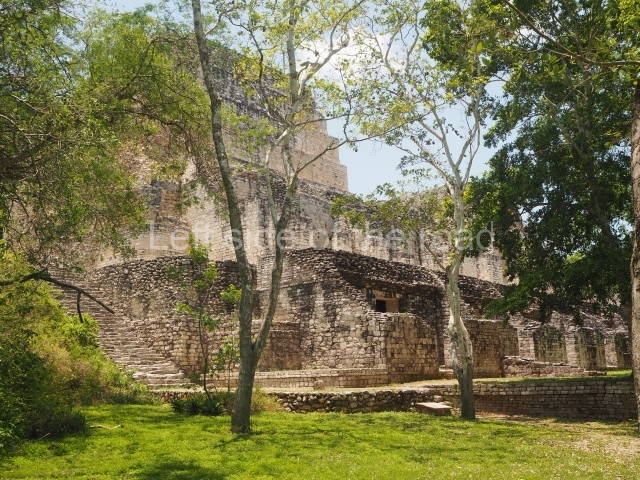
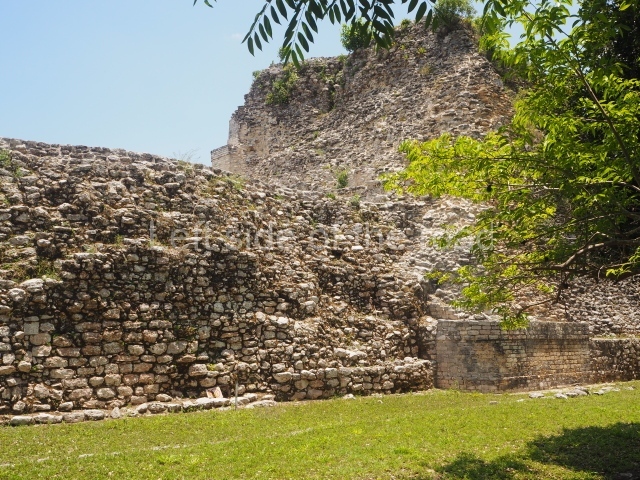
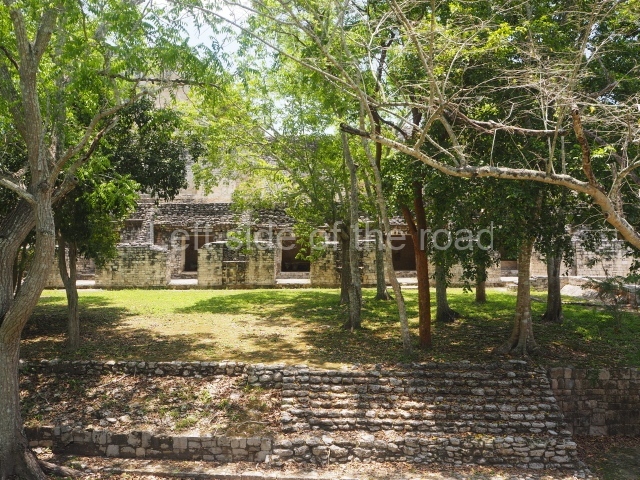
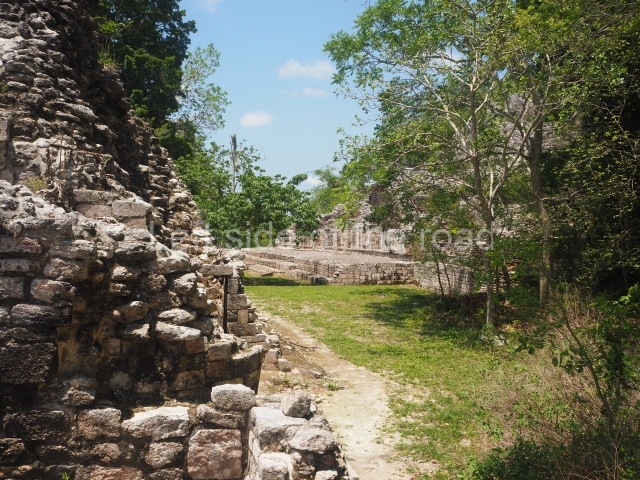
This is situated 130 km east of Escarcega, on Federal Road 186 to Chetumal. It is some 300 km from Campeche. To the immediate north-west of the modern community of the same name, the main buildings at Becan are protected by a moat and a perimeter wall, which enclose an area of approximately 12 ha. The moat is 1,890 m long, 16 m wide and 2.5 m deep, while the perimeter wall is as high as 3.6 m in certain sections. It was only possible to cross the moat at seven bridges located at different points around it. Nowadays, access is via one of these bridges, situated in the east section. In the late 20th century certain specialists attributed a defence function to the moat, but the subsequent study and physiographic analysis of both the exterior and interior areas have led to the conclusion that it was used for channelling and draining rain water, thus avoiding flooding. Outside the area delimited by the moat a large number of lesser constructions have been found; these served as dwellings, granaries, shrines, cultivation terraces, stone walls, etc., used by the vast majority of the population who maintained the governing family at Becan. These ruins are similar to those of the nearby sites of Chicanna, 2 km to the south-west, and Xpujil, 8 km to the east. The name Becan has only recently been coined and is formed from Yucatec Maya words meaning ‘serpent path’. It is also the name for the groove worn away by the rain water, and some people therefore believe that it is simultaneously a metaphor for the moat and its curved course.
Timeline, site description and monuments
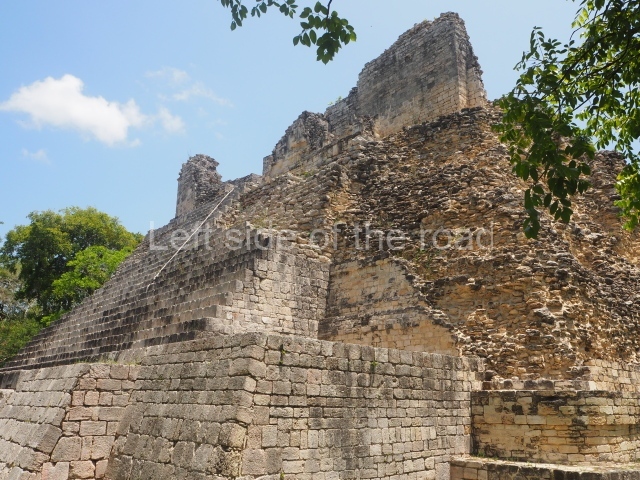
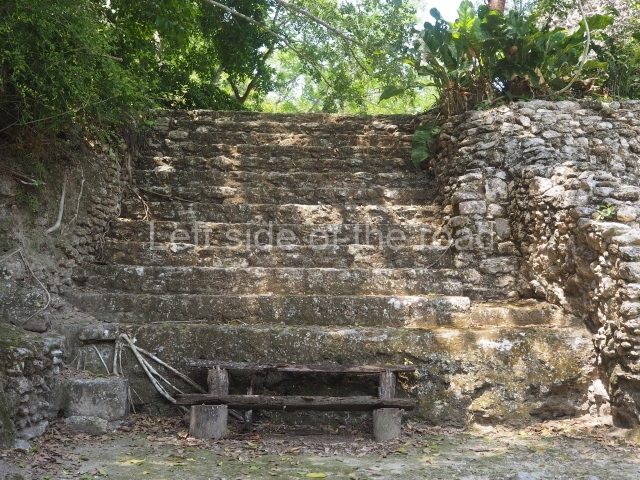
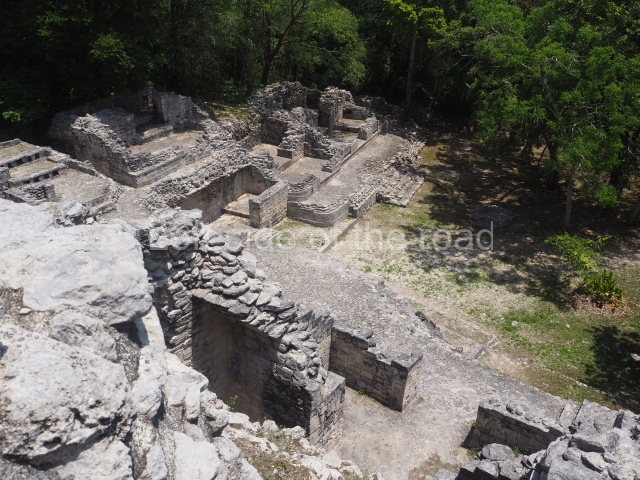
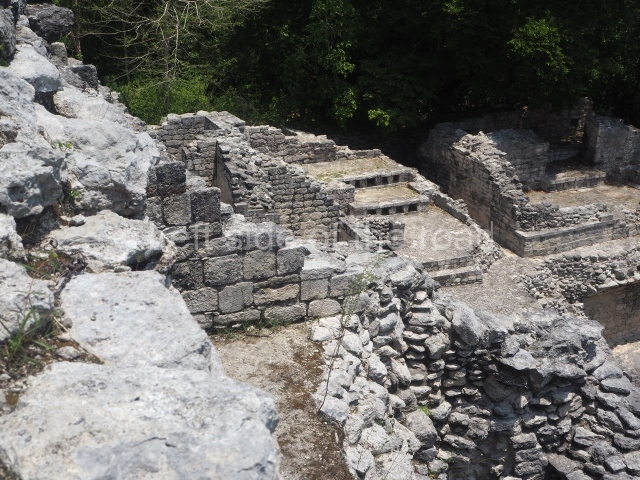
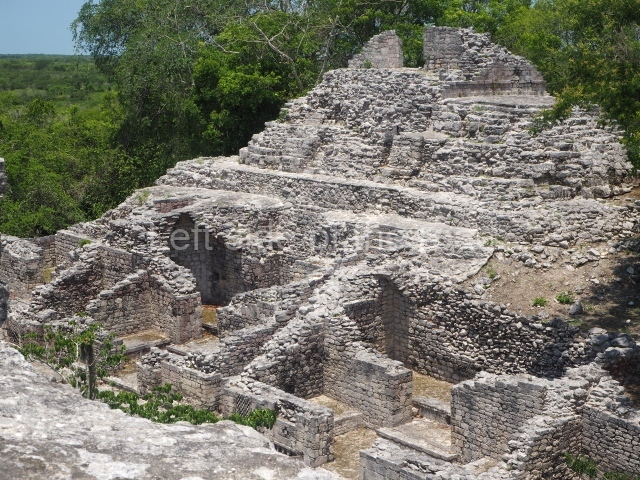
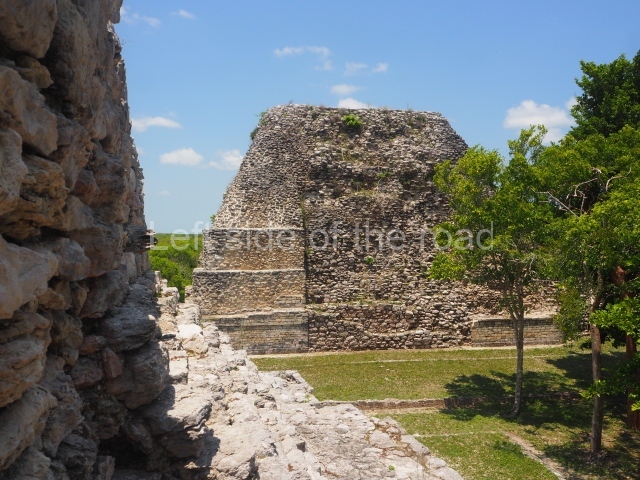
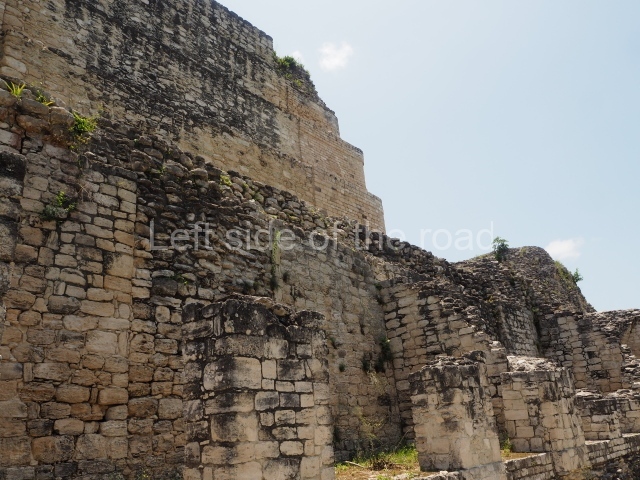
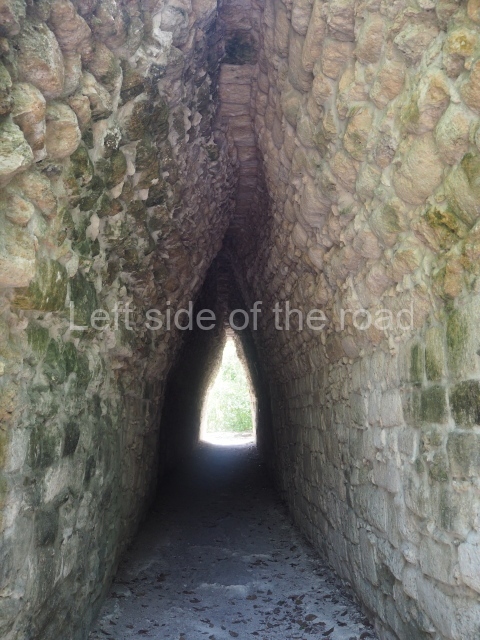
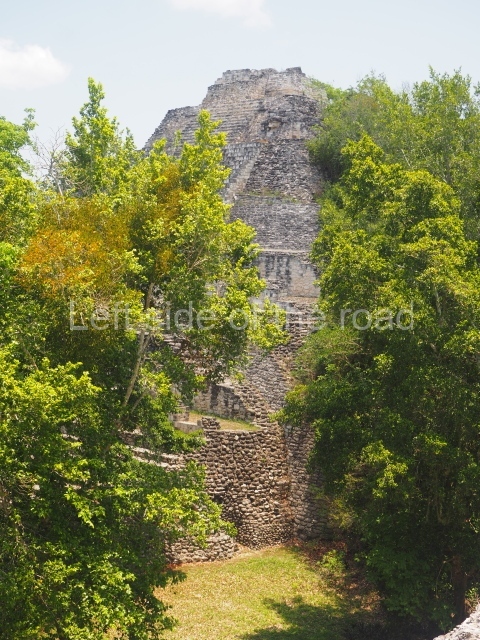
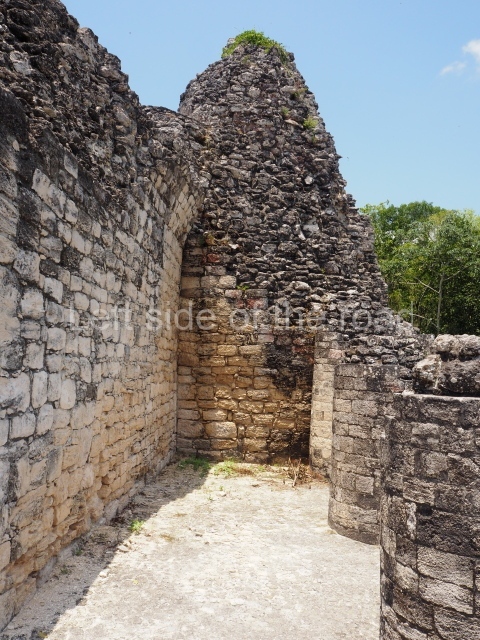
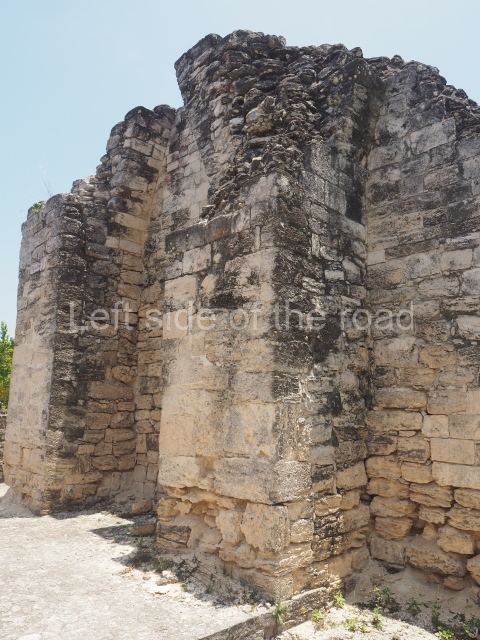
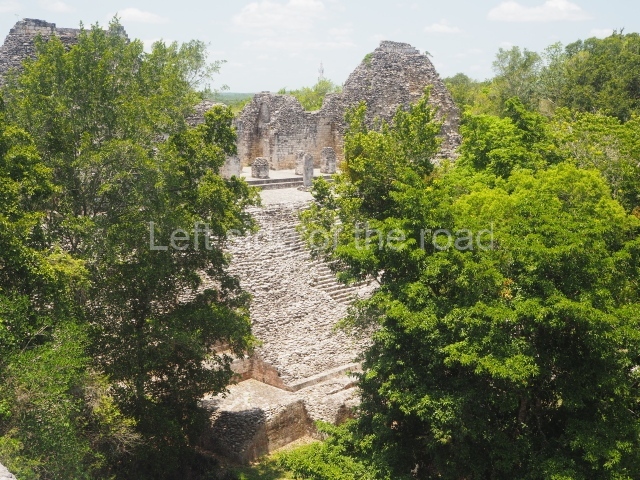
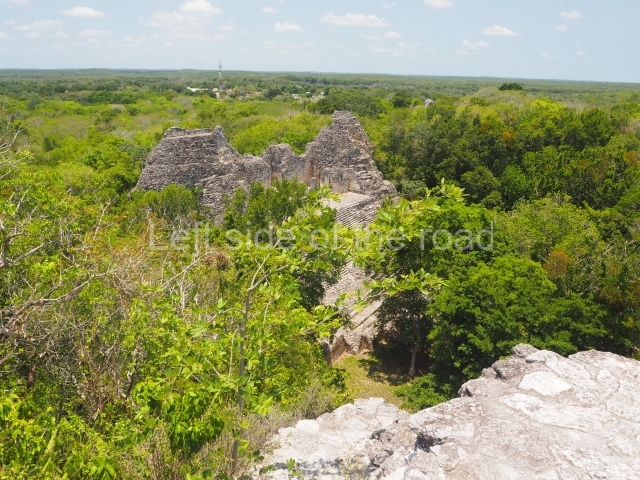
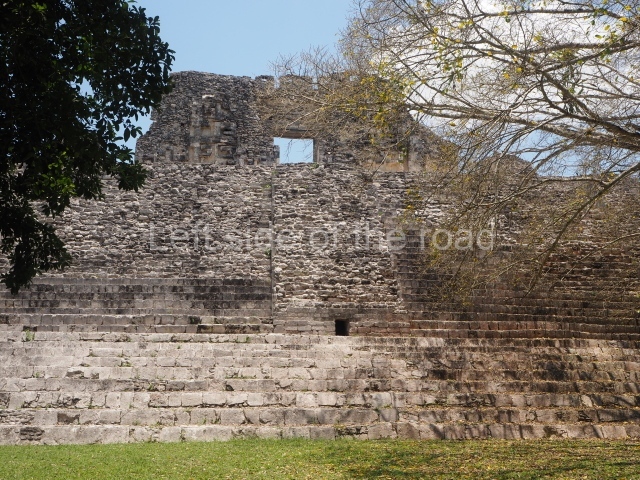
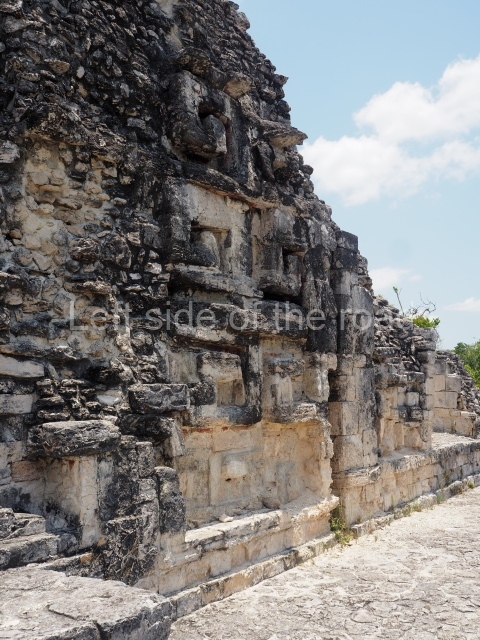
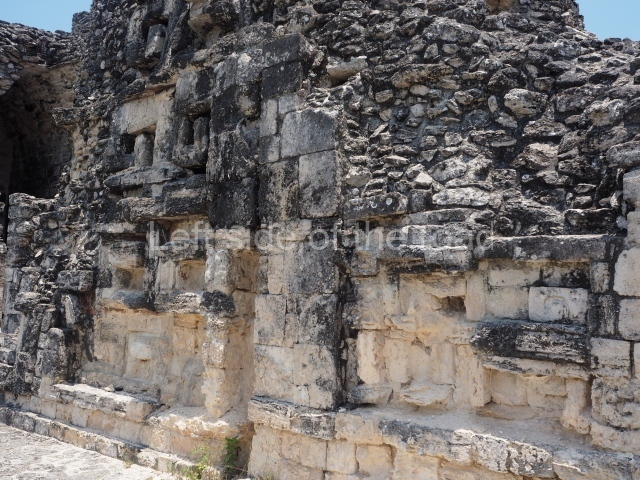
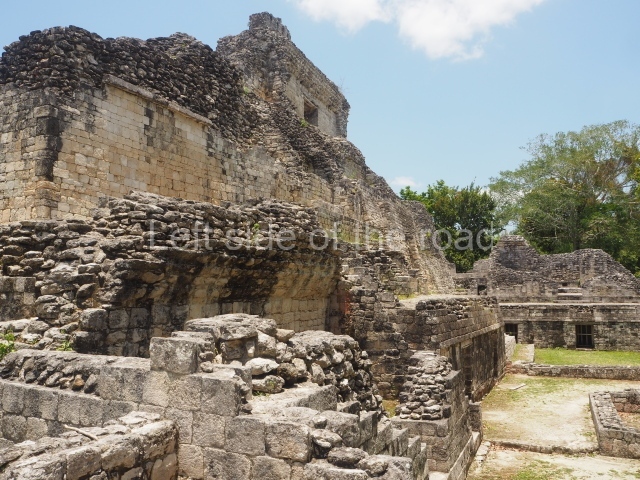
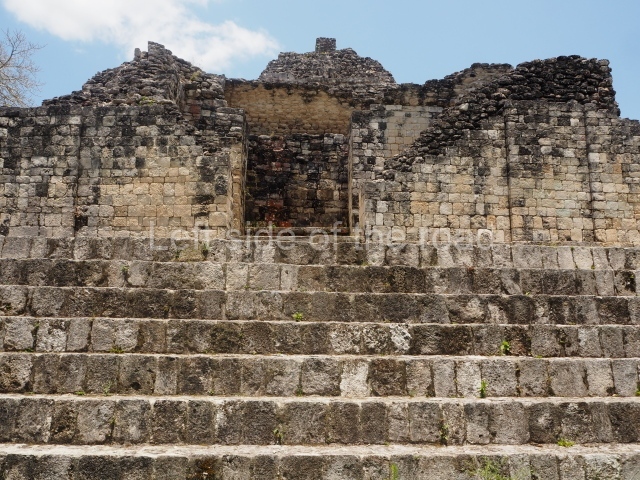
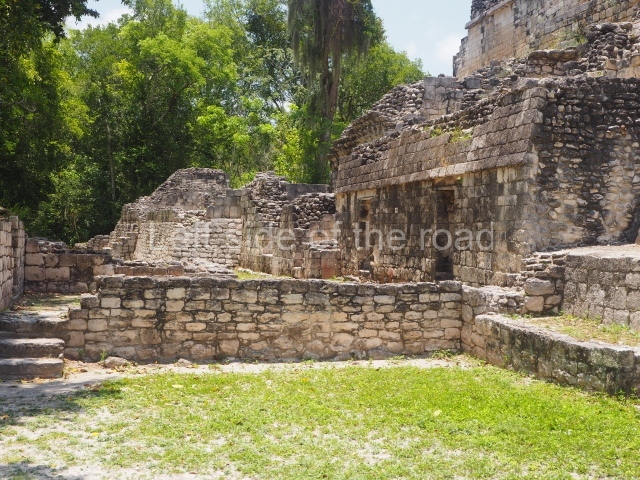
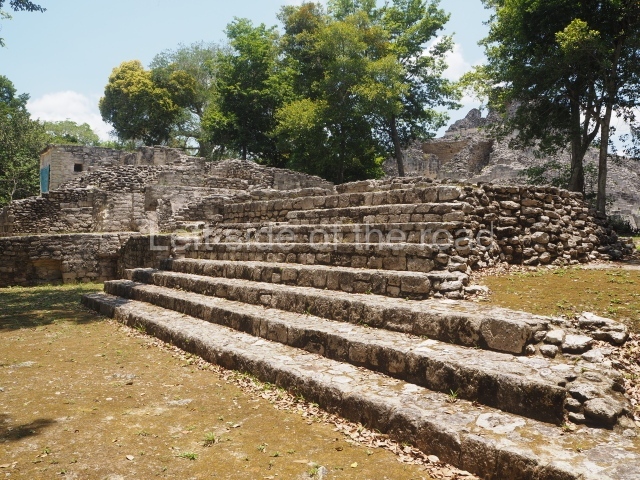
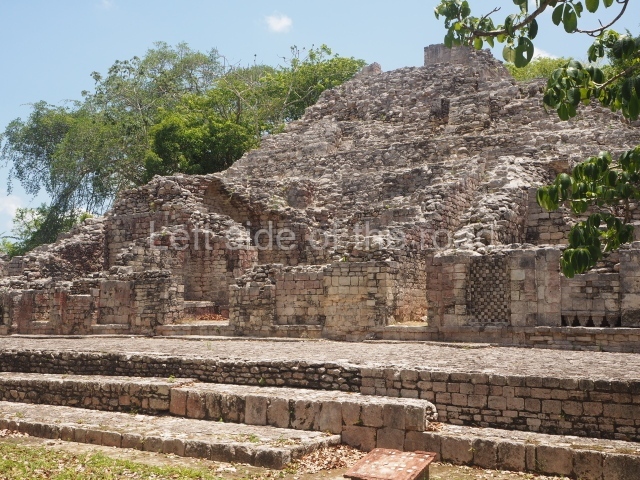
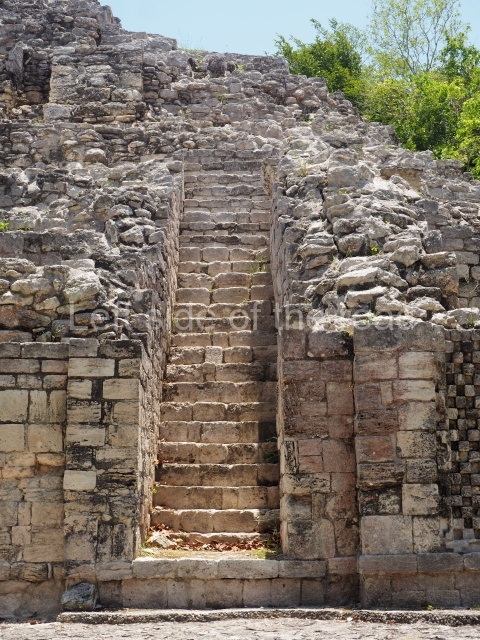
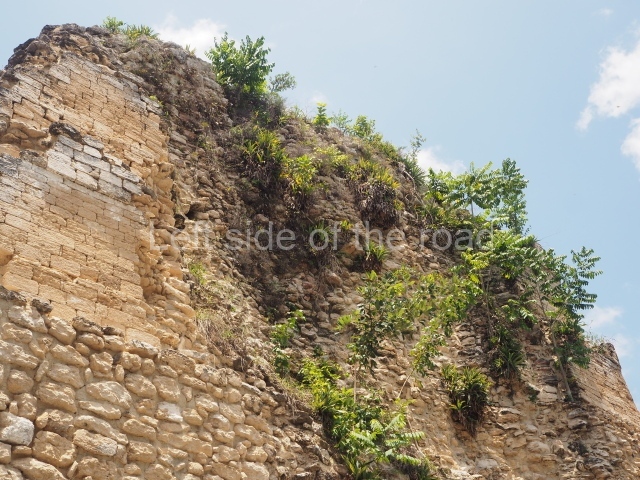
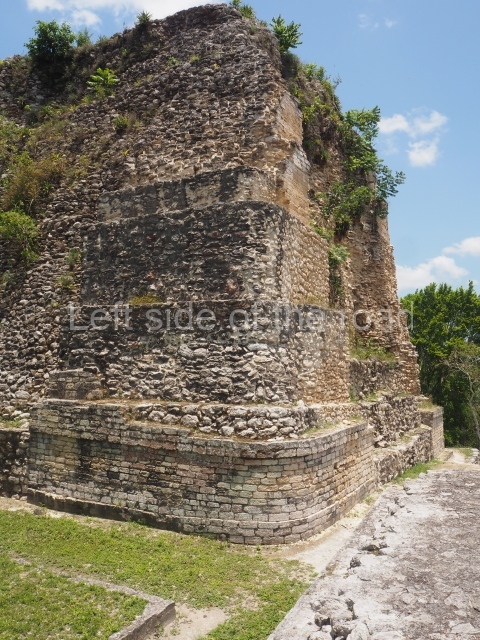
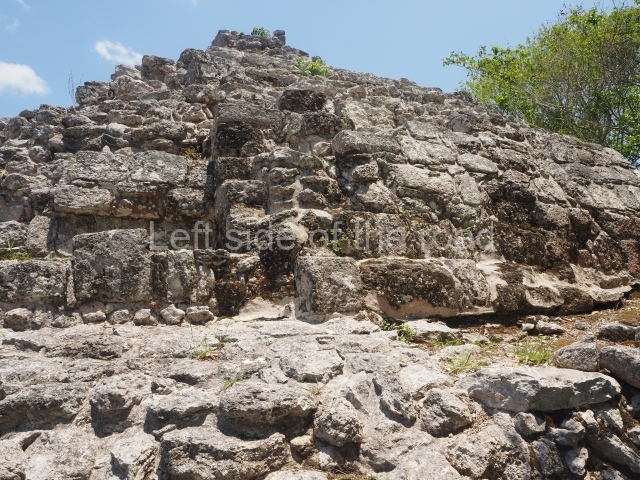
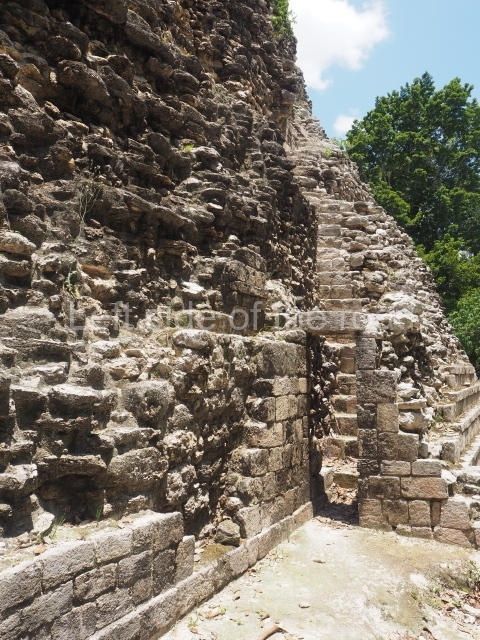
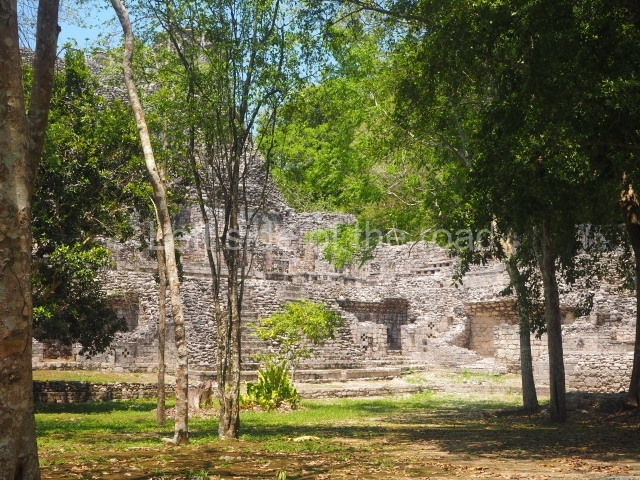
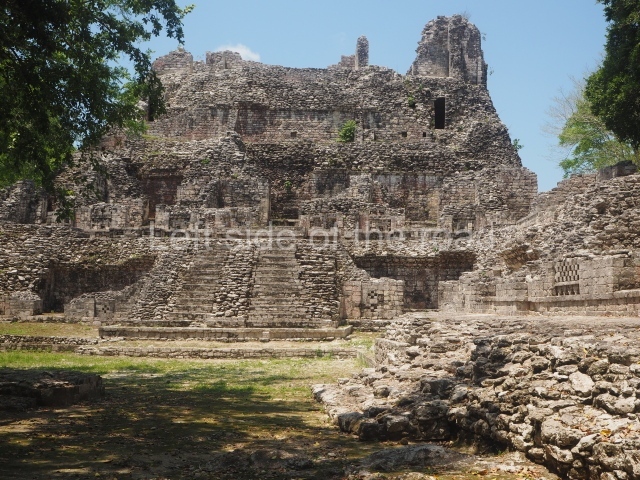
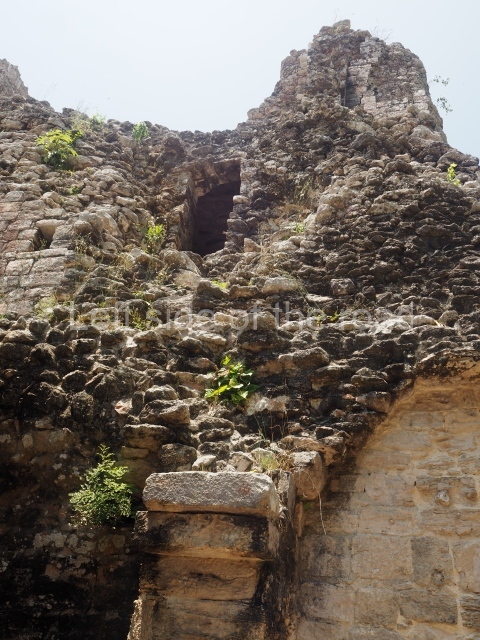
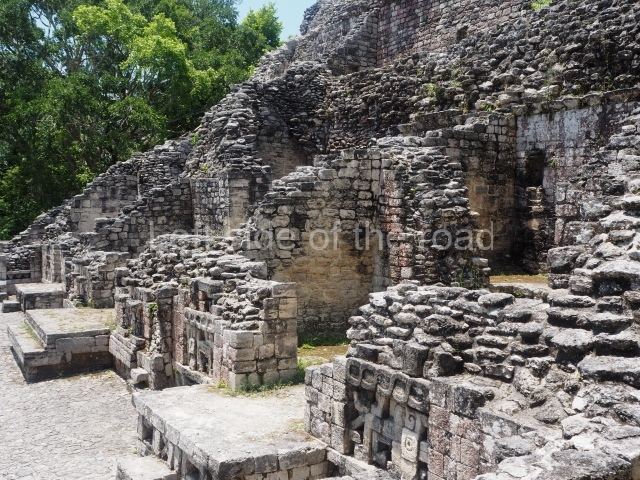
The oldest remains date from 600 BC, while the concentration of population and resources turned it into a regional capital between AD 600 and 900. During the Postclassic period (AD 1000-1450), the central government gradually disintegrated and its place was occupied by other sites with greater political influence. By the time the conquistadors arrived, Becan was completely covered by rainforest. The site contains monumental constructions in the Rio Bec architectural style, which is characterised by high twin towers, near-vertical non-functional stairways, rounded corners and false temples atop the pyramids. On some buildings, the main facade is adorned with the face of Itzamnaaj, a powerful terrestrial deity. Its open jaws served as the central entrance to the building. The tour of this site commences at Plaza A or the East Plaza, composed of structures I, II and III.
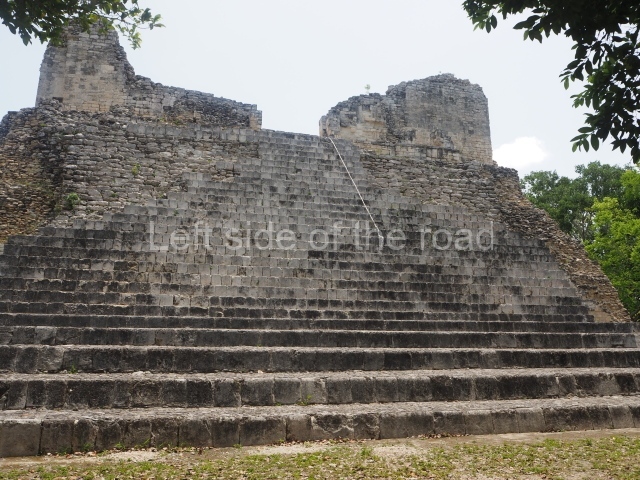
Structure I.
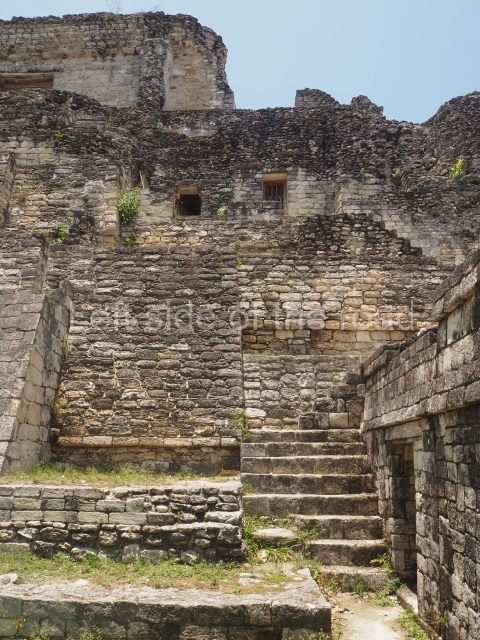
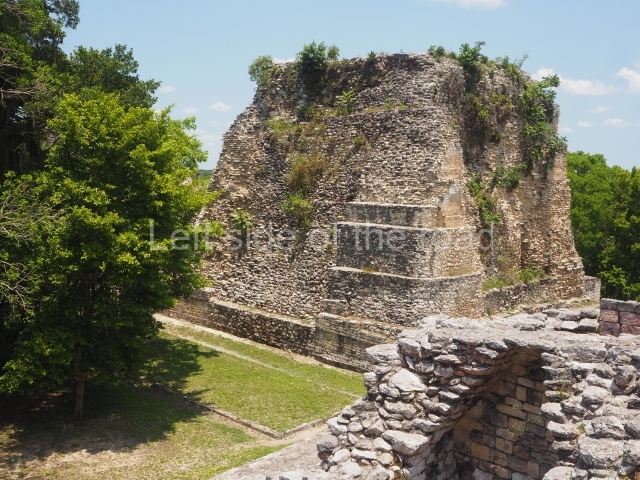
This is distinguished by its monumentality, with two solid lateral towers that rise 15 m above the plaza. The top of each tower has four openings – now sealed for protection from the rain – which were used for astronomical observations. Immediately south of the structure, the Maya architects constructed vaulted, two-storey buildings with 15 rooms on the ground floor and another six on the top floor. Construction commenced around AD 300 and the latest remodellings occurred in AD 1000.
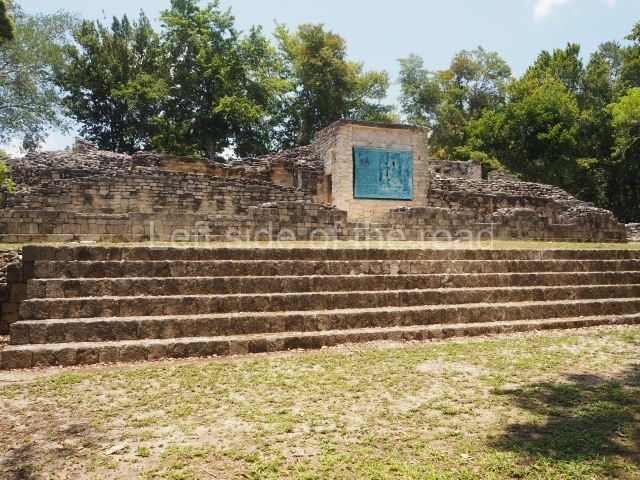
Structure II.
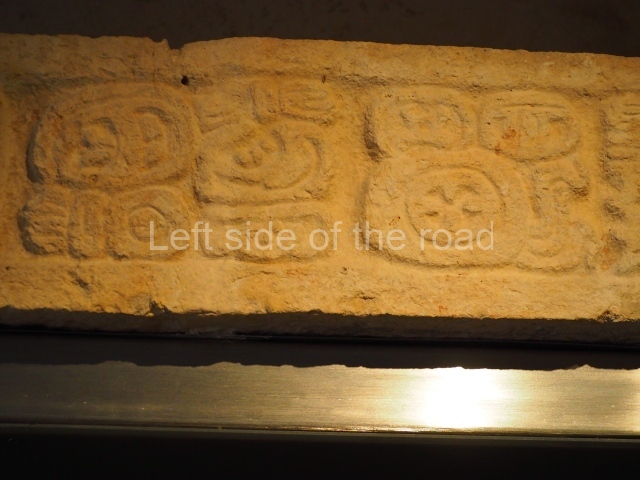
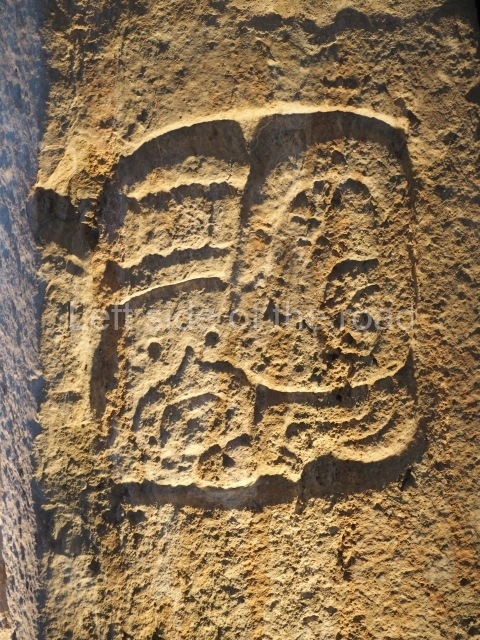
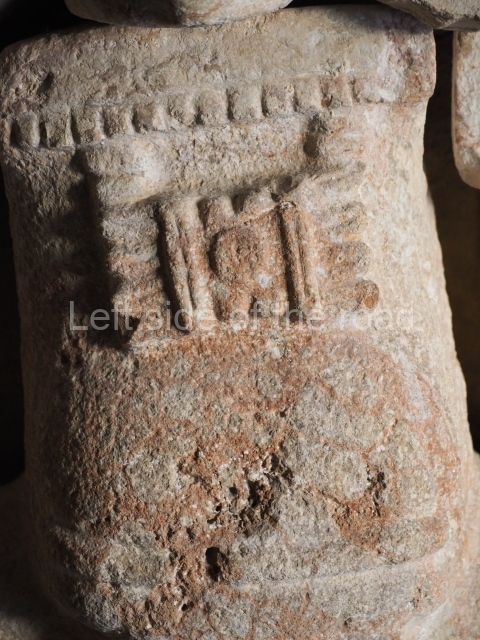
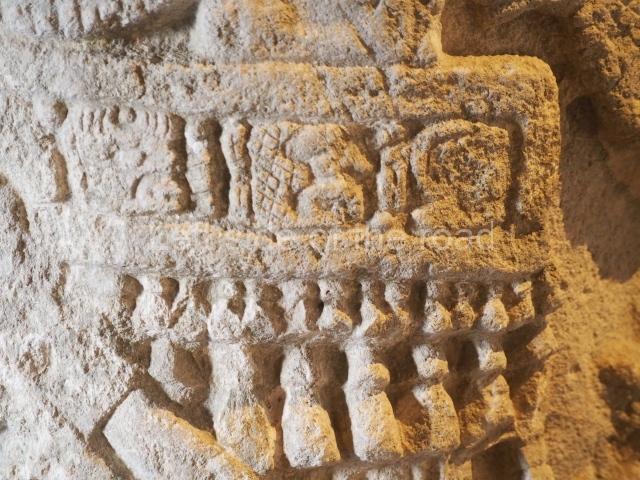
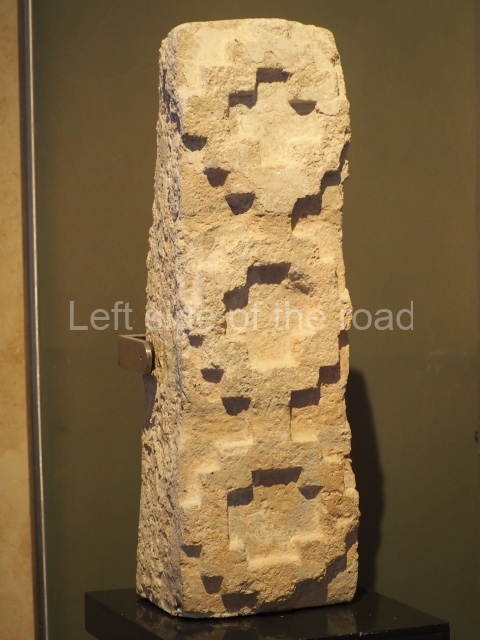
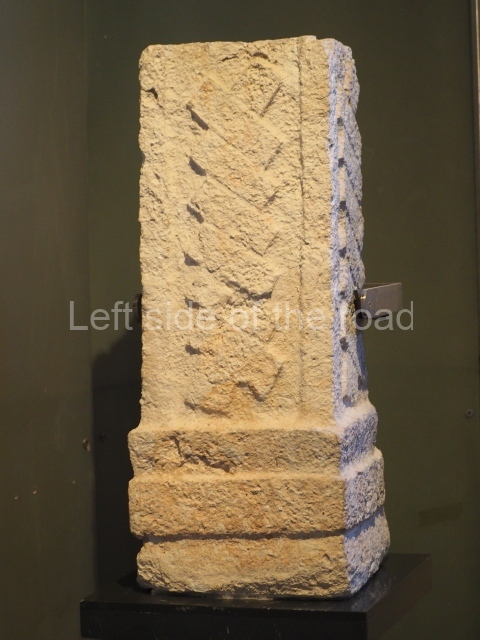
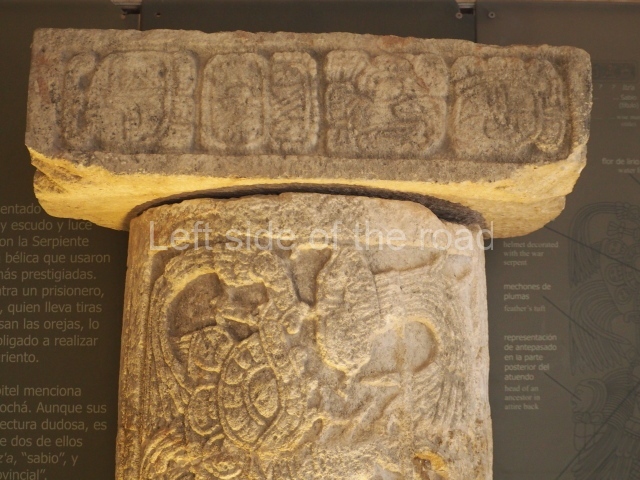
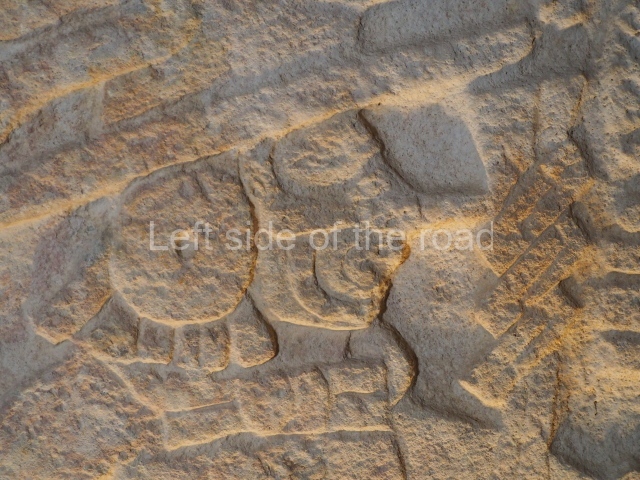
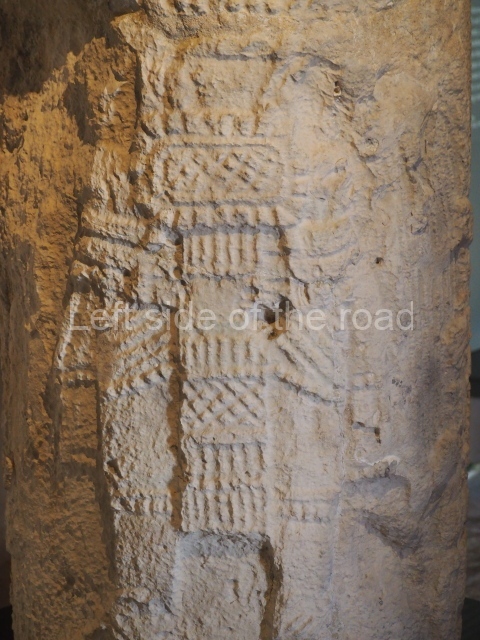
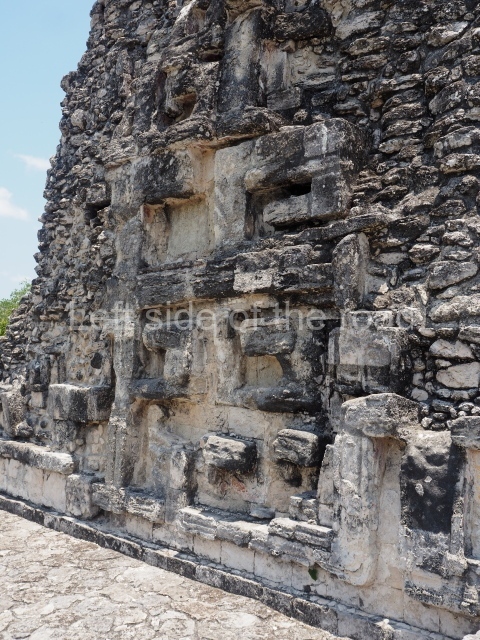
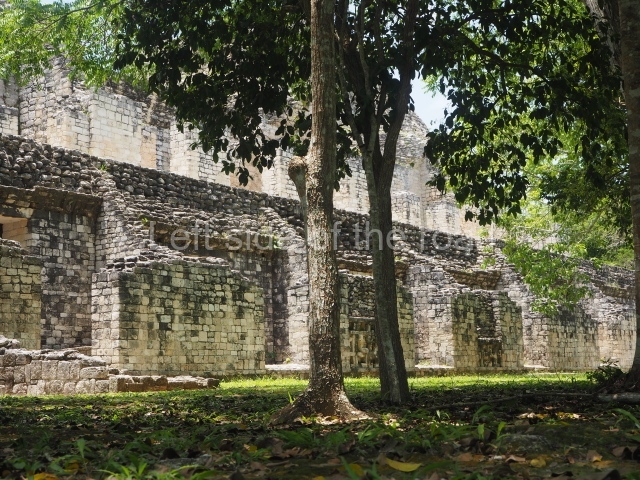
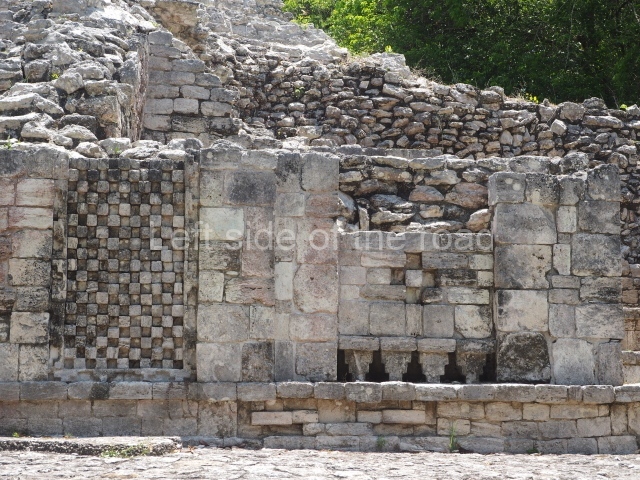
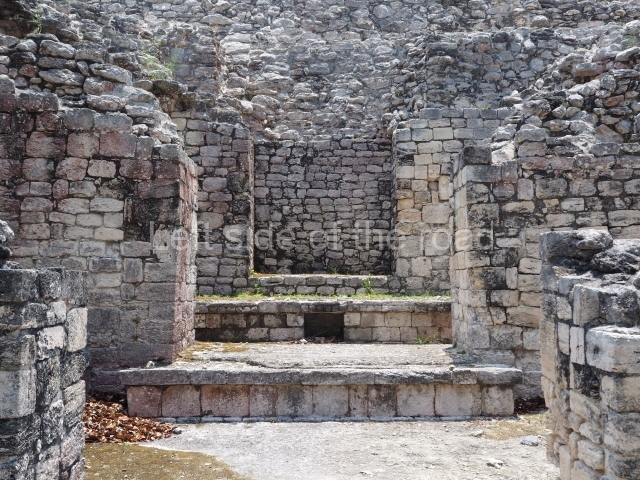
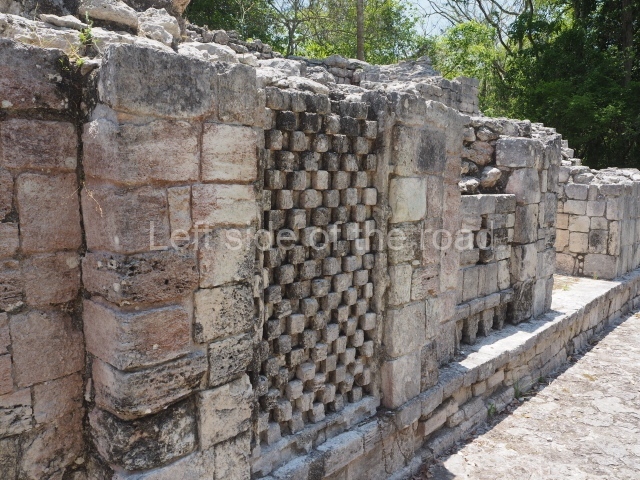
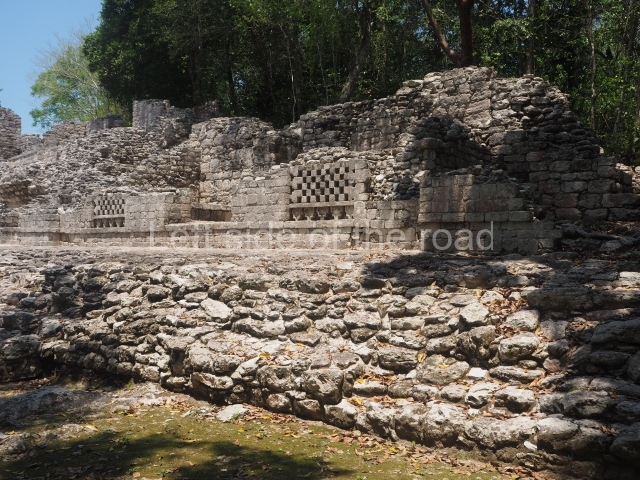
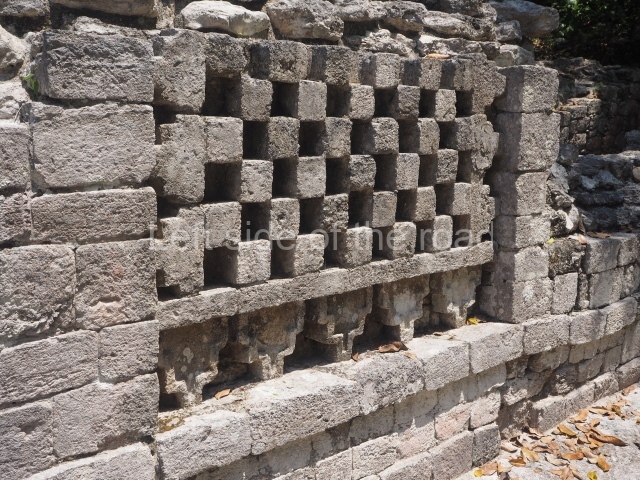
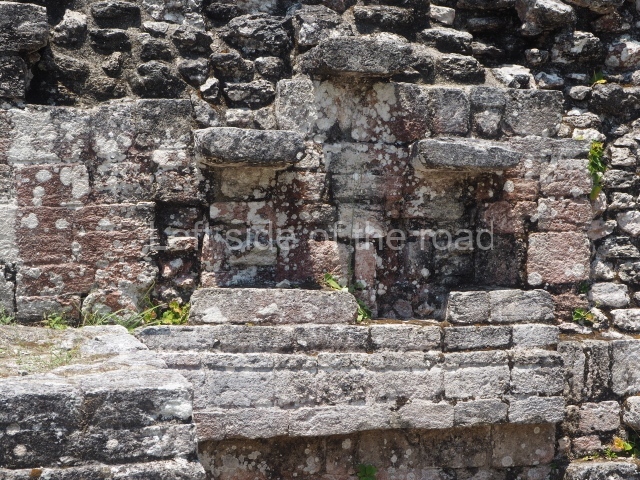
This is situated on the west side of Plaza A. The only part that has been explored is the facade on this side, which is 43 m long and approximately 15 m high, and parallel rooms. The rooms at the back have masonry benches, denoting their residential function. The facade was richly decorated with vertical panels displaying a chessboard pattern or small high and low-relief squares, and Ik symbols (second day in the Tzolkin Calendar) along the bottom of the walls. The stonemasonry is exquisite, and can still be appreciated today over 12 centuries later. Two tombs were found in the central bay, both elaborately made and covered with corbel vaults although never occupied.
Structure III.
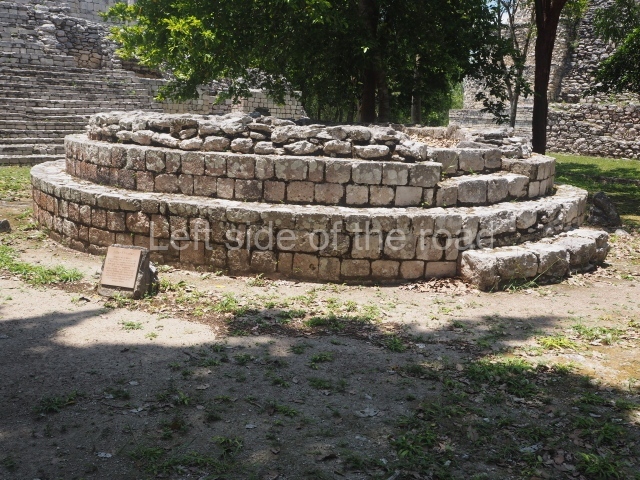
This is situated opposite the previous structure, occupying the east side of the plaza, and is approximately 50 m long. It was constructed in several stages and the final modification included a broad stairway leading to the second tier and directly facing a circular altar in the plaza, which measures 6 m in diameter and stands just over one metre high. The irregular inclusion of the latter element, which is neither in keeping with the axes of symmetry nor the monumentality of the surrounding constructions, suggests that it corresponds to the Terminal Classic (AD 900-1000).
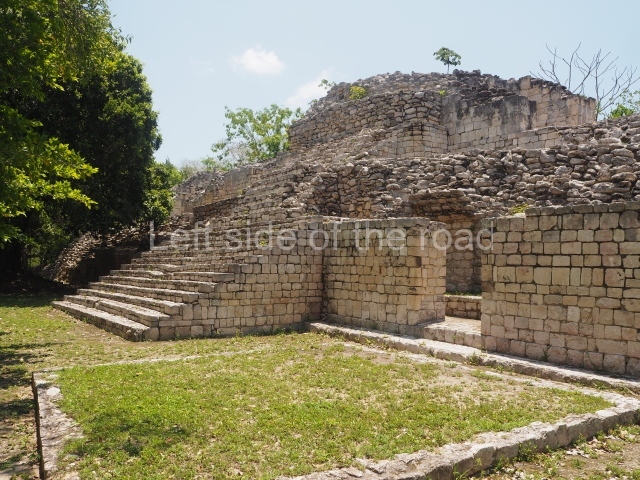
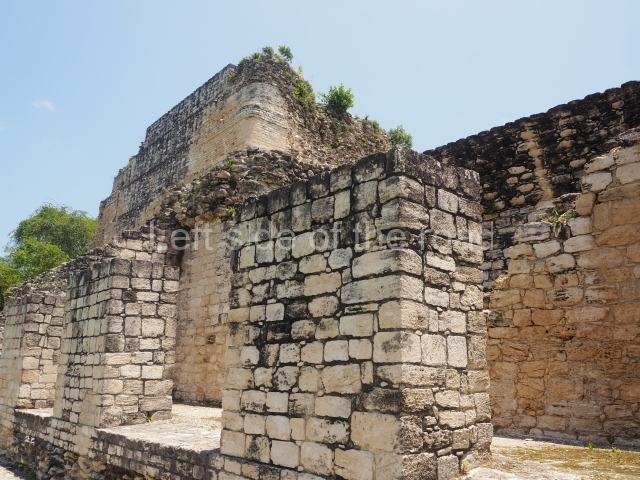
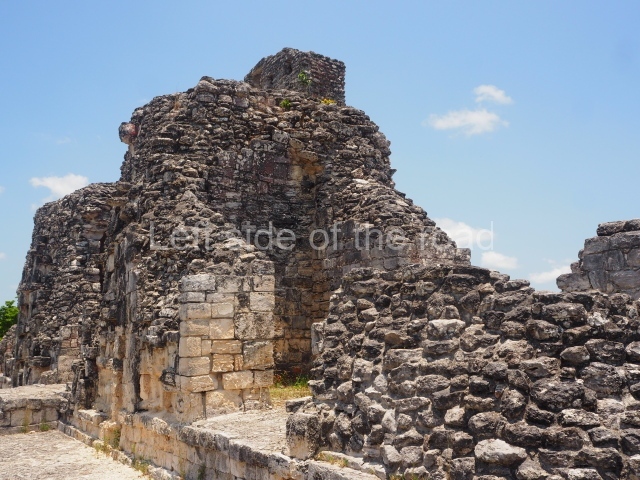
Structure IV.
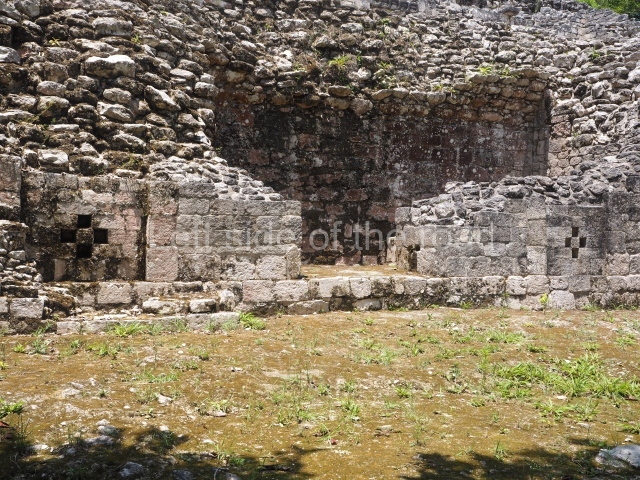
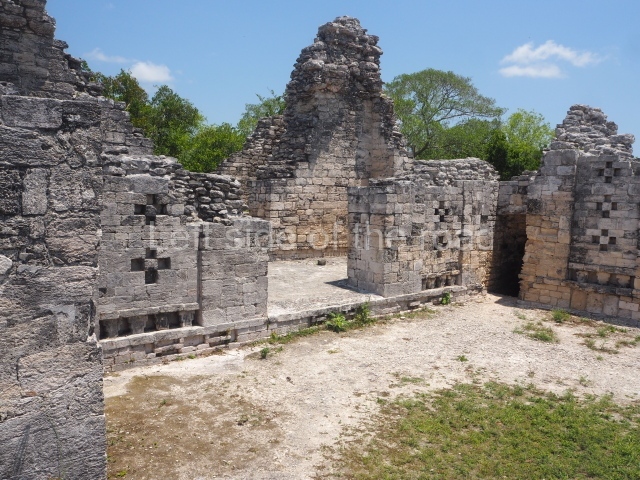
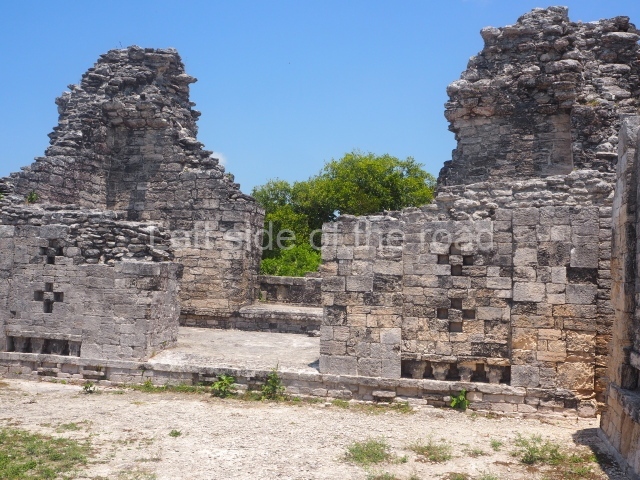
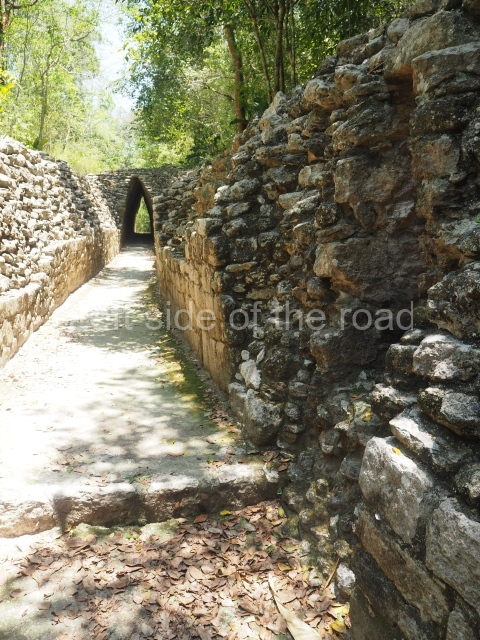
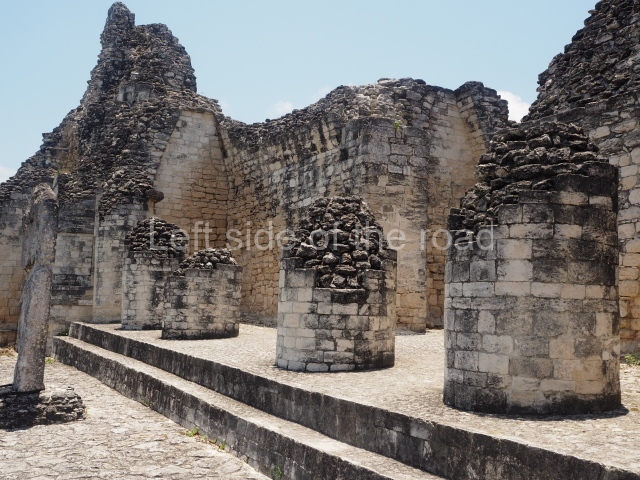
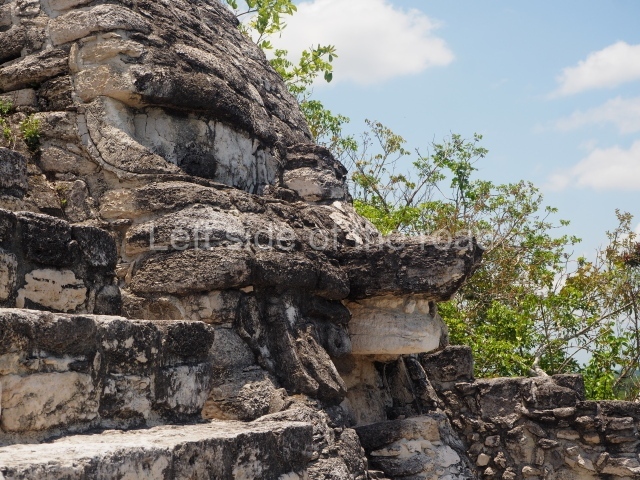
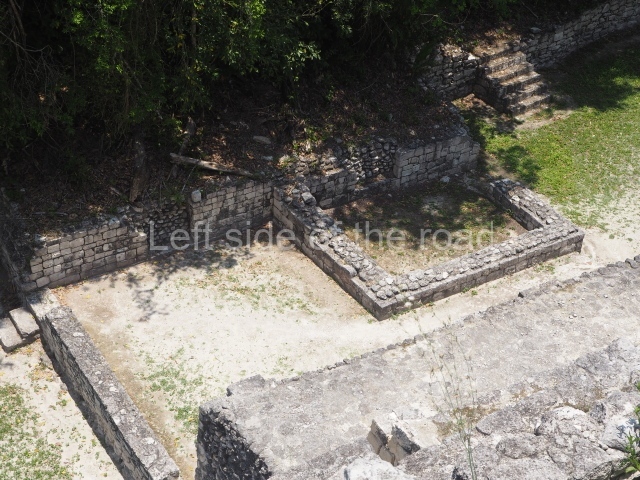
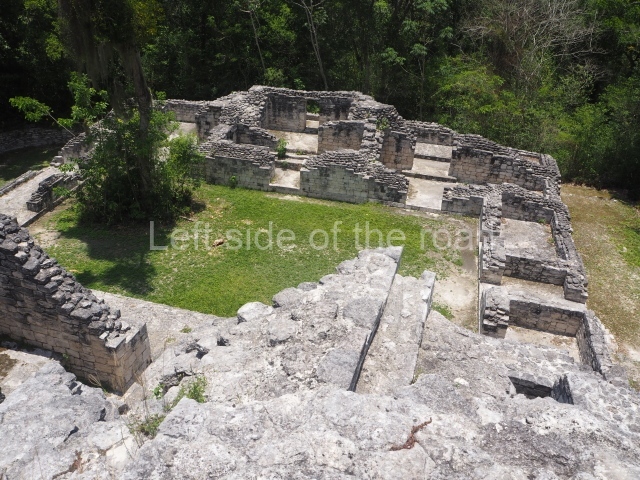
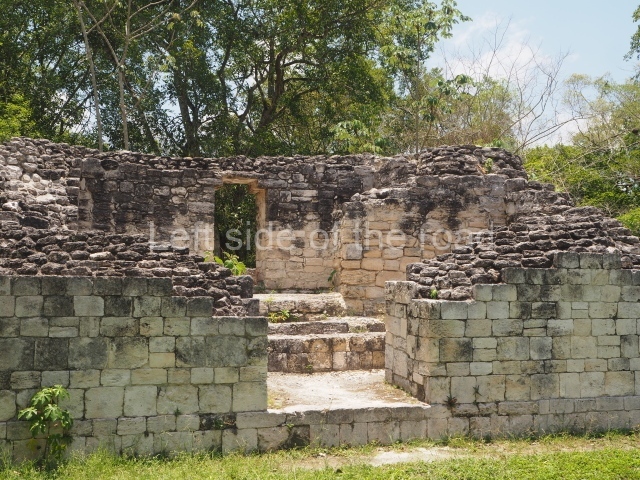
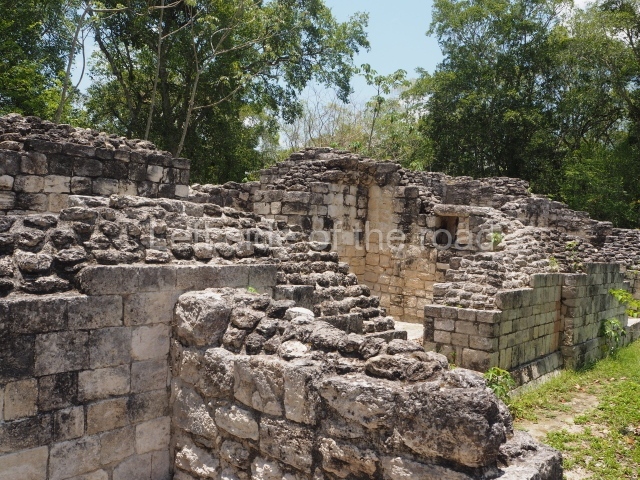
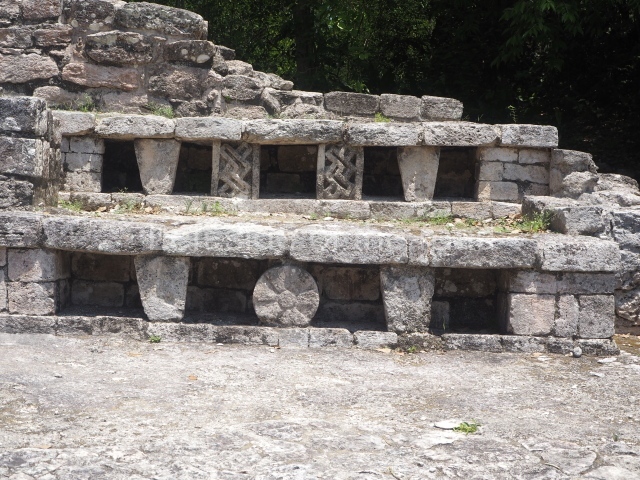
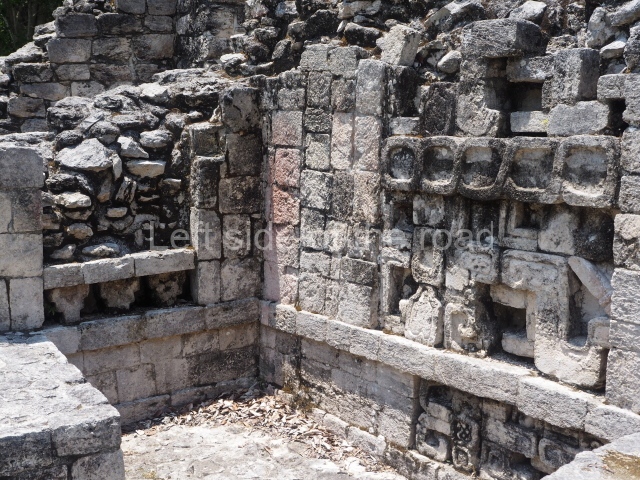
This is an interesting example of Rio Bec architecture: it has rounded corners and once sported non-functional stairways on its east and west facades. It seals the north side of the plaza and its entrance leads to a courtyard surrounded by rooms of varying sizes. The wall decoration includes stylised stone-mosaic zoomorphic masks. The north facade contains other constructions that once had vaulted roofs and were distributed on three levels, the terrain descending only just over 6 m. Further north is another annexe comprising six rooms with benches. Just beyond this is a long corridor, almost 60 m in length. Part of the vaulted roof can still be seen. The west end of this corridor leads to Plaza B, where structures VIII, IX and X are open to visitors.
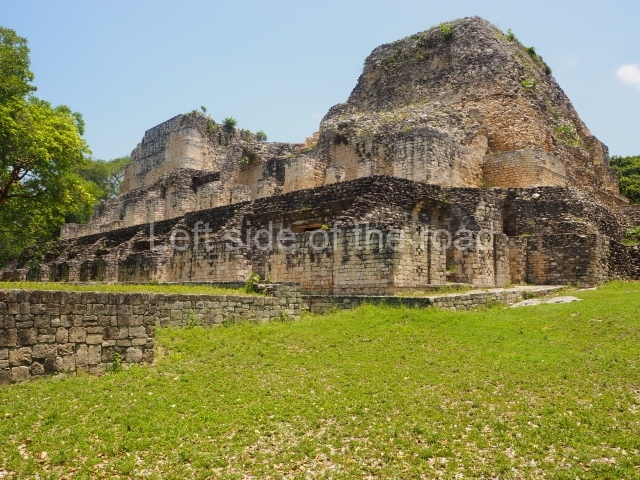
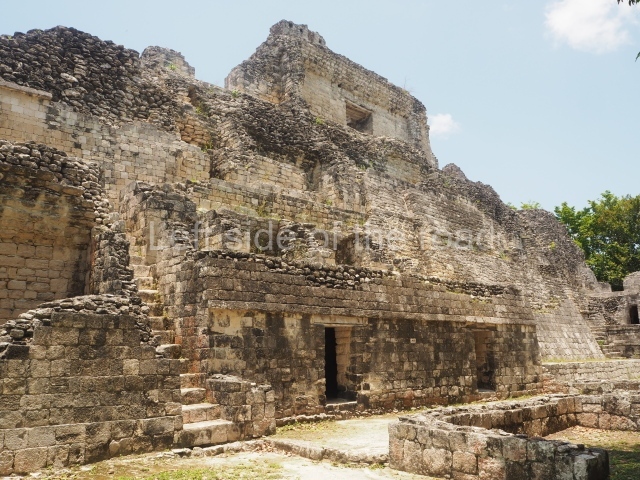
Structure VIII.
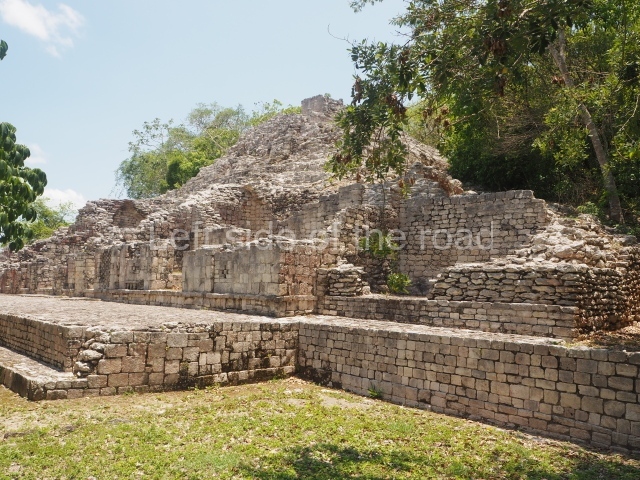
This is another of the monumental works in the city, with towers at its north and south ends, as well as the remains of a magnificent mask on the central facade. It once had nine rooms at the top and from the middle section it is possible to make out the buildings of the nearby Xpujil in the east. Beneath the platform (45×20 m), ten high-ceilinged (8 m) narrow chambers were found, none of which had stucco cladding, ventilation or natural light. It has been suggested that these were used for a variety of rituals, such as fasting, praying and auto-sacrifices or bloodletting; another suggestion is that they were used for storing surplus goods. Whatever the case may be, their practical purpose was to save many tons of construction material.
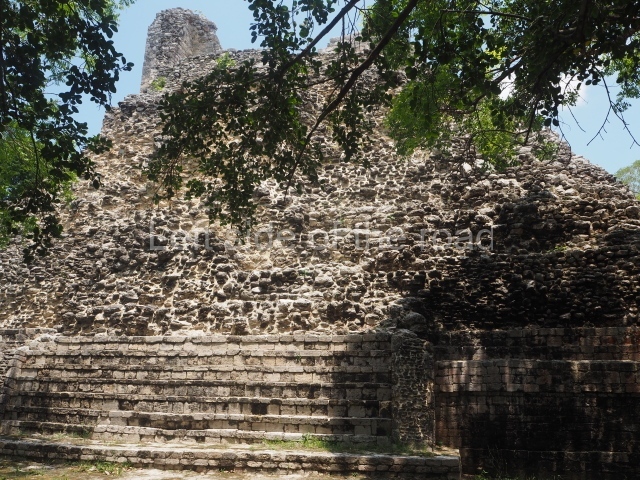
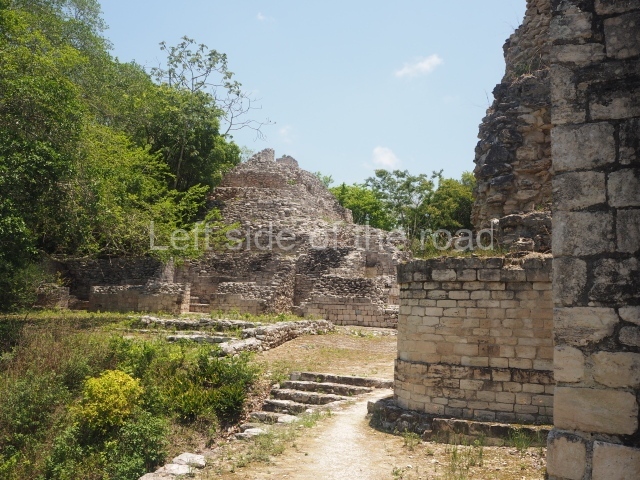
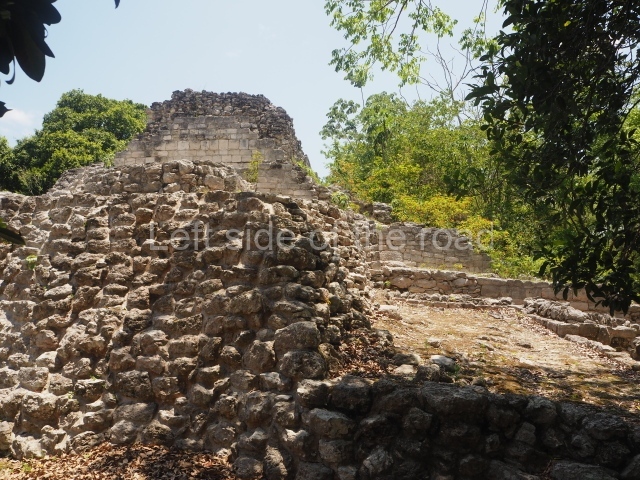
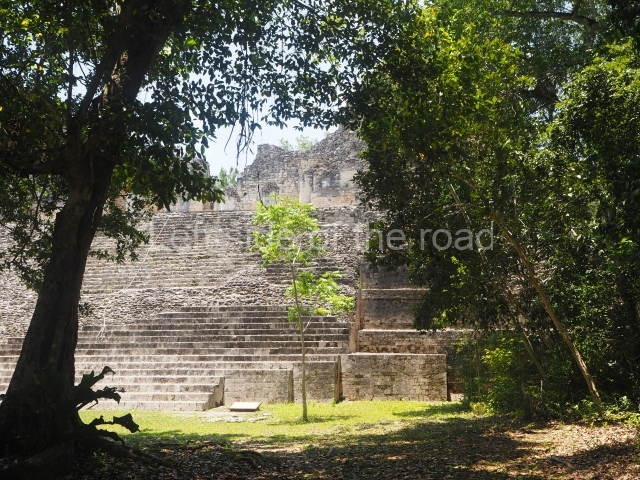
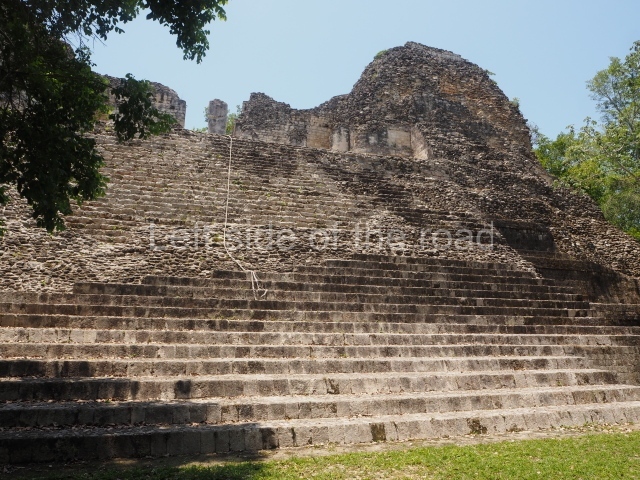
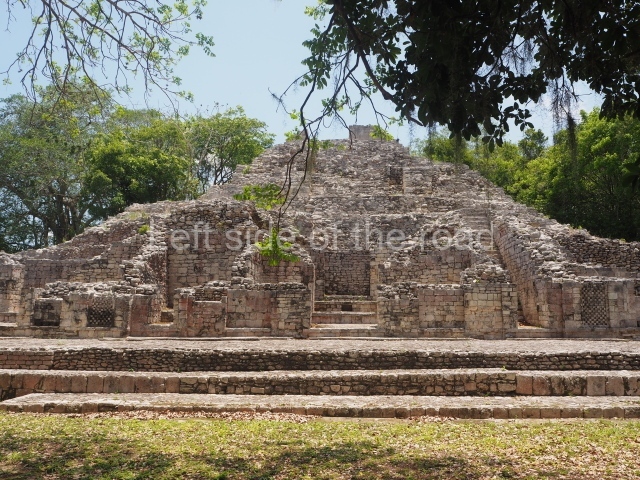
Structure IX.
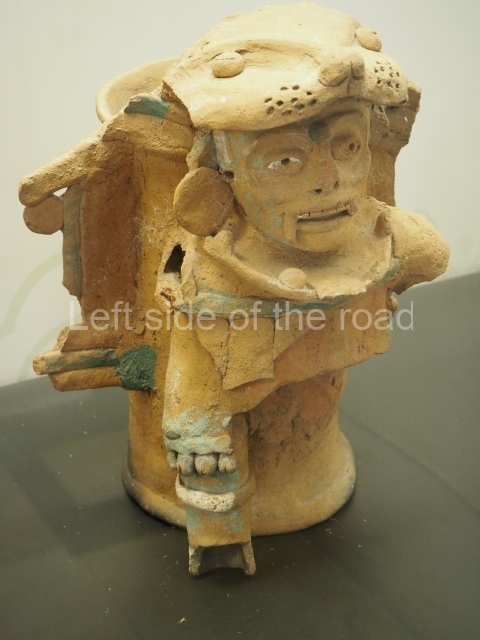
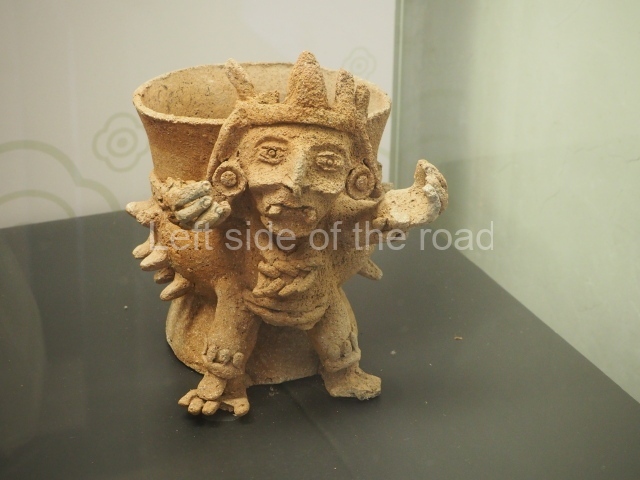
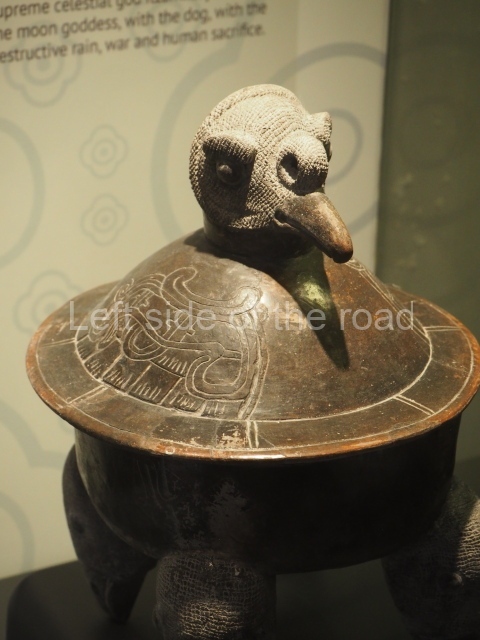
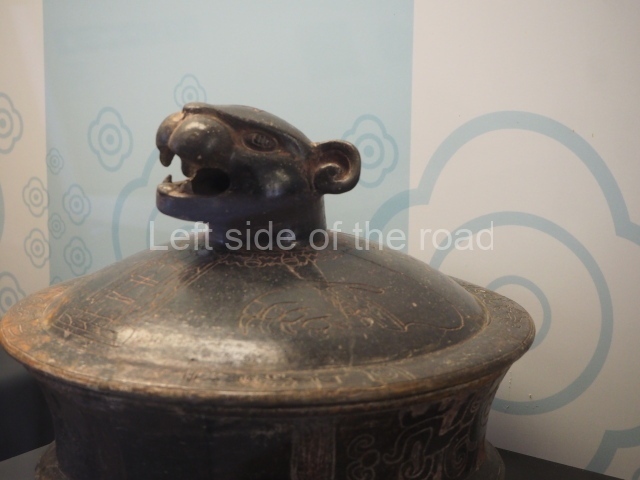
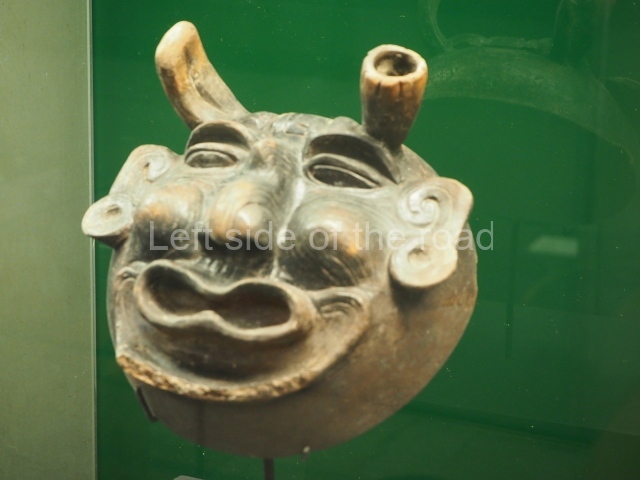
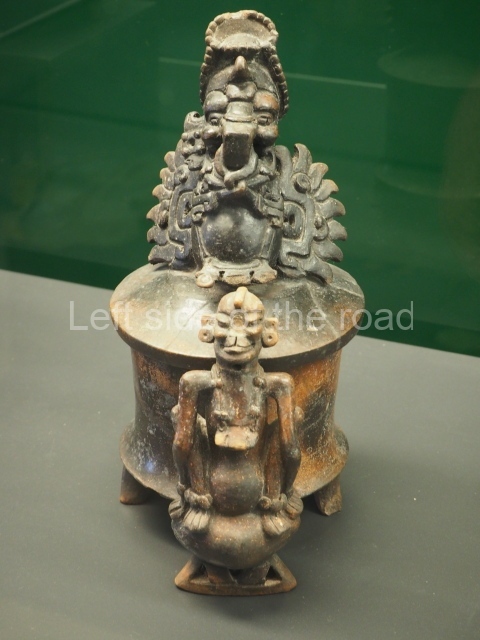
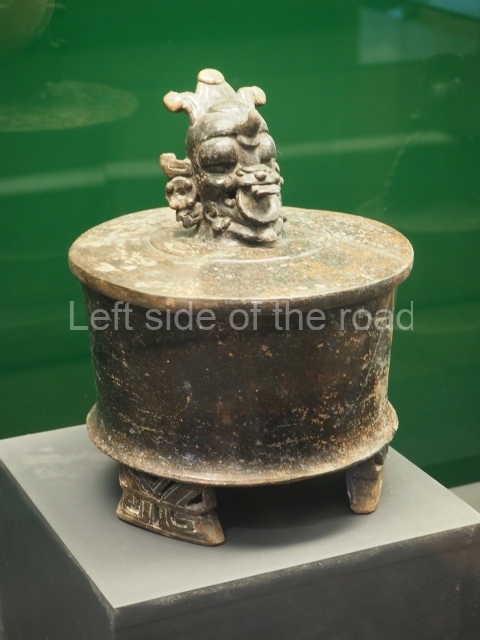
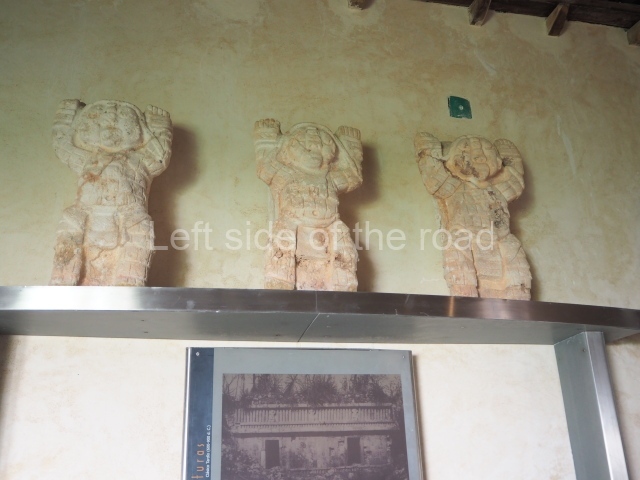
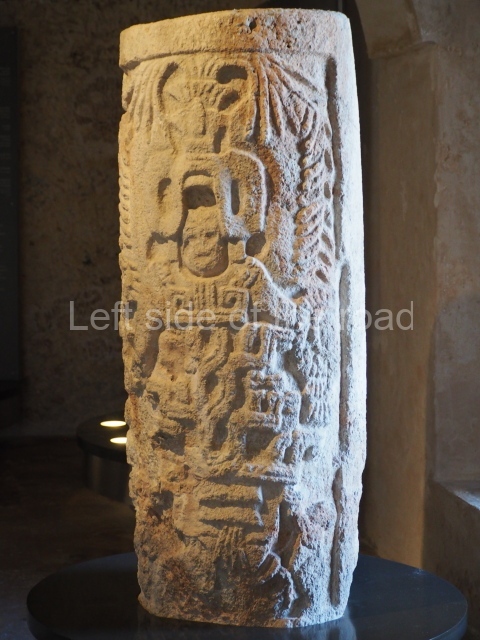
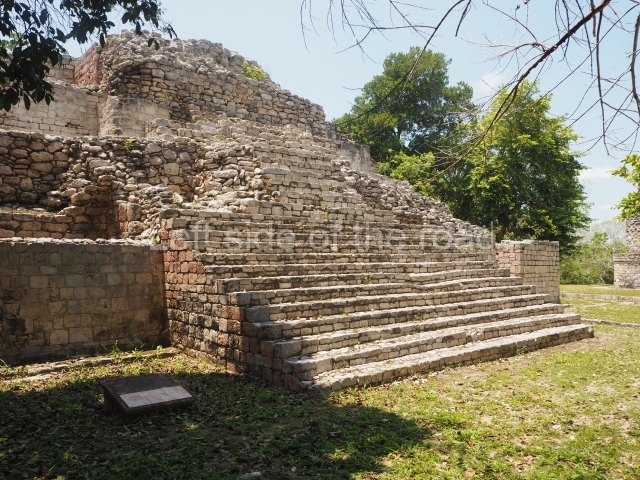
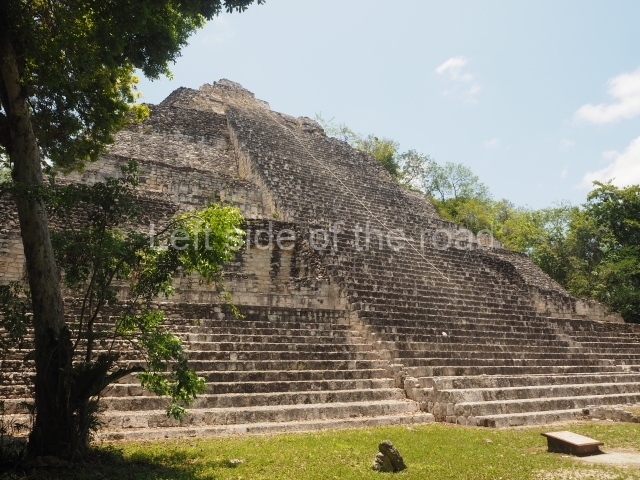
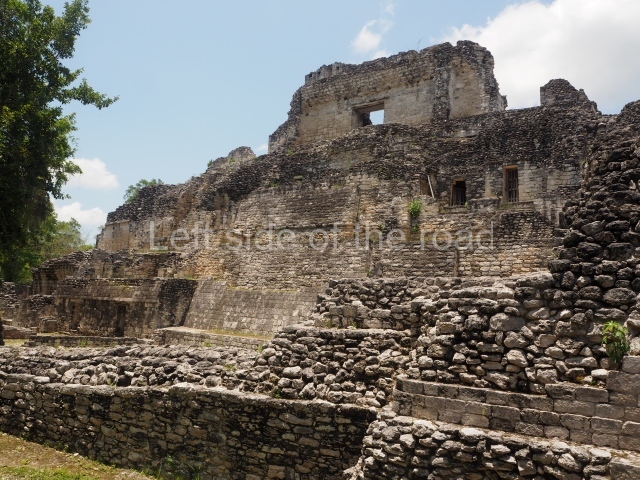
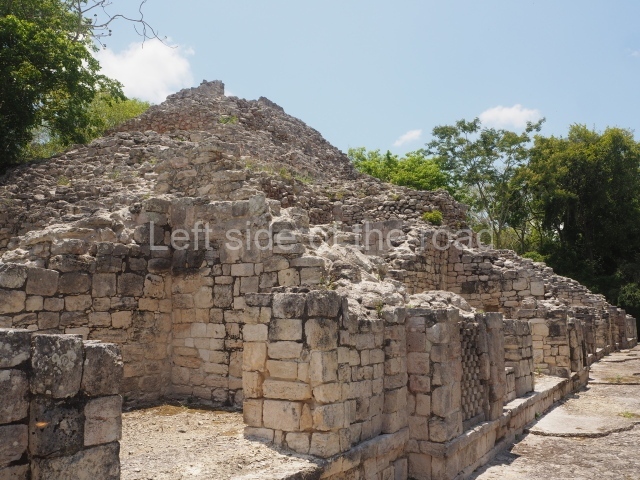
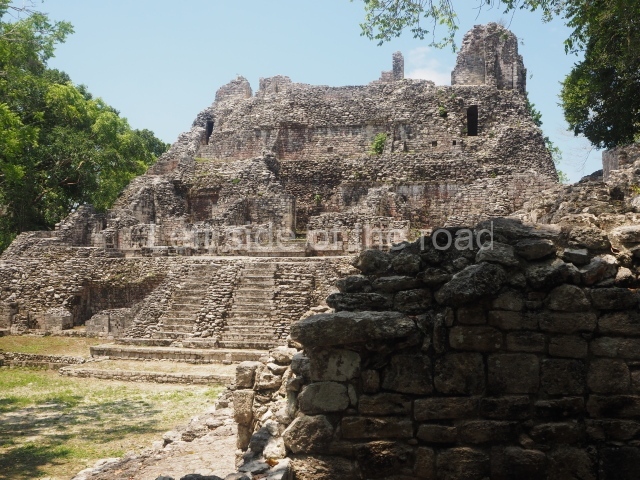
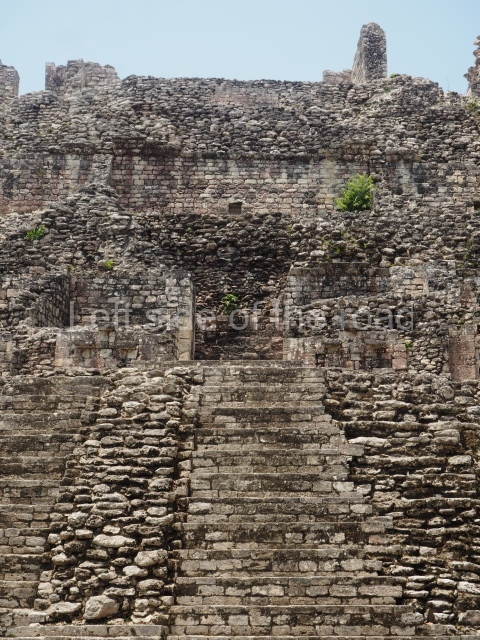
This is the highest one on the site (42 m). It displays three architectural phases. The first dates from the Late Preclassic (100 BC-AD 250), when four vast stepped volumes were built, their only access on the south side, and a temple at the top. The platform displayed masks combining human and feline features. A second construction stage during the Early Classic (AD 250-600) is confirmed by the architecture of the top temple and a rich offering of 15 vessels with extraordinary archaeological merits in terms of their timeline, epigraphy and symbolism. The third phase occurred during two specific points of the Late Classic (AD 600-900), when several rooms were added at both sides of the stairway at the middle of the front facade. In Postclassic times (AD 900-1400), anthropomorphic incense burners were placed amid the ruins of the top temple.
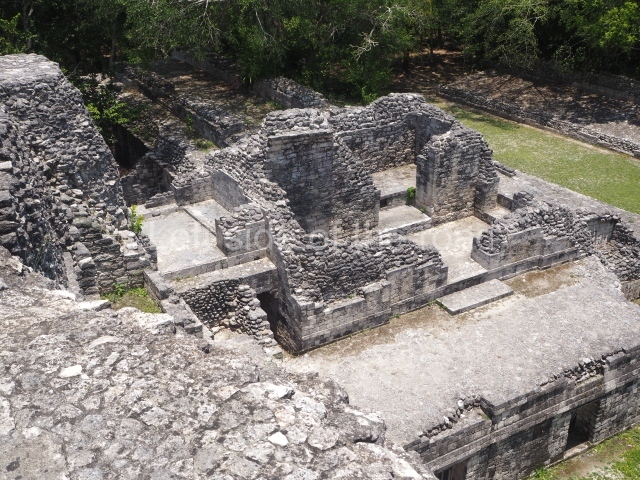
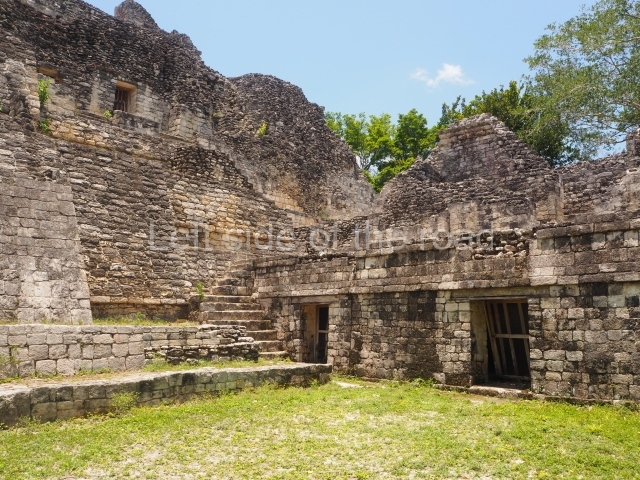
Structure X.
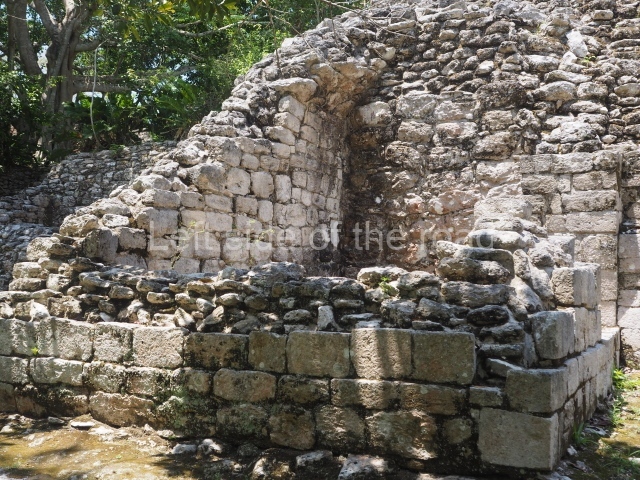
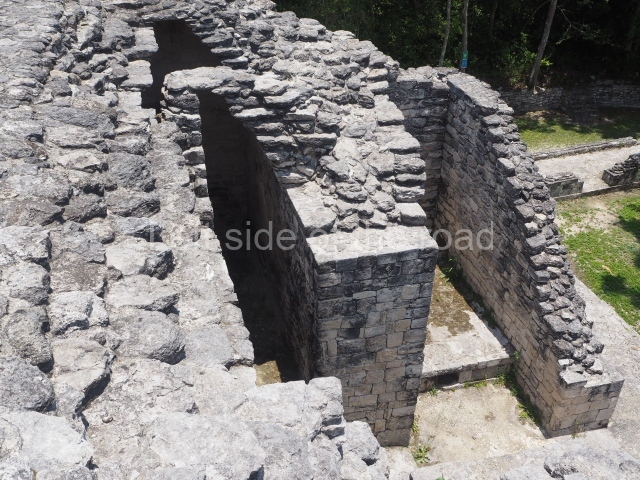
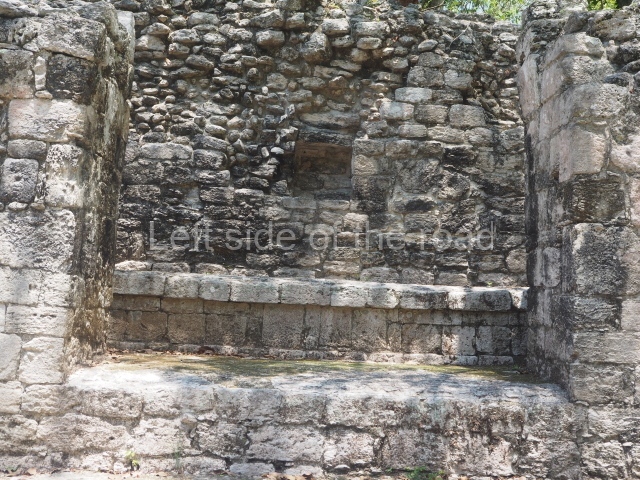
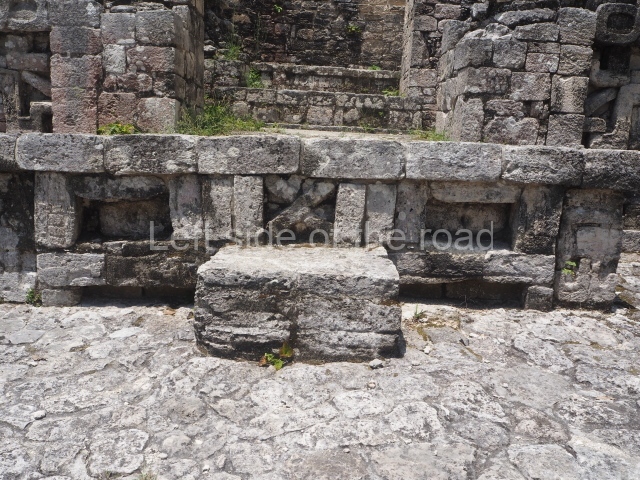
This pyramid platform is smaller than the previous one, standing 14 m above the plaza, and has a stairway on its east side. At the top of it are several rooms arranged in pairs, and at both sides, on a lower tier, another series of rooms which once had corbel-vault ceilings. The excavations conducted on the west side revealed a palatial complex containing close on 70 rooms distributed around courtyards to the north and south. Most of these rooms have benches, niches in the walls and interior accessories (a type of curtain rod) for hanging fabrics or animal skins to filter the sunlight. The gradual completion of the buildings, the creation of open and closed areas, access control and an evident restriction on the use of the space all occurred between AD 750 and 1000, during the height of Becan’s splendour.
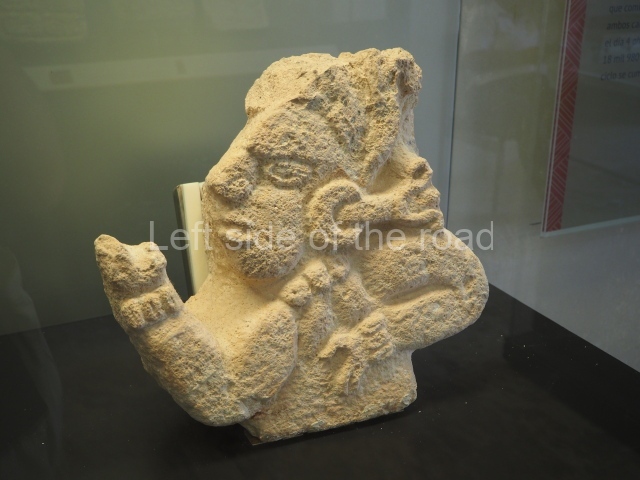
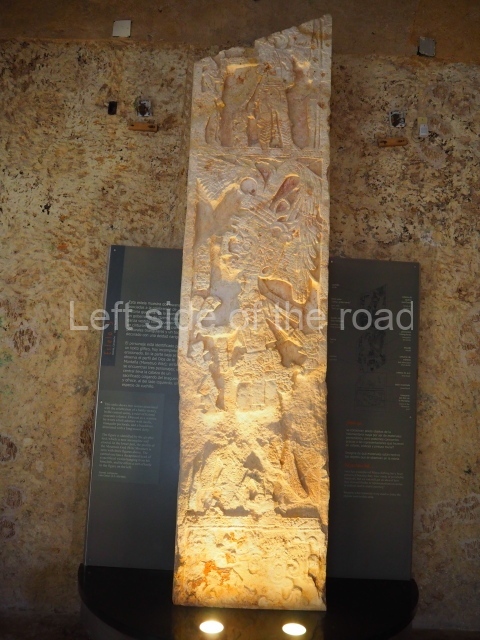
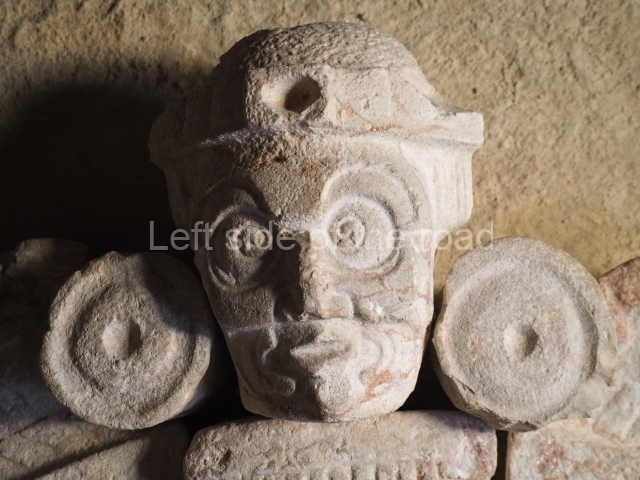
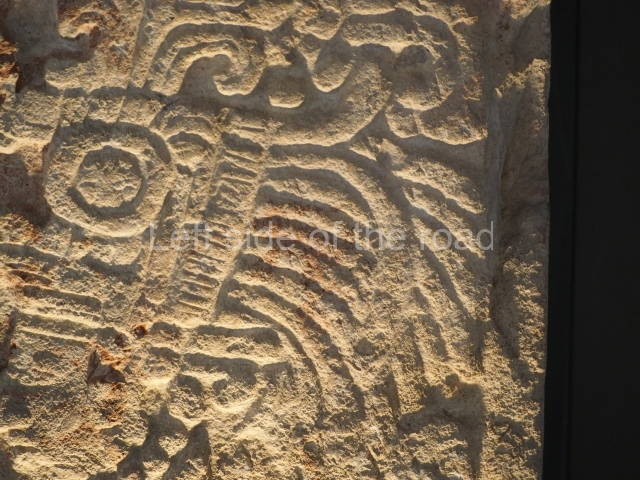
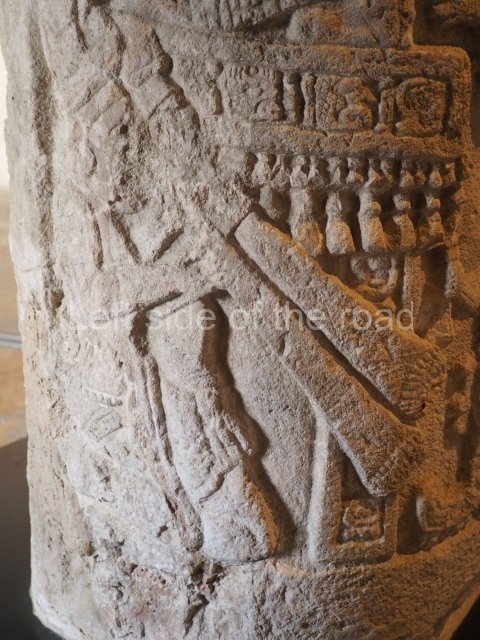
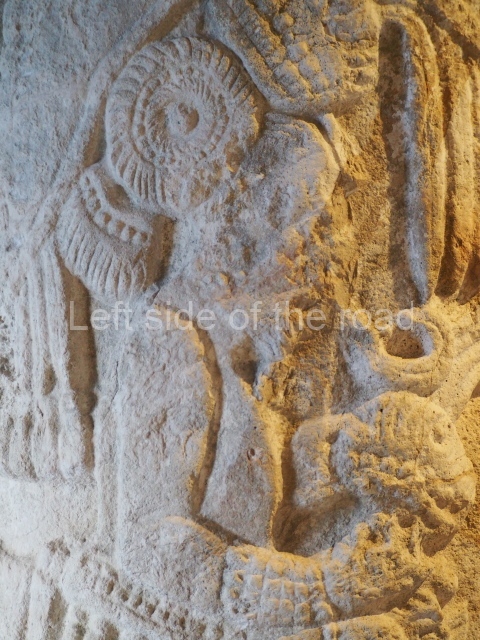
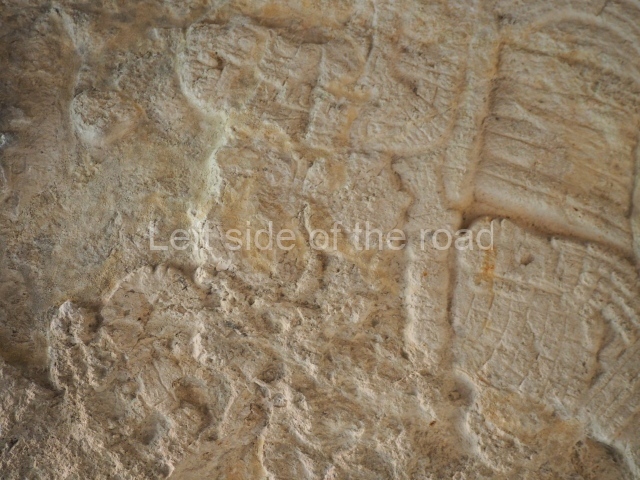
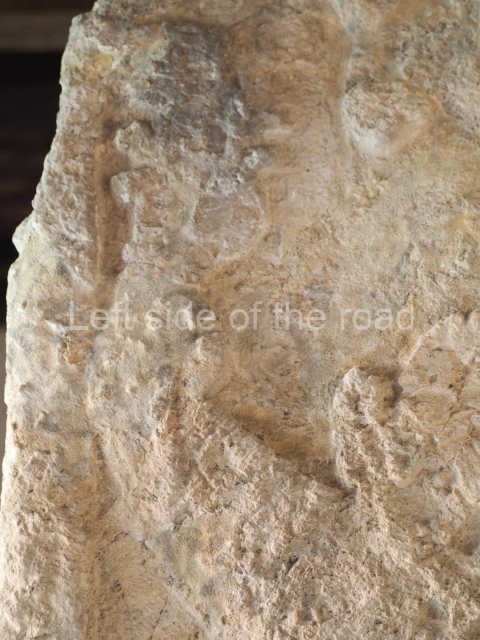
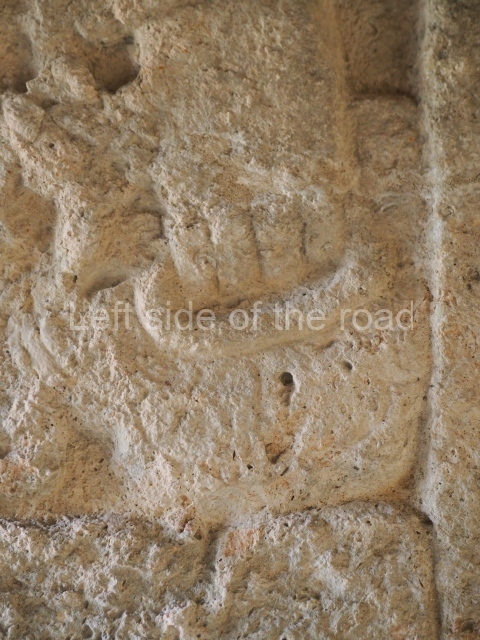
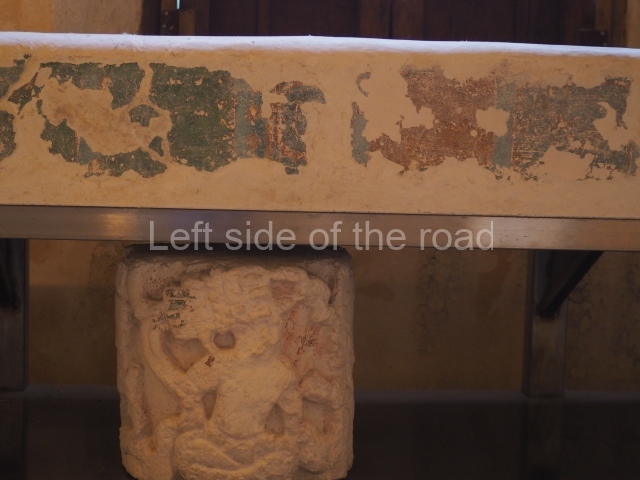
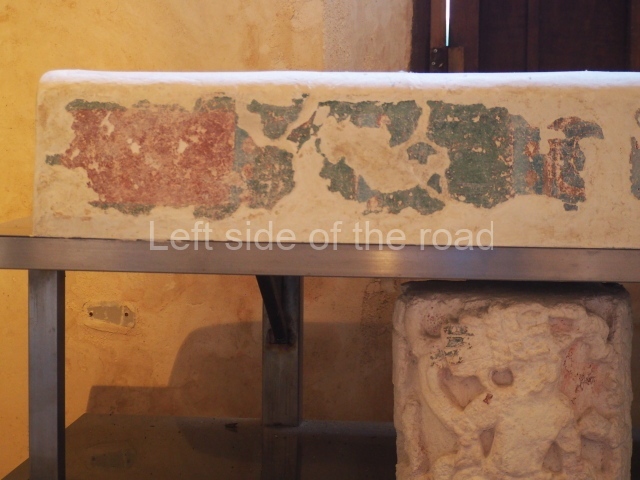
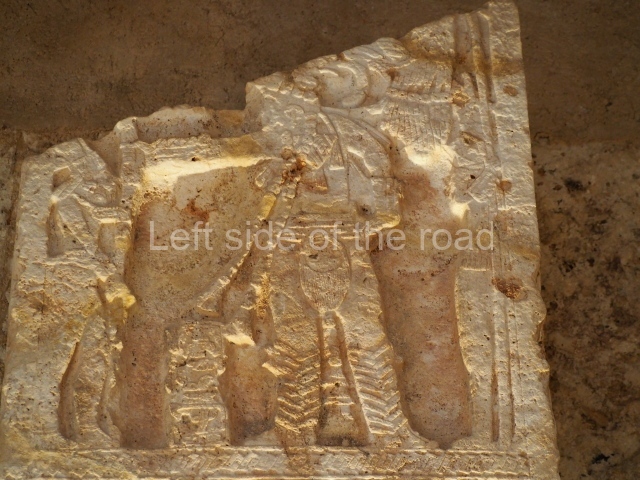
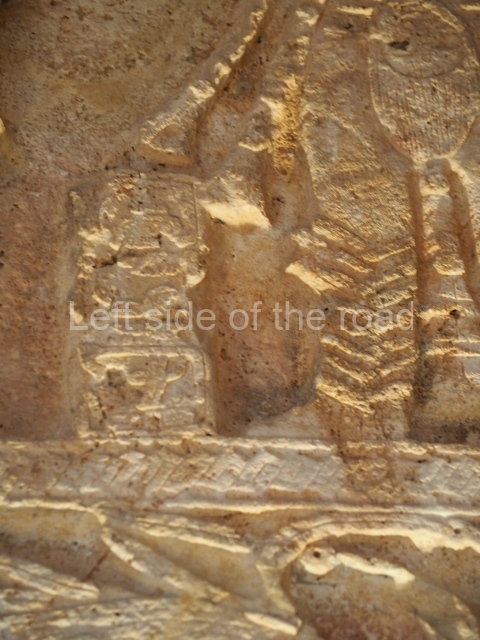
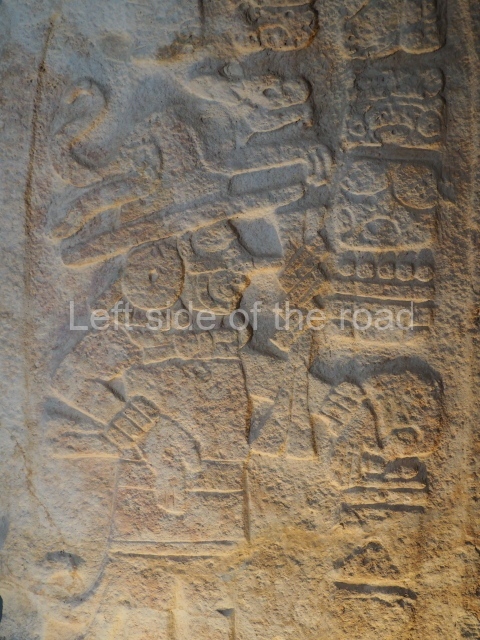
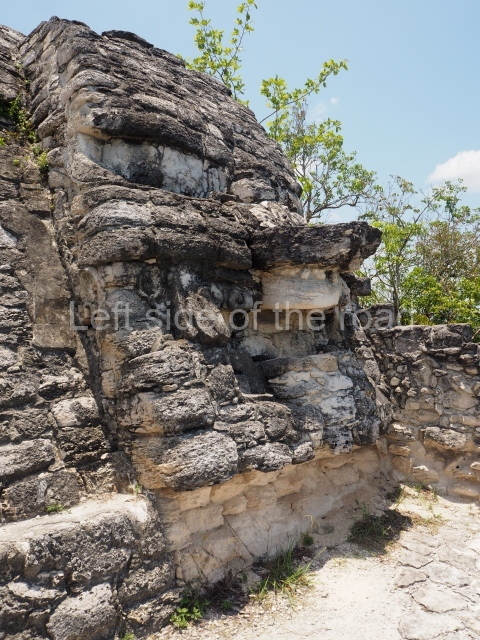
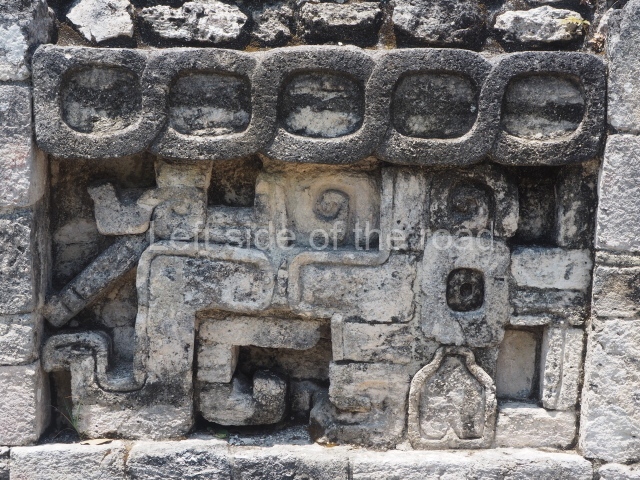
Stucco frieze.
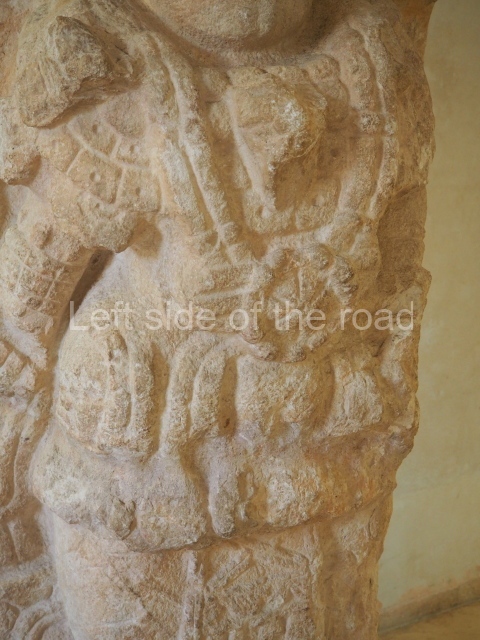
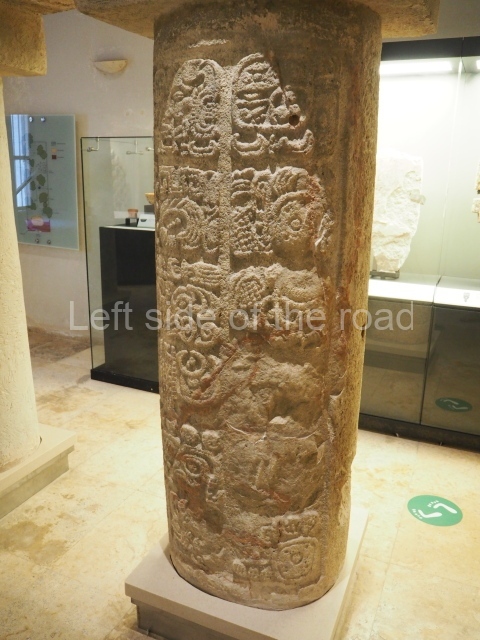
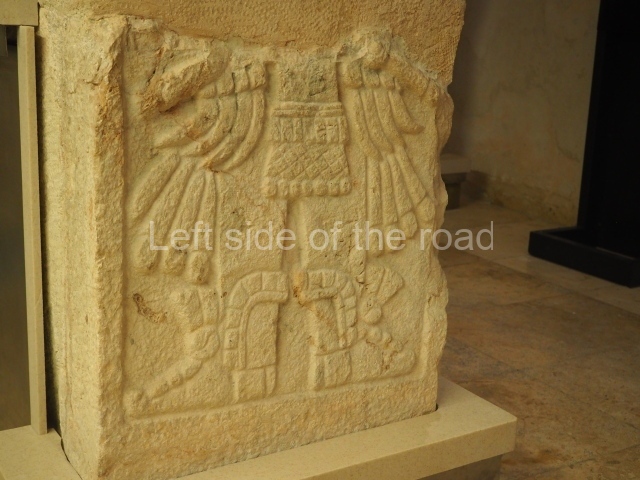
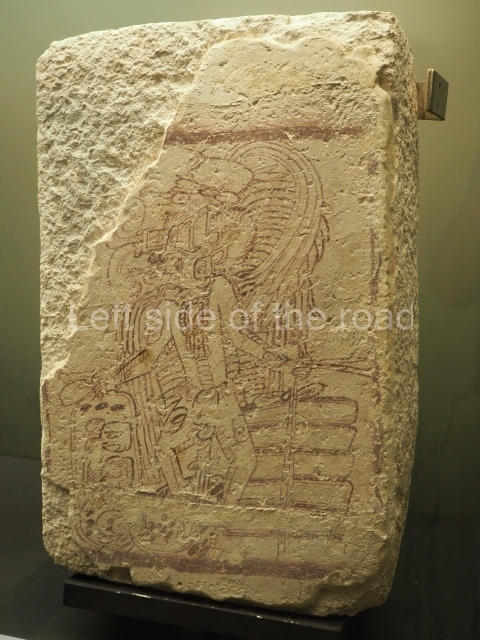
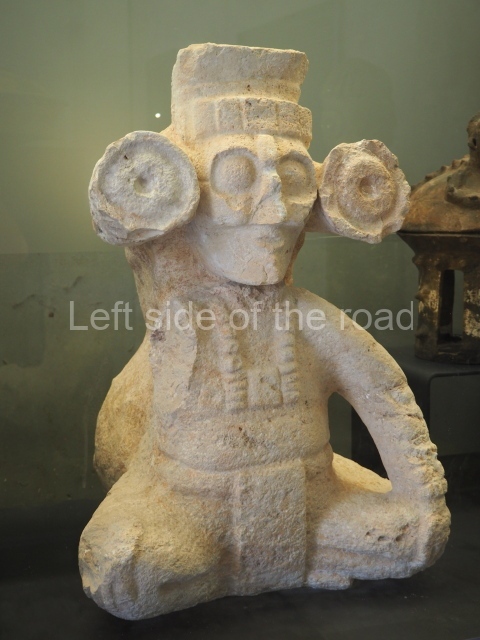
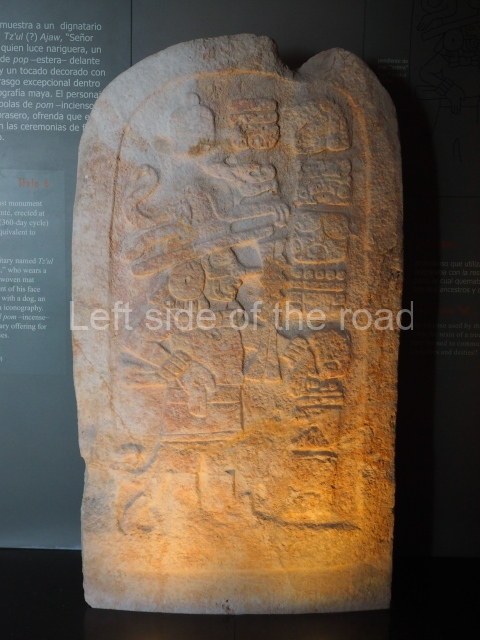
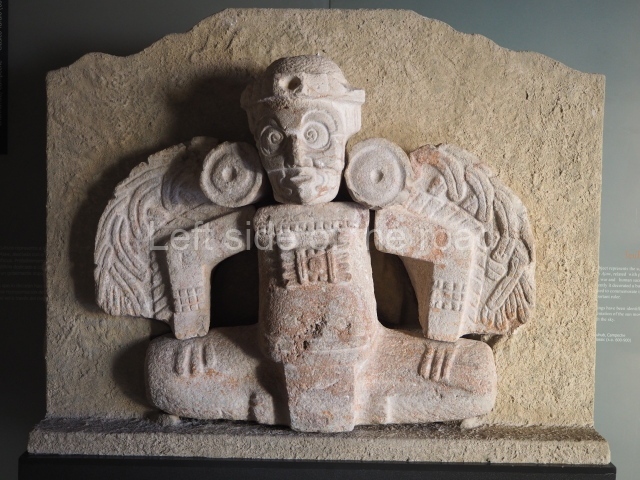
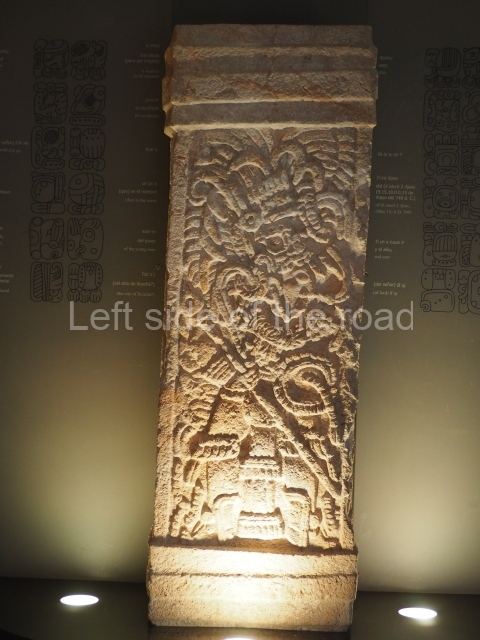
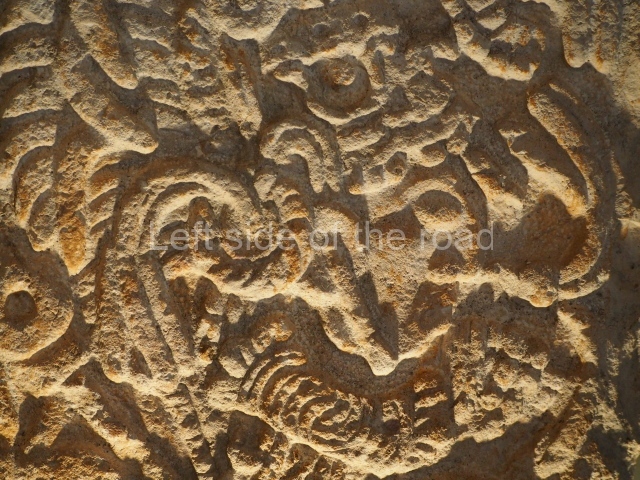
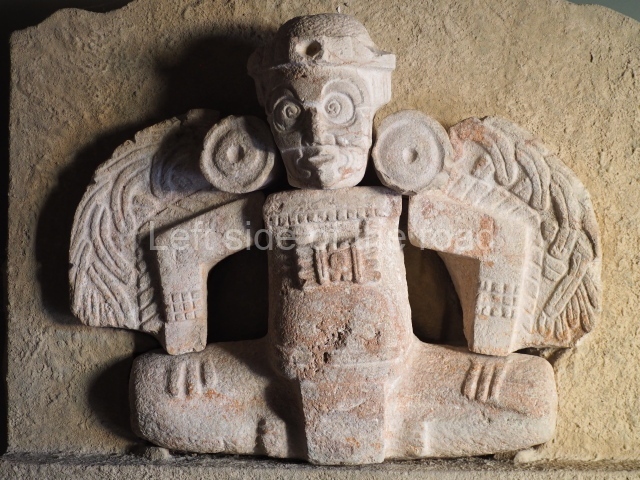
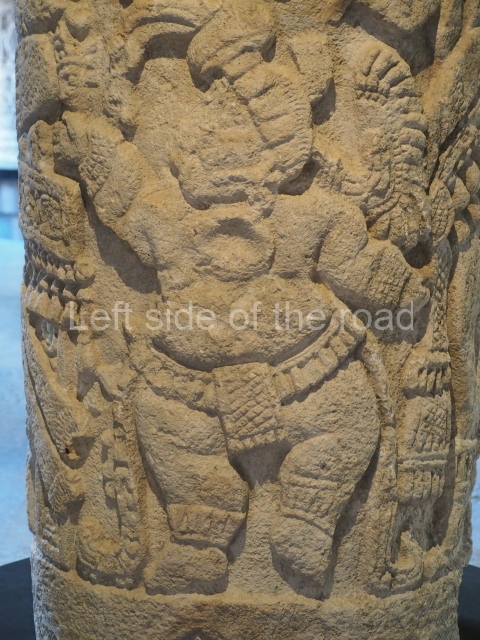
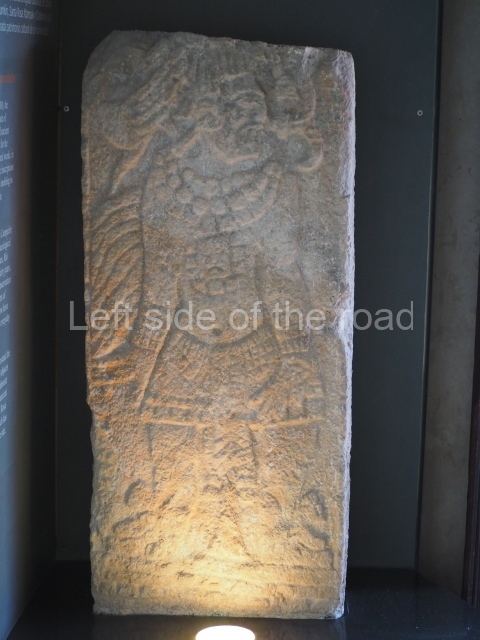
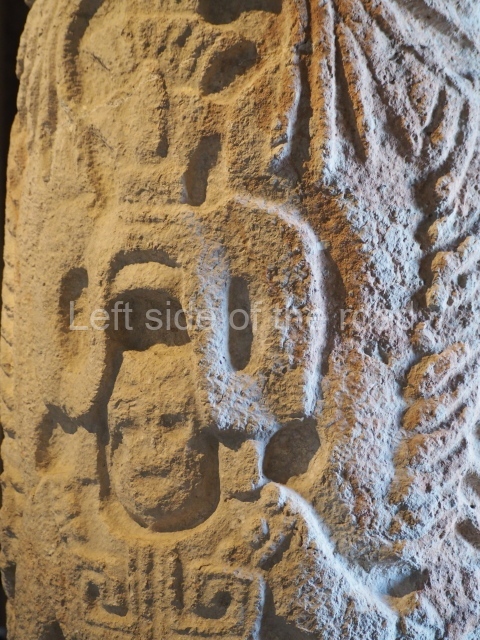
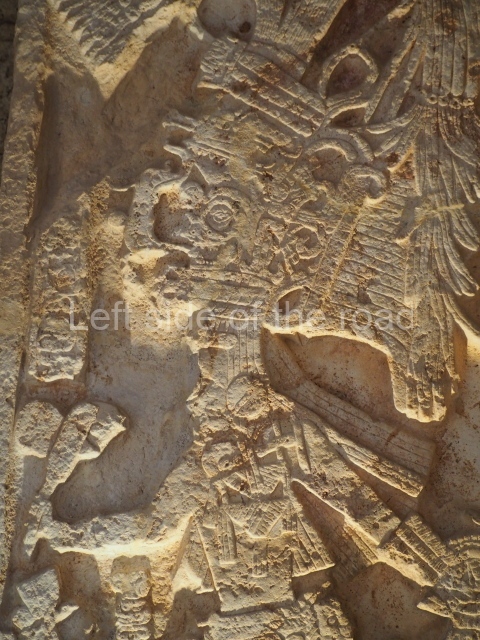
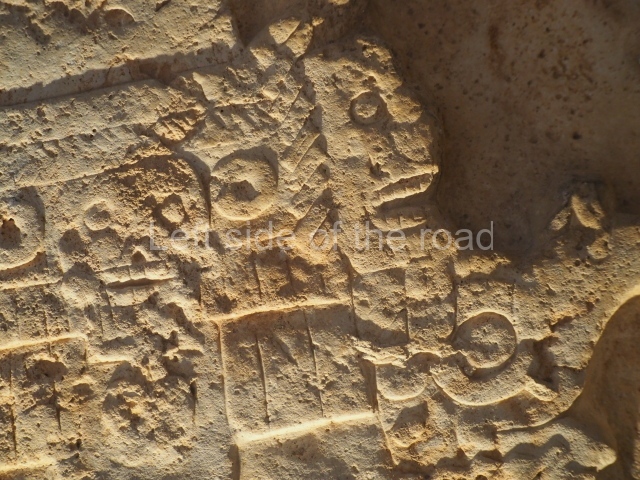
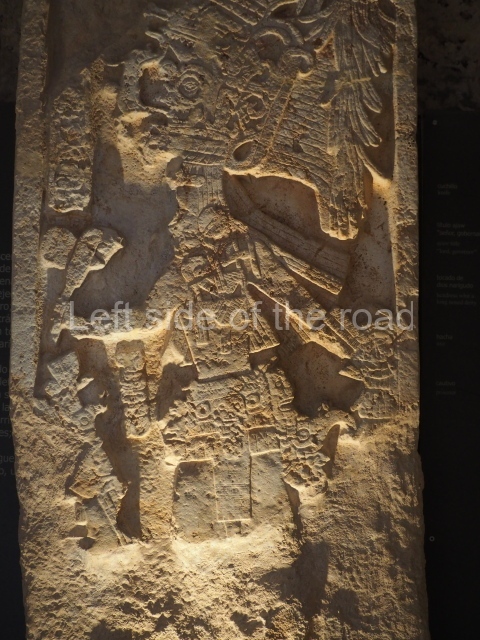
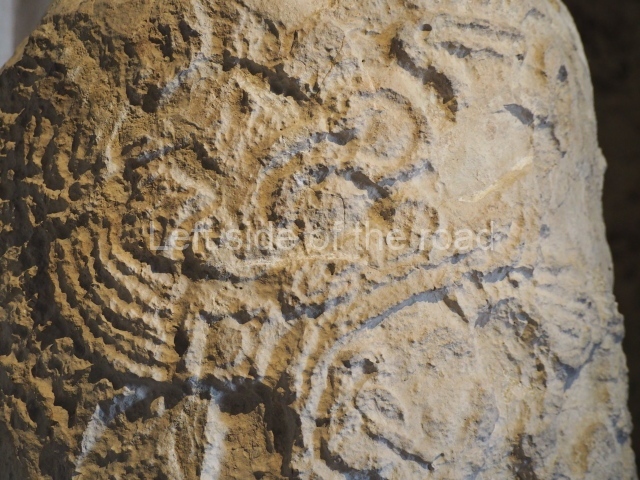
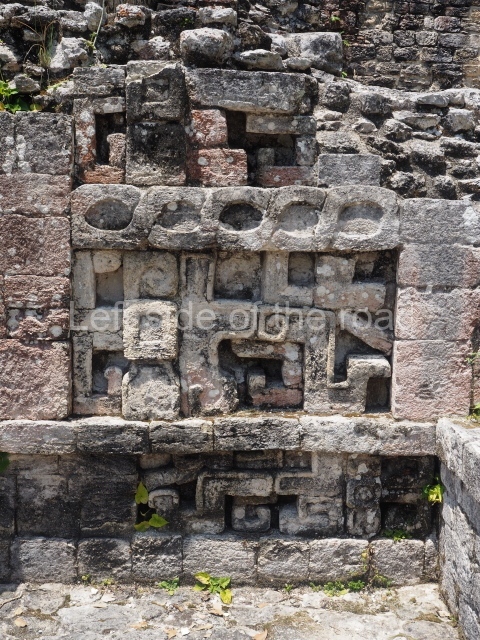
This polychrome stucco frieze was found to the south of Structure X, in one of the rooms in the aforementioned courtyards. It appears to be the portrait of a high-ranking official wearing nose rings made of round beads and large ear ornaments. The face rests on a small mask and the headdress displays another two masks, superimposed. Behind it, on both sides, it is possible to discern the profile image of the Earth Monster, with blazing eyelashes and open jaws. The figure is situated beneath the 01 symbol, or entrance to the underworld, characterised by a cavity with four lobes. This evidently represented his sojourn in the other world. The comparison of this motif with similar stucco motifs found at Balamku, Placeres and Kohunlich suggest that it dates from around AD 400.
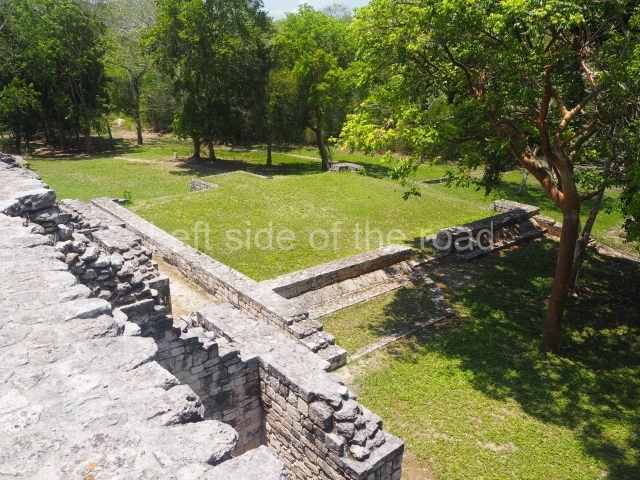
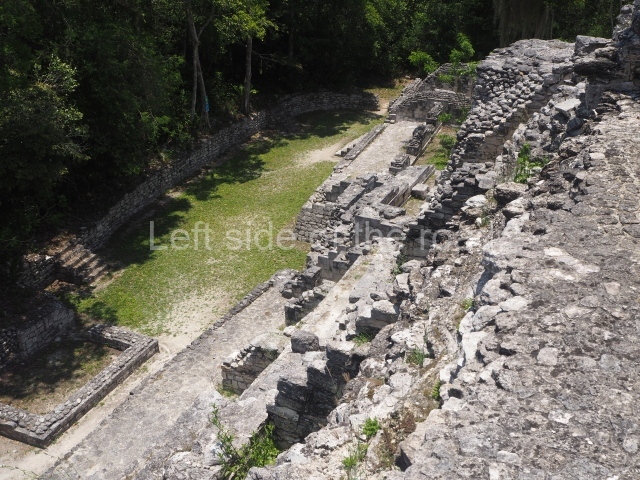
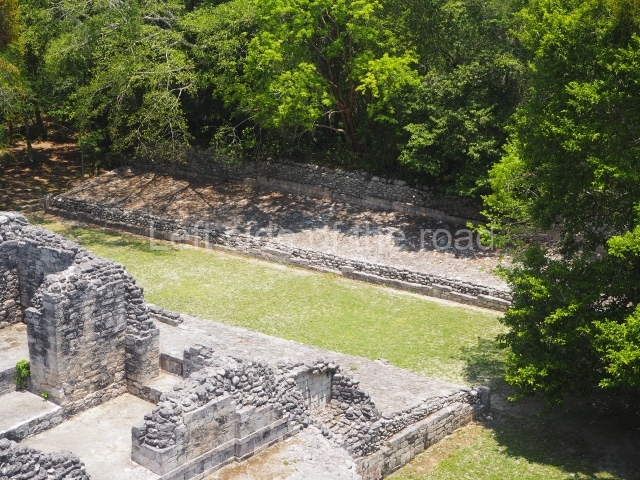
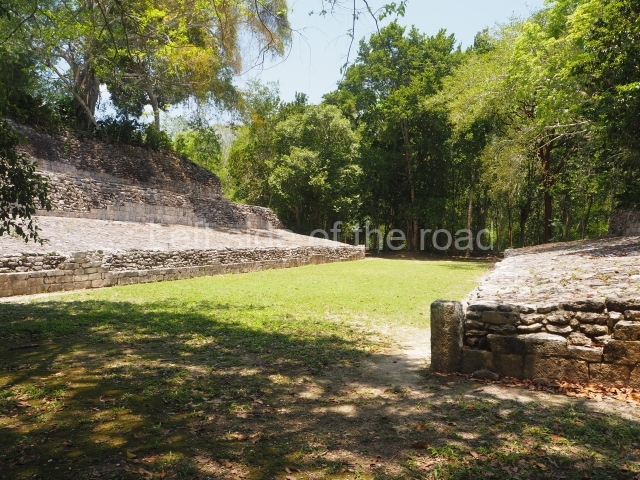
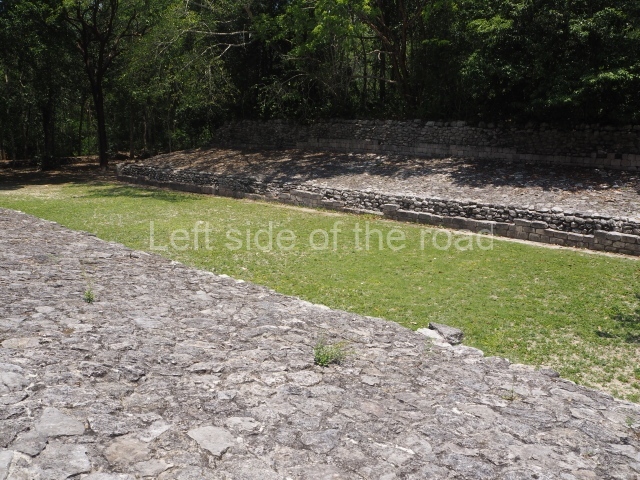
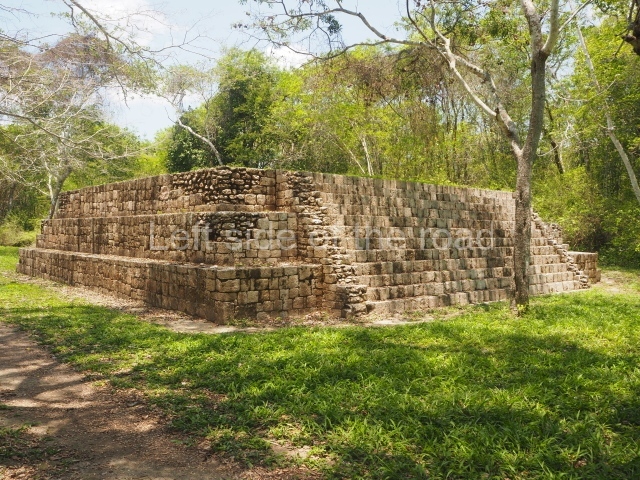
Ball court.
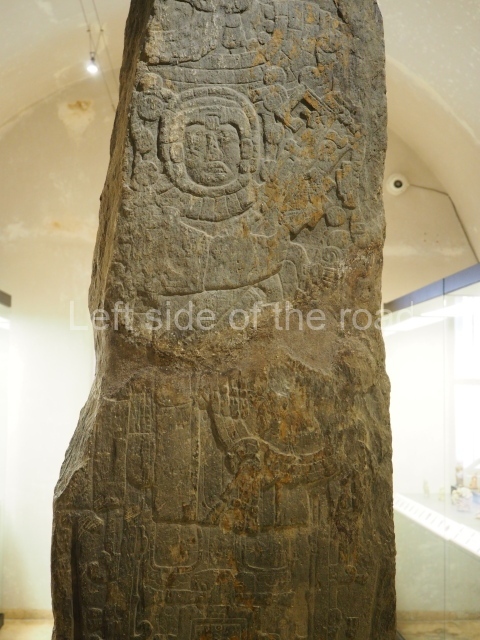
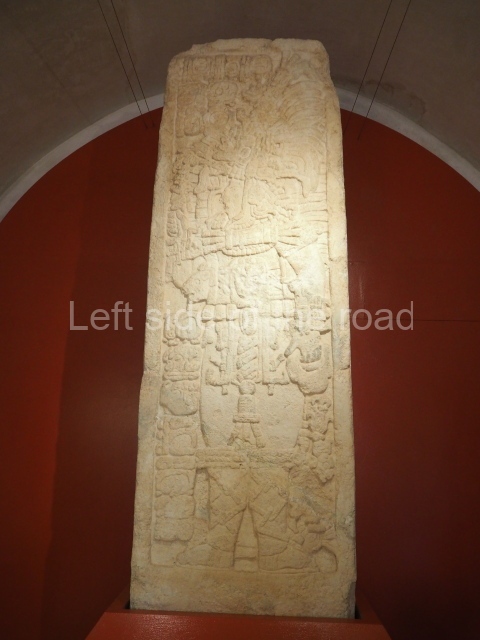
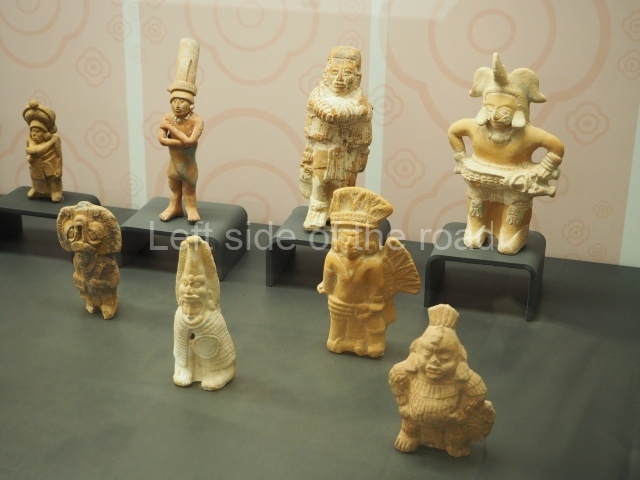
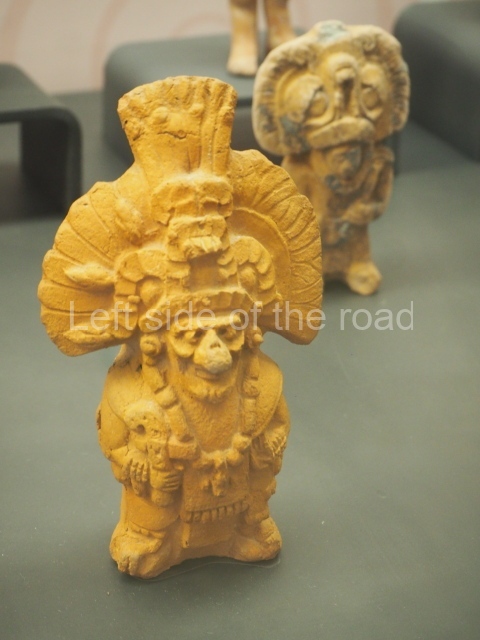
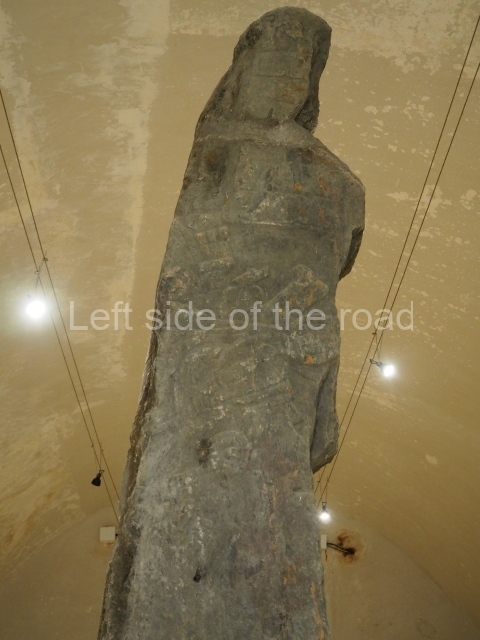
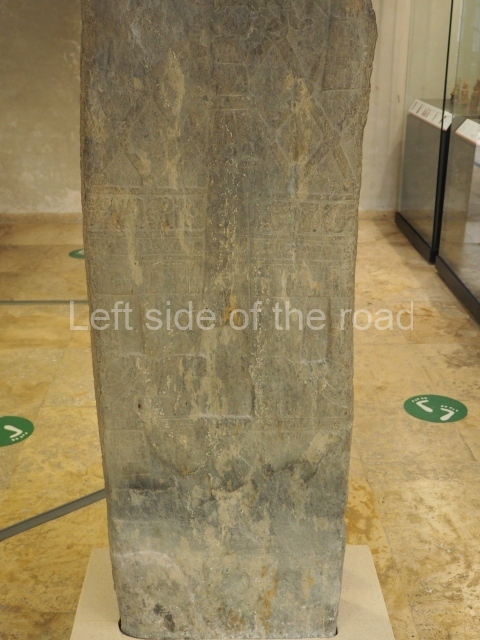
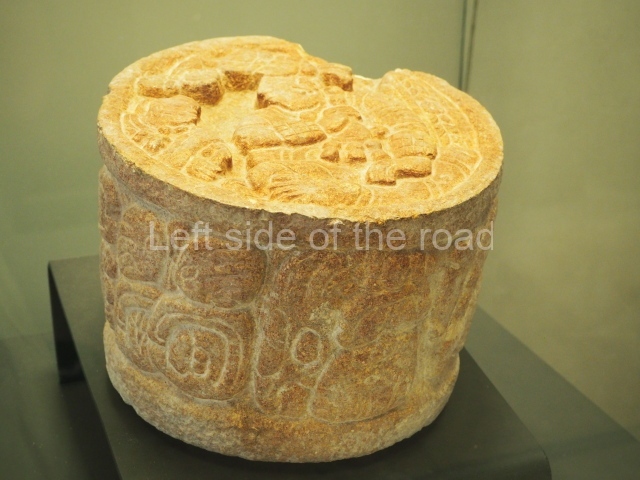
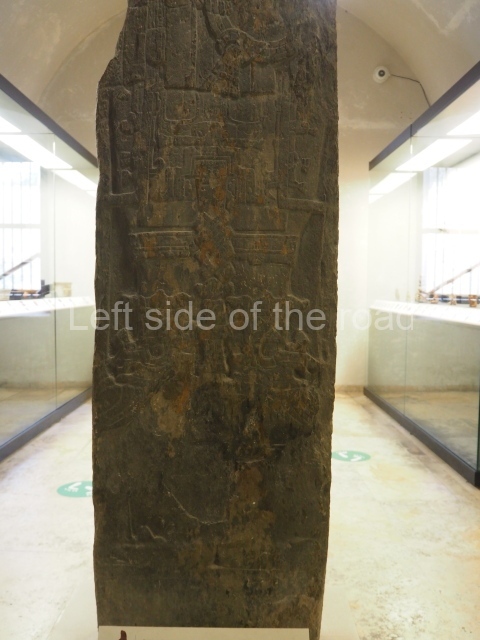
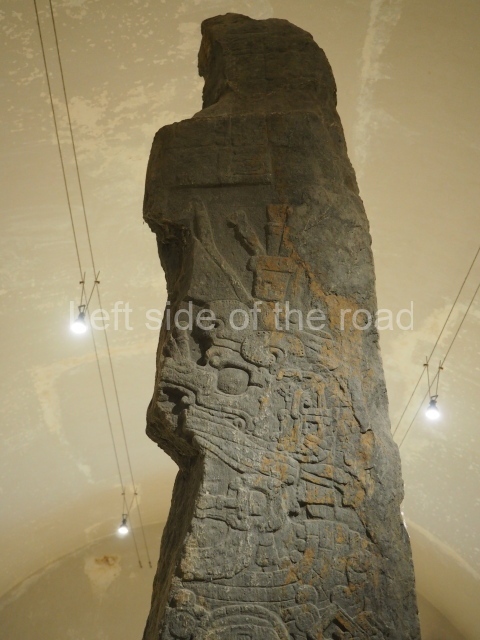
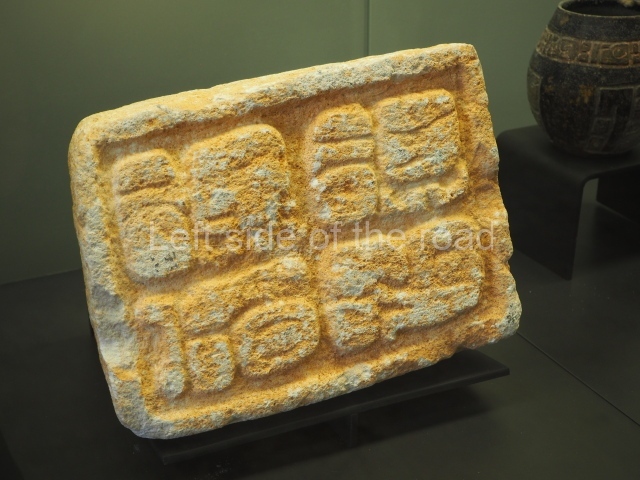
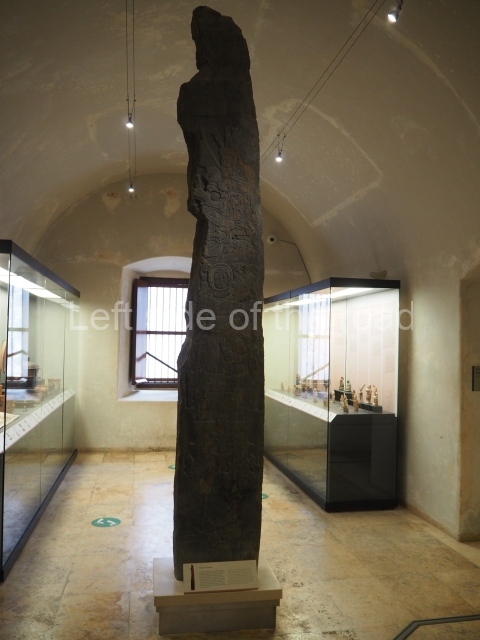
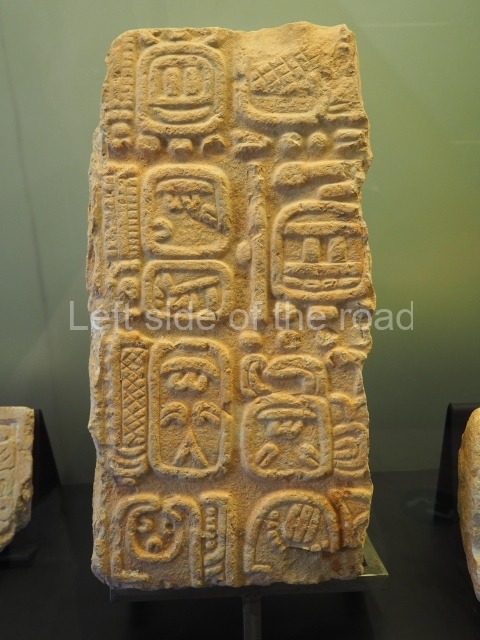
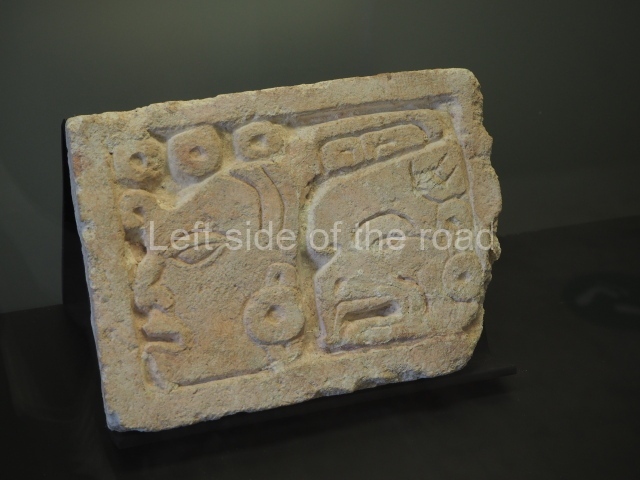
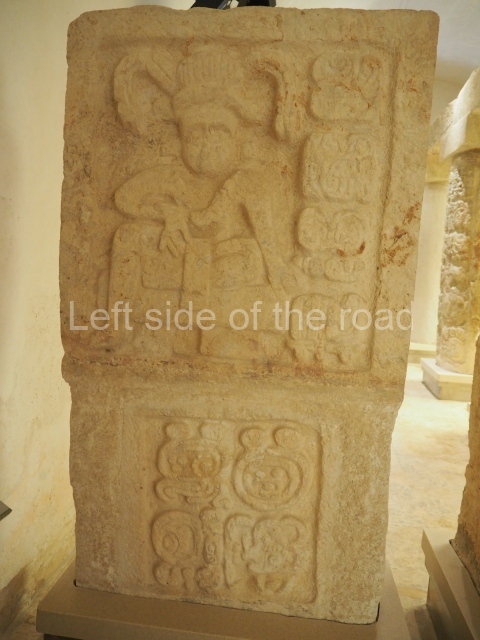
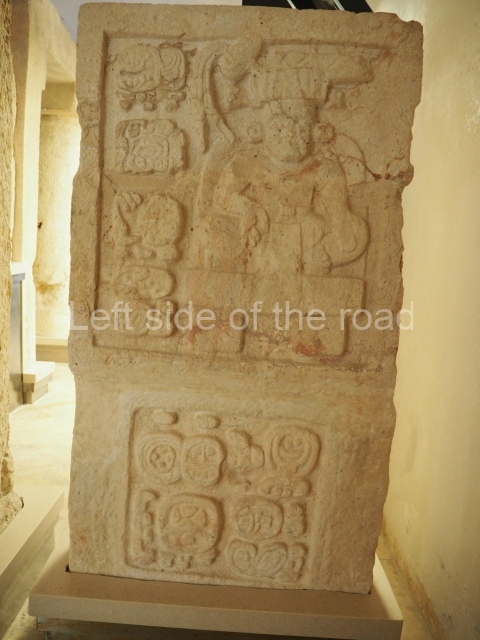
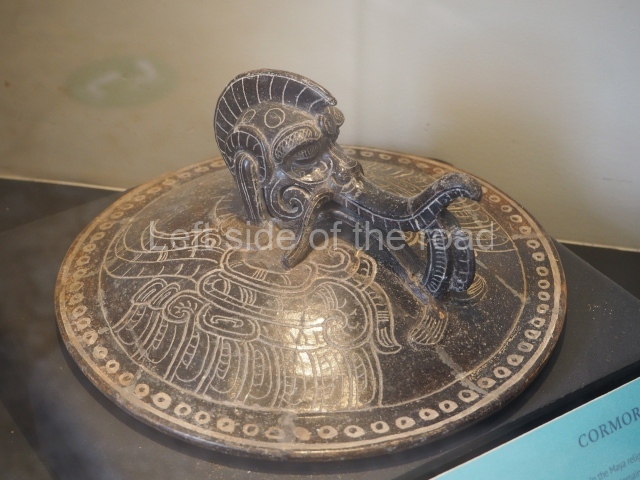
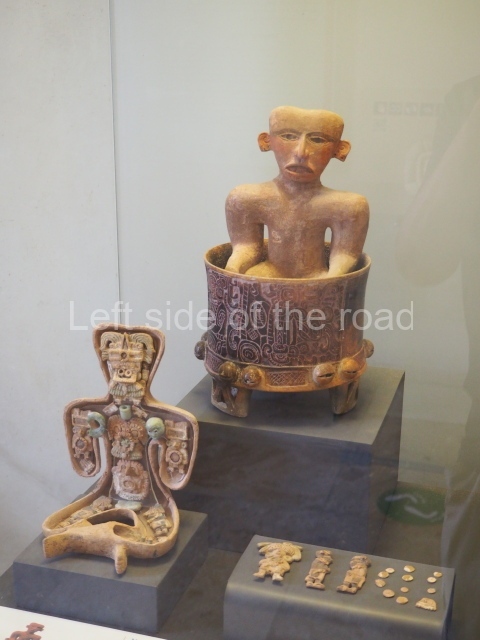
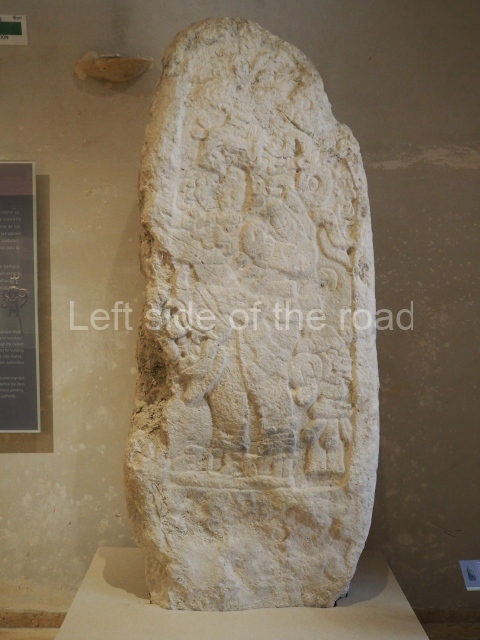
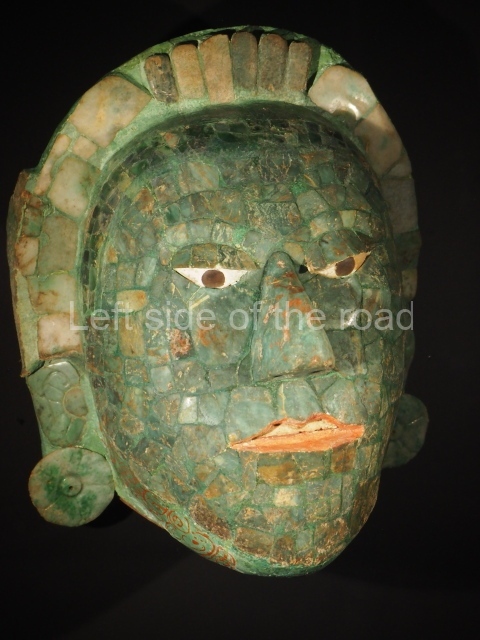
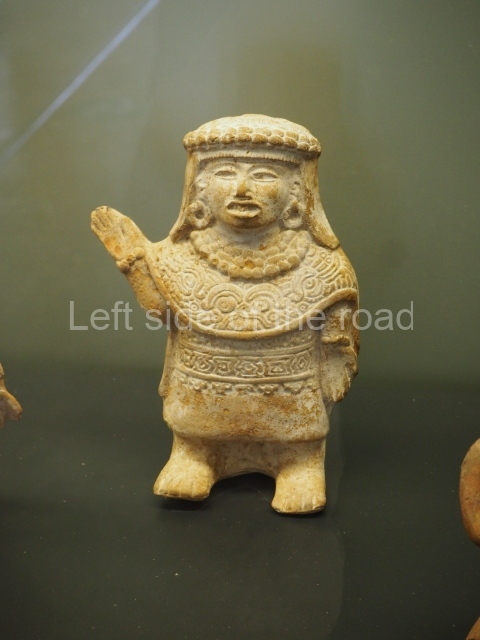
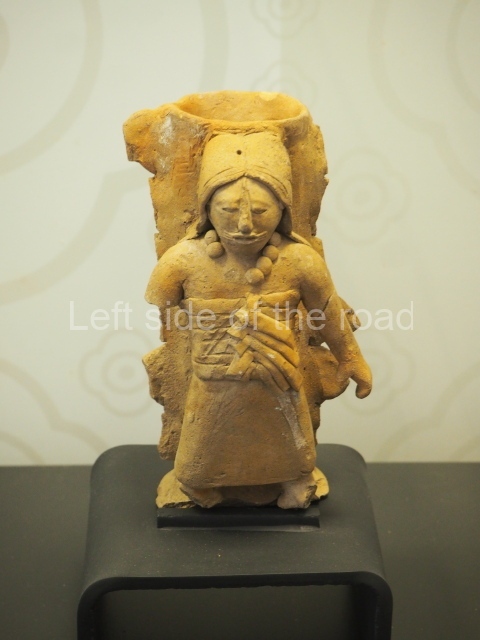
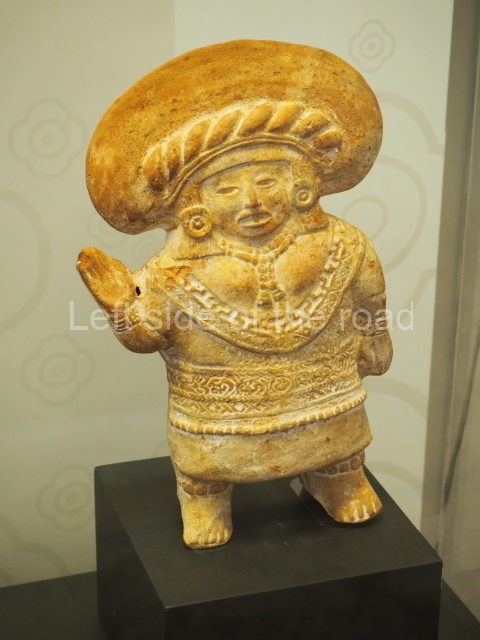
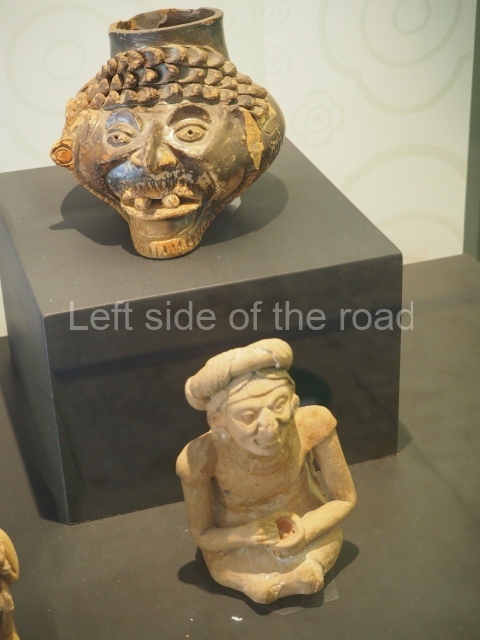
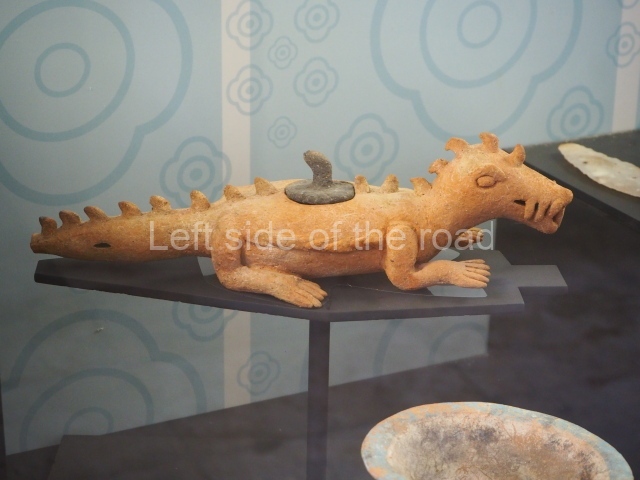
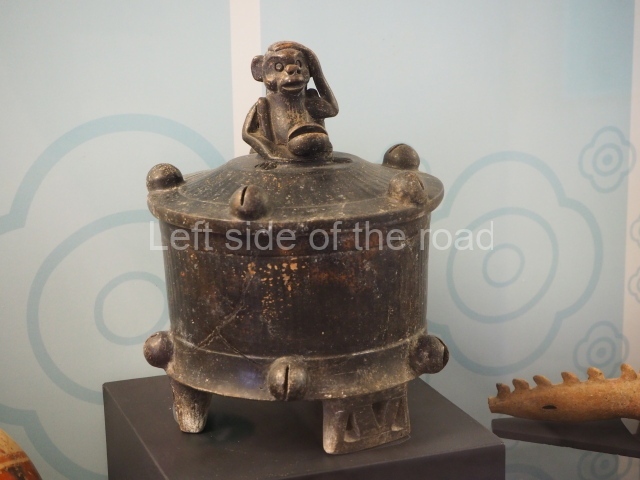
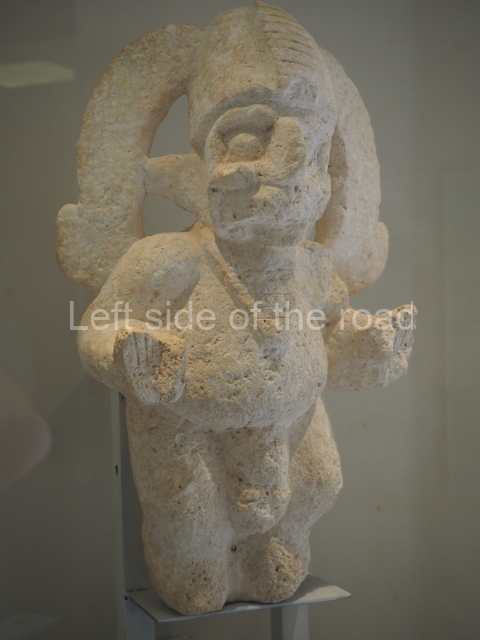
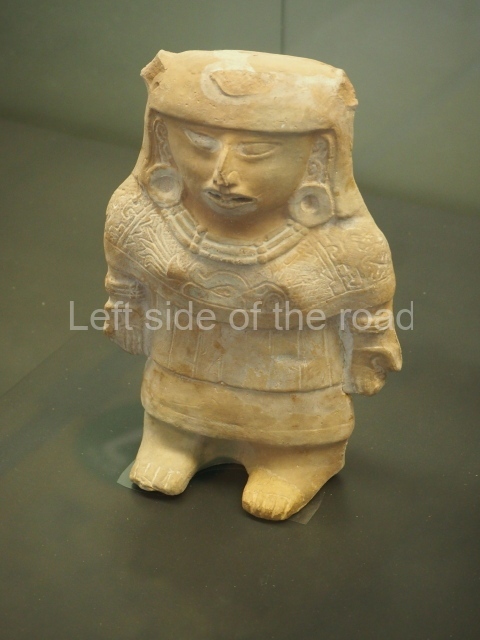
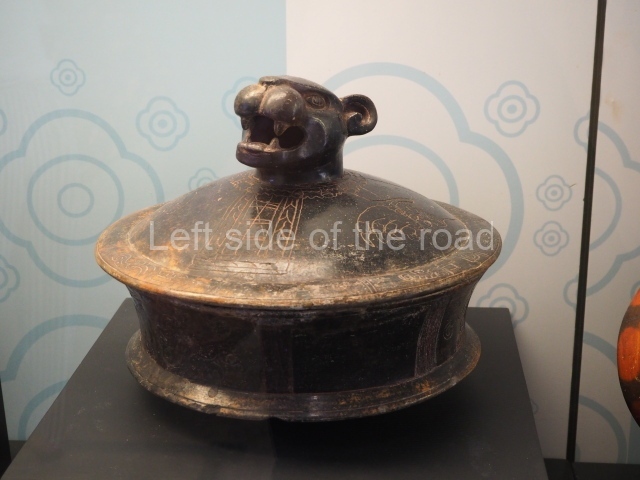
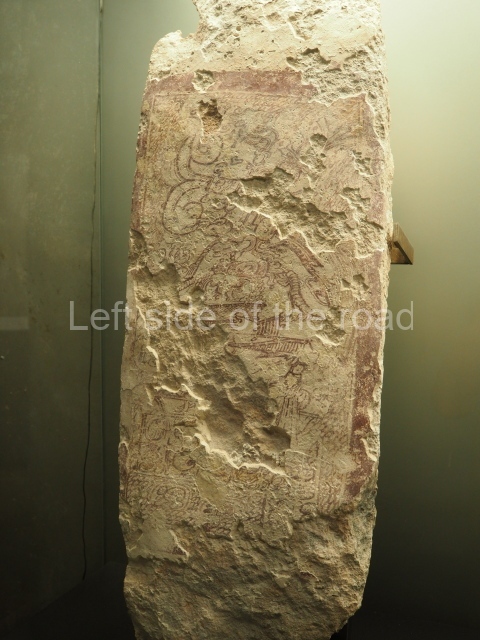
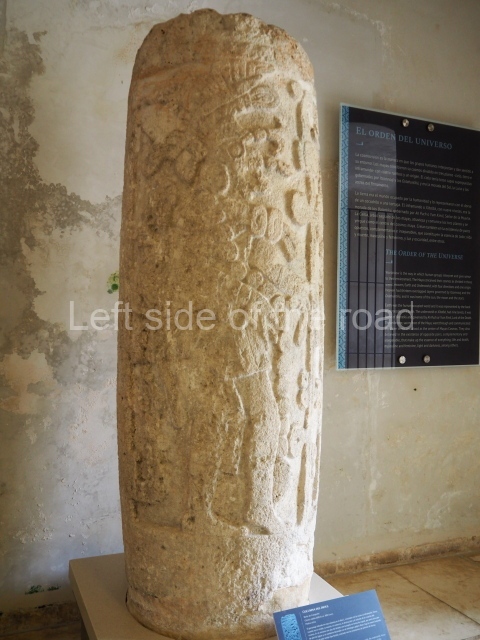
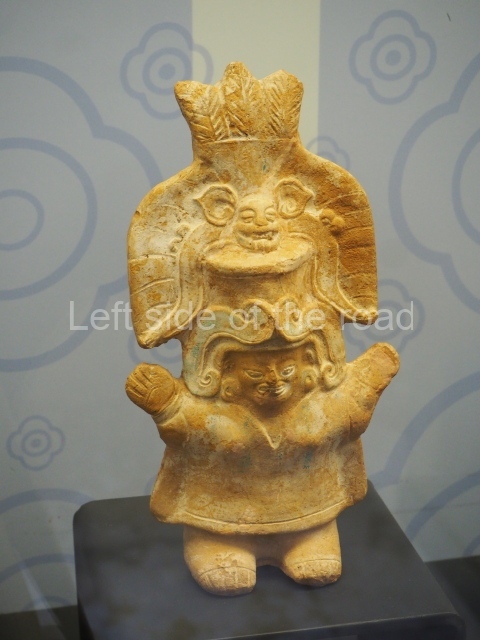
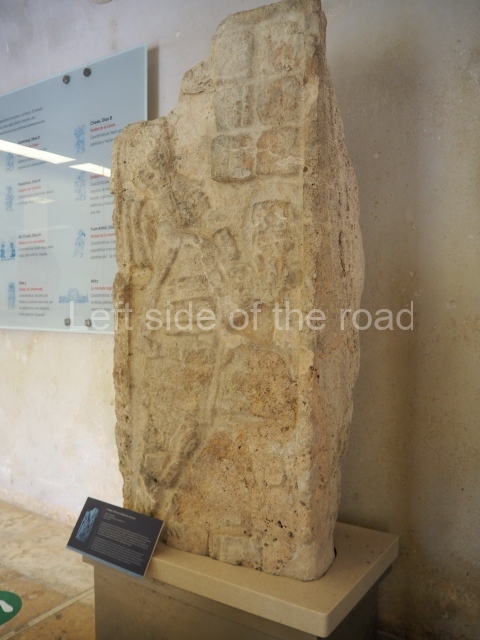
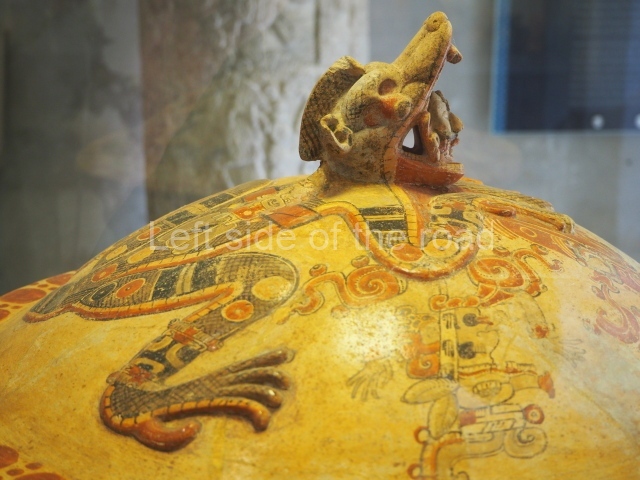
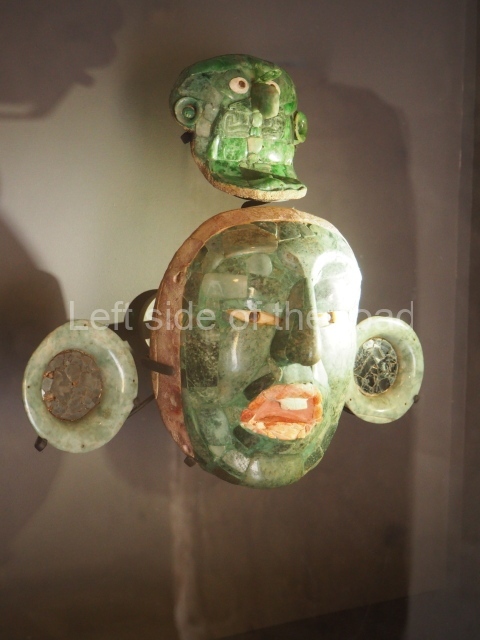
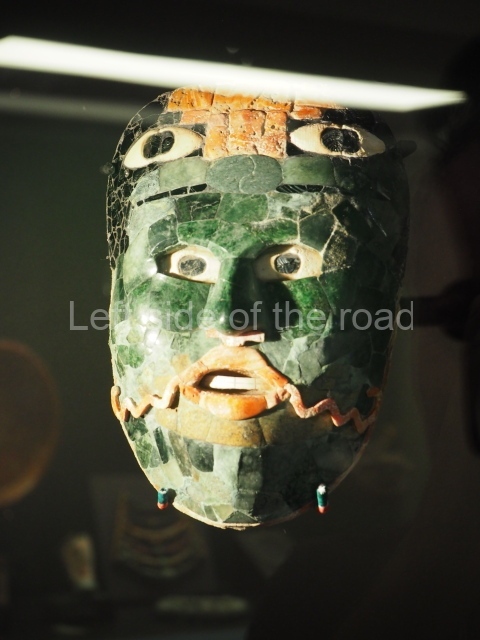
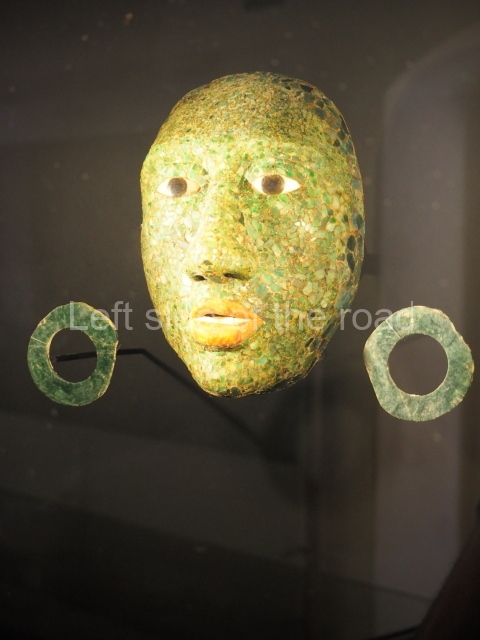
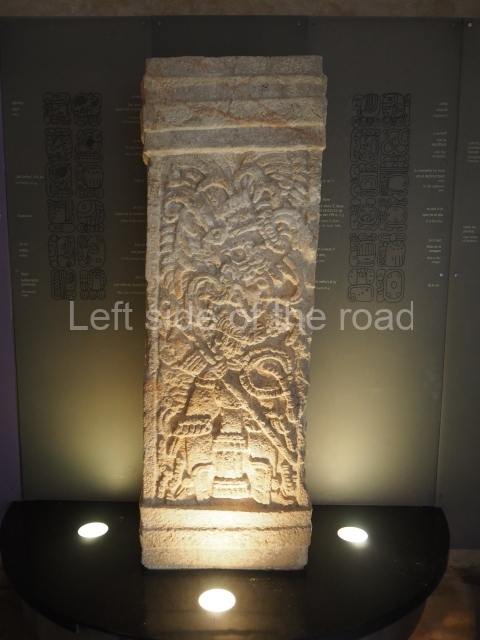
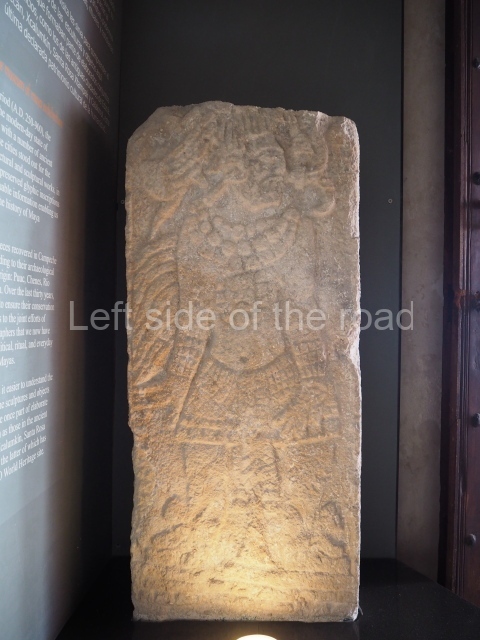
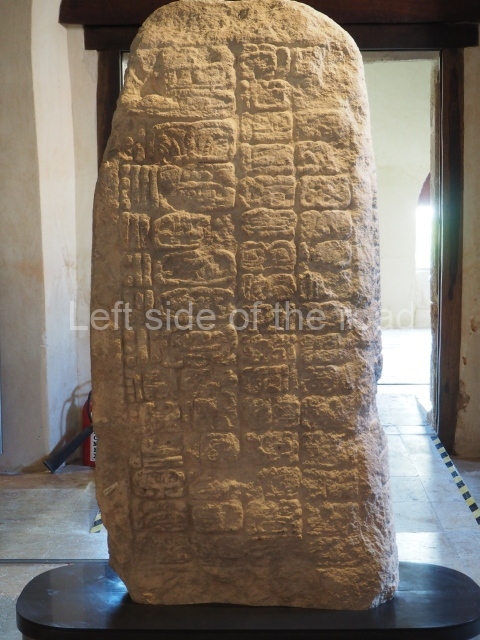
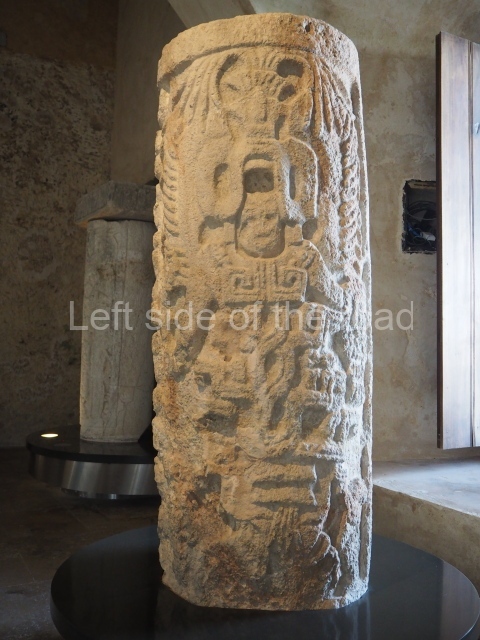
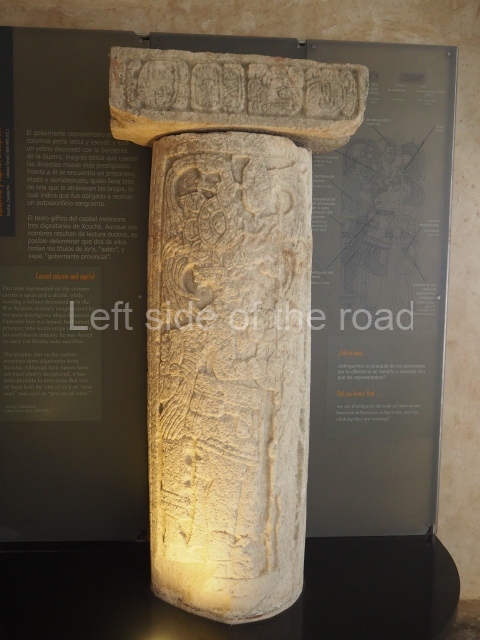
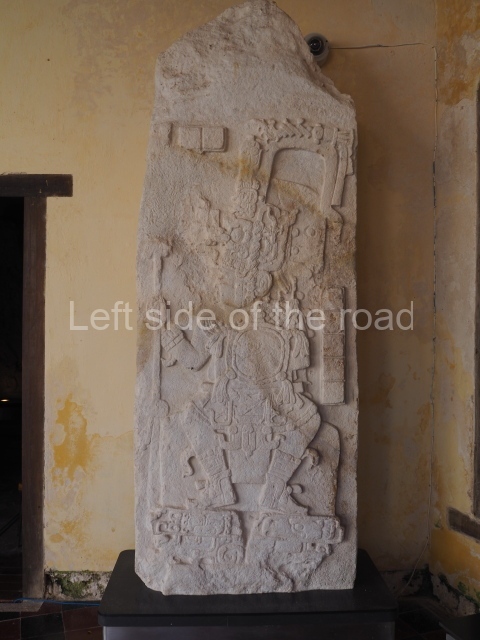
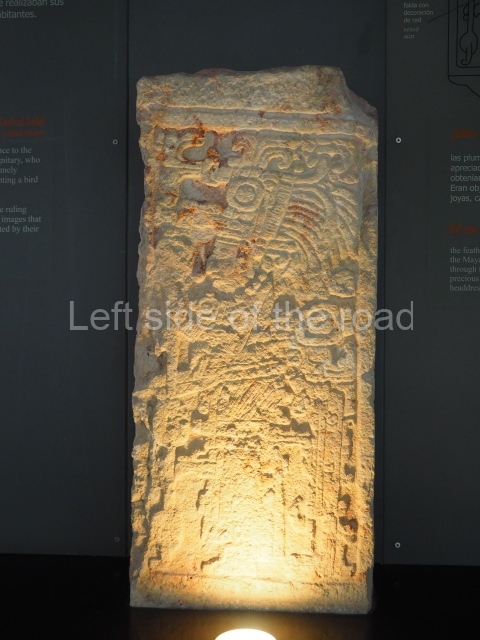
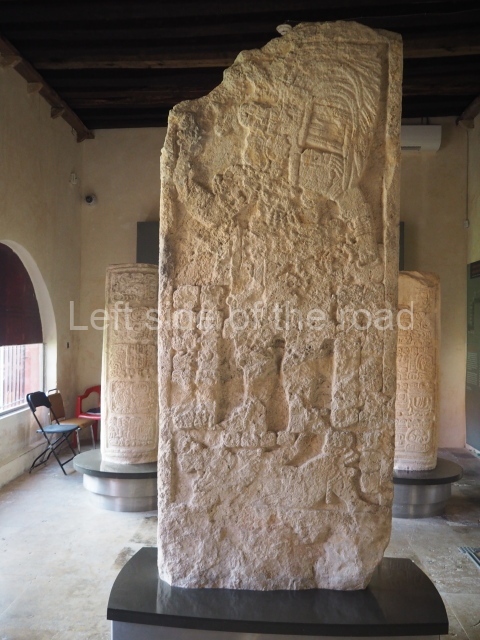
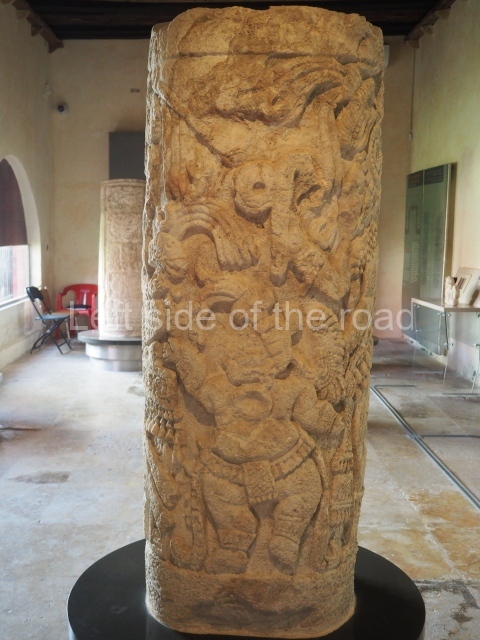
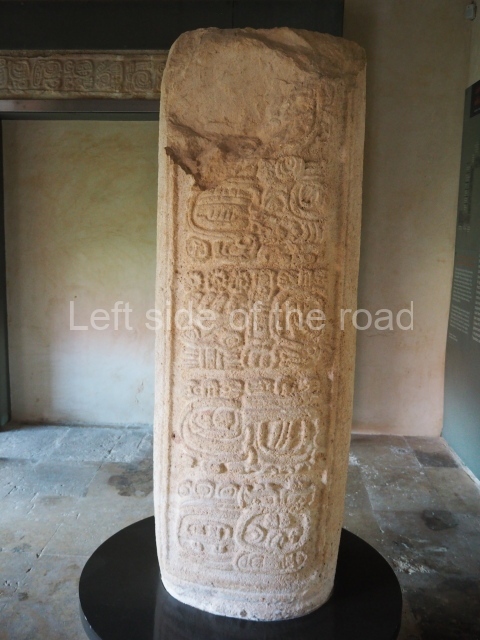
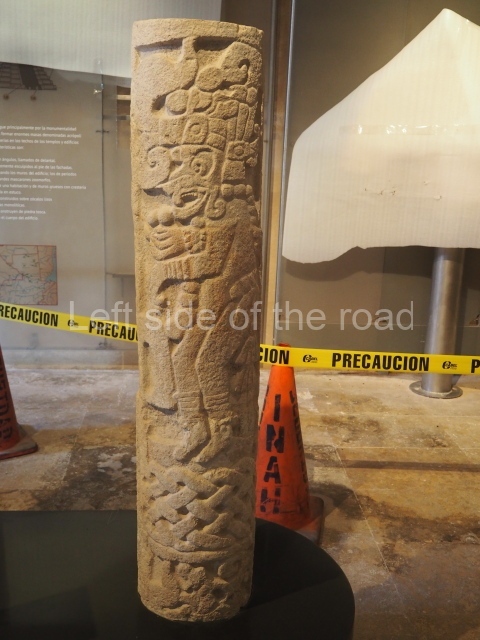
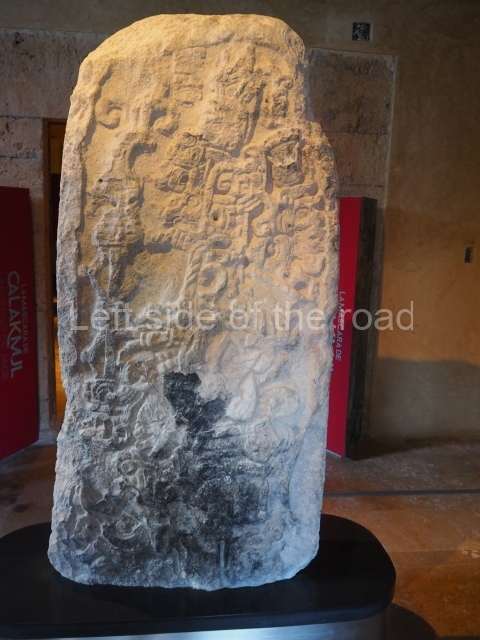
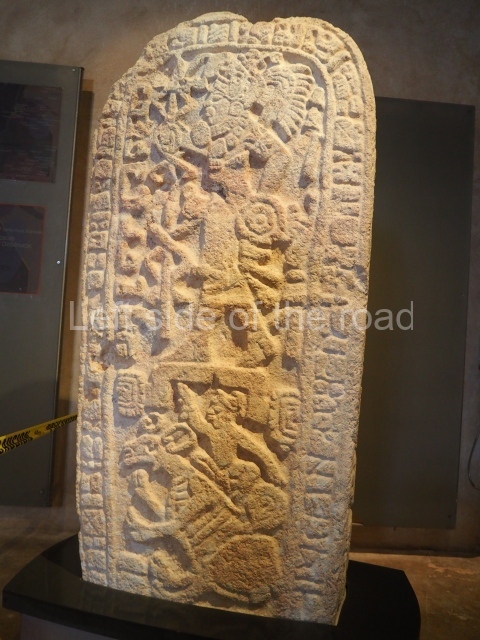
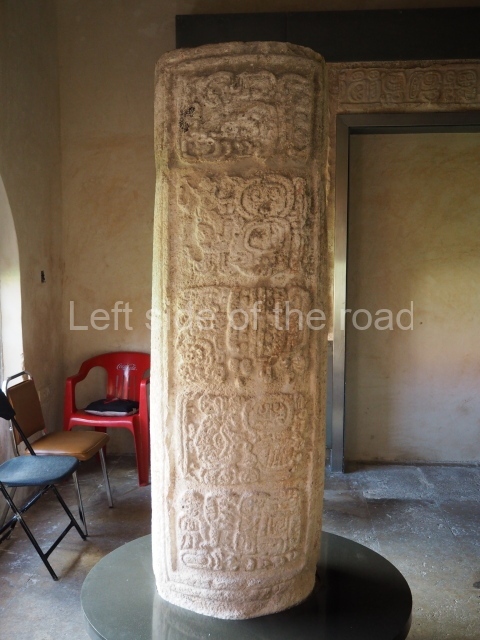
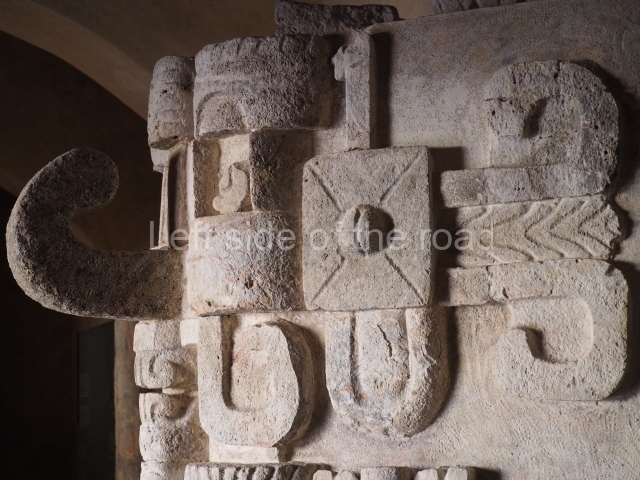
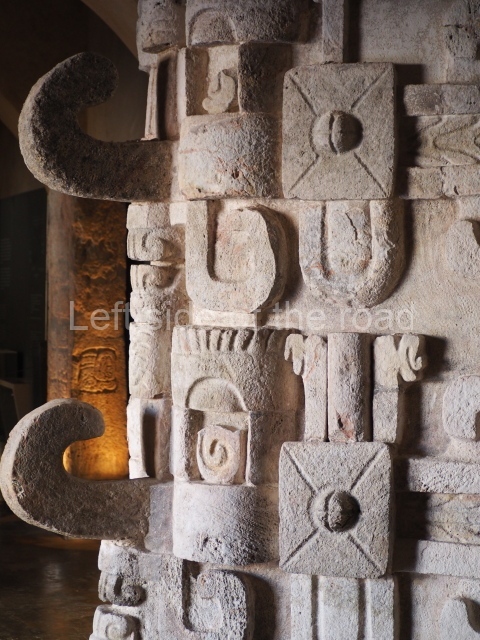
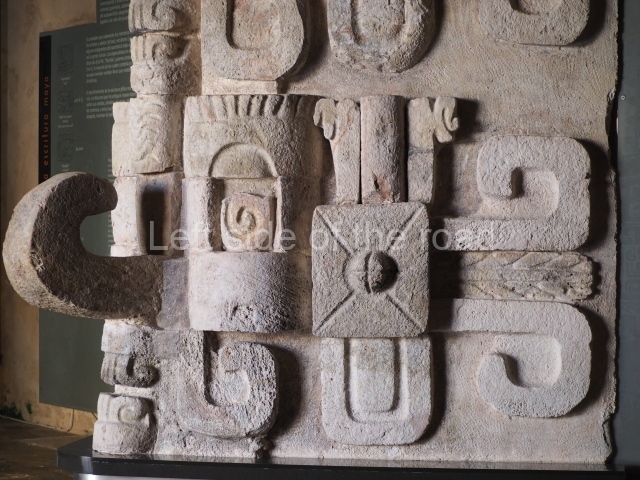
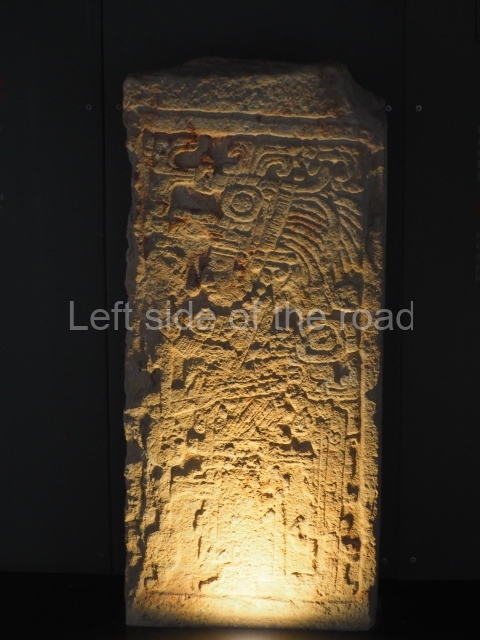
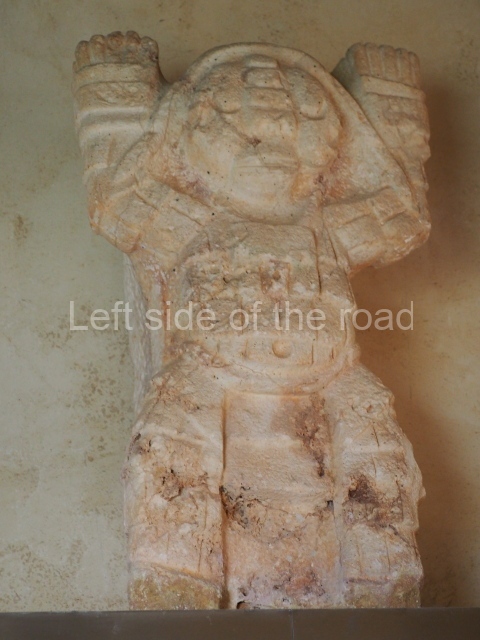
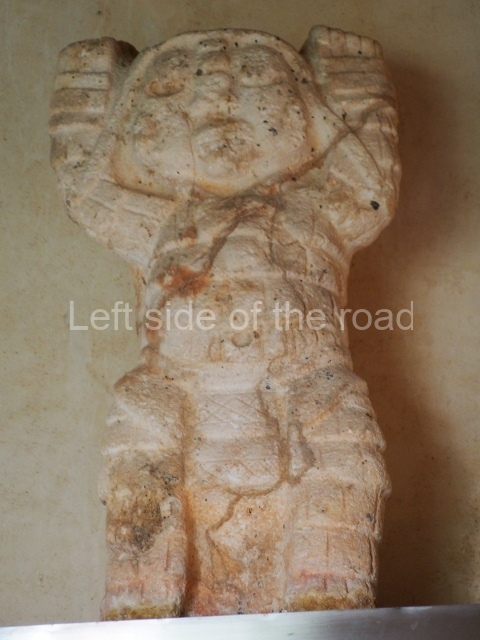
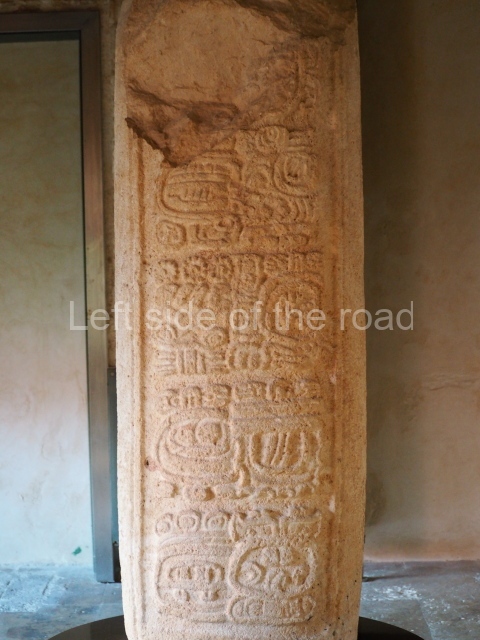
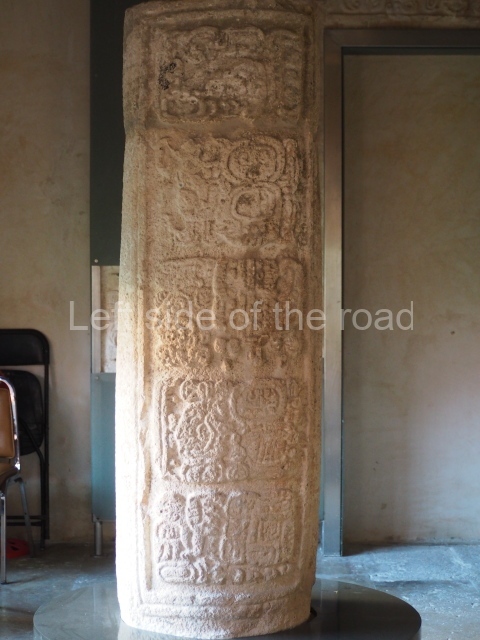
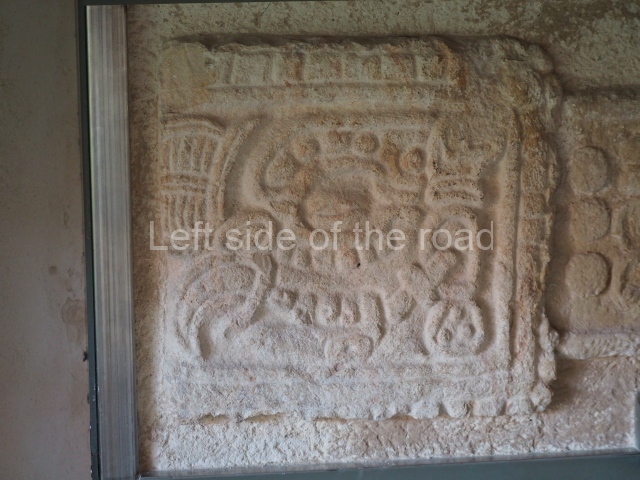
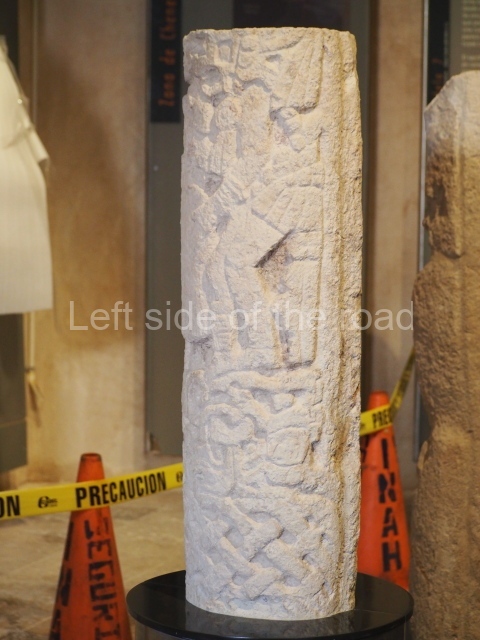
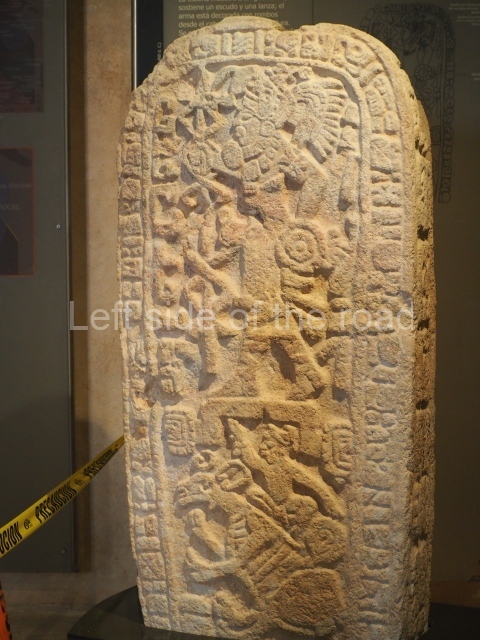
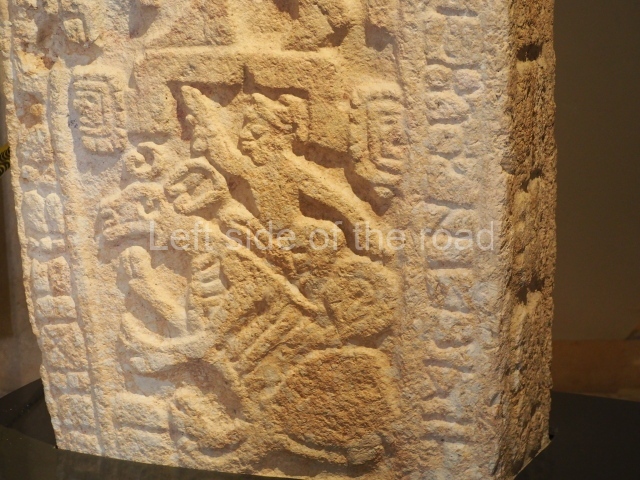
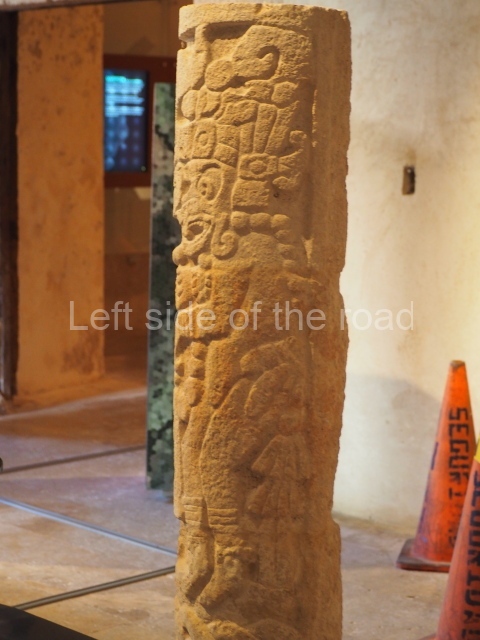
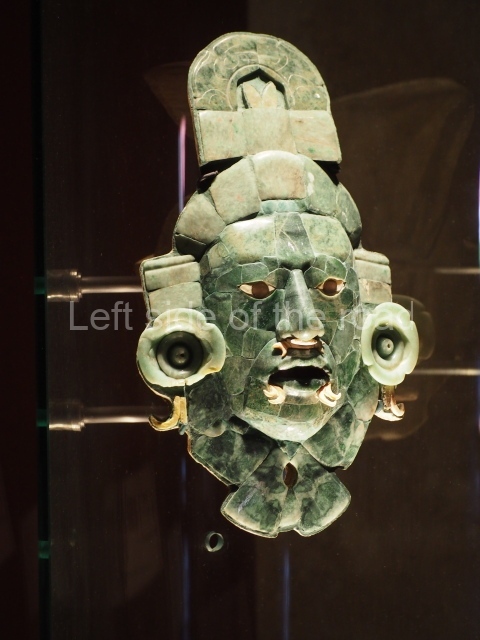
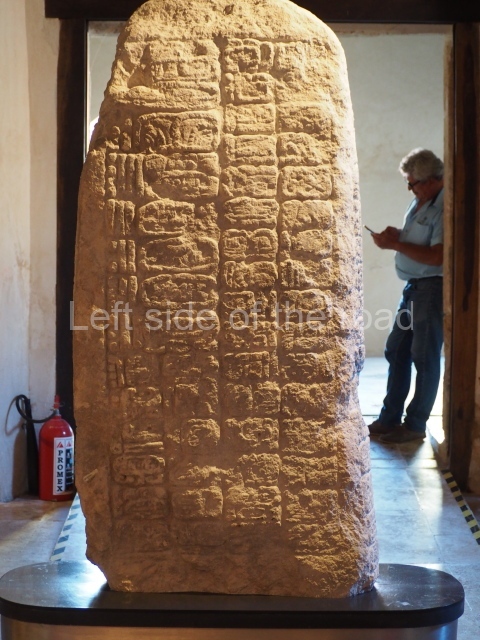
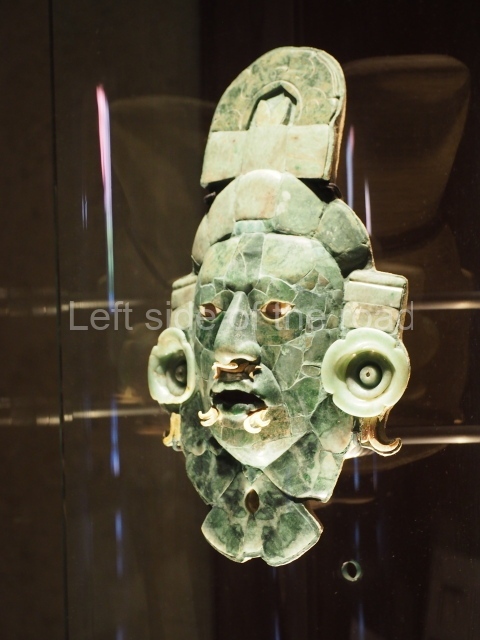
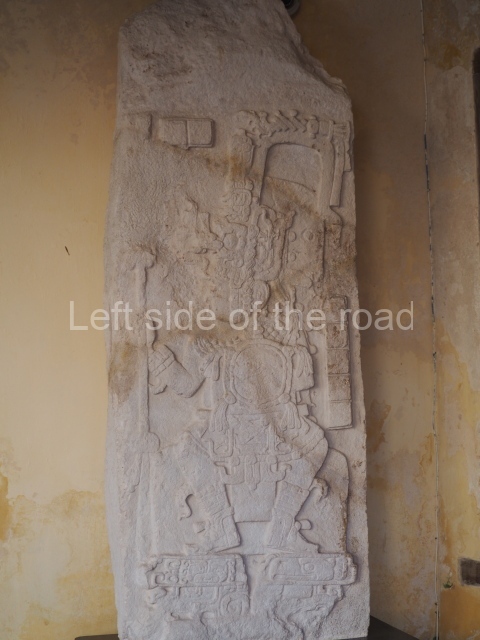
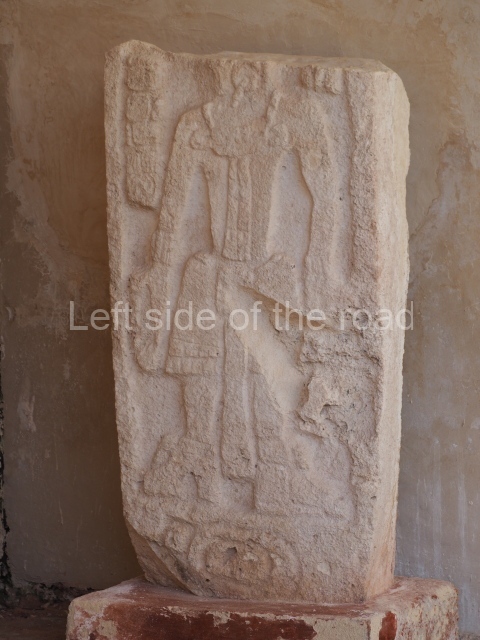
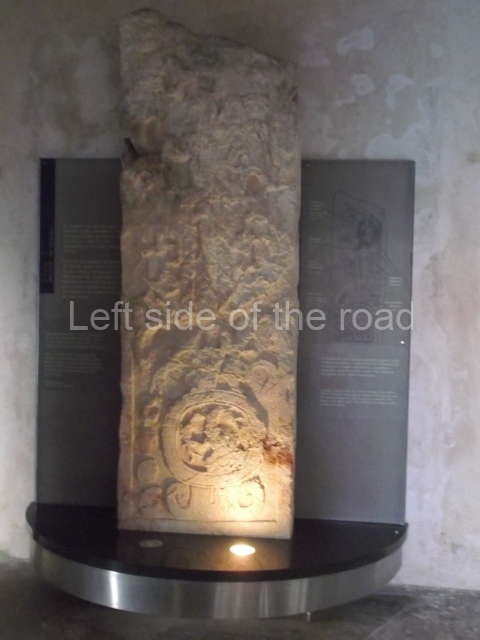
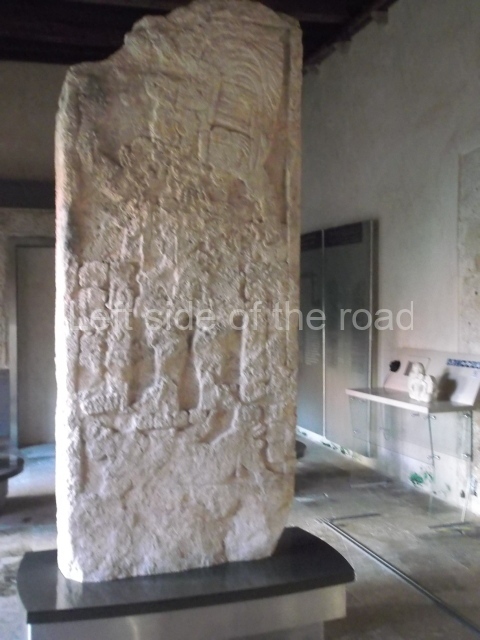
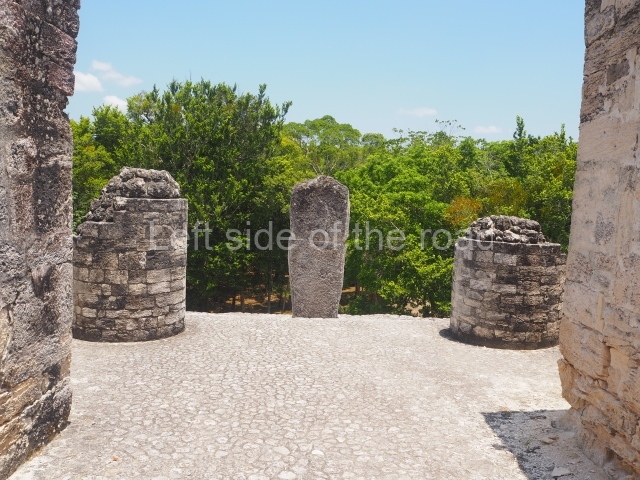
The west section is occupied by Plaza C, whose east side is delimited by the main ball court at Becan. This is composed of two parallel north-south constructions which form a play area 32 m long and 9 m wide. No rings or stone markers were found during the exploration of this space. There are traces of various stelae at Becan, but little is known about their inscriptions or reliefs because some of them were smooth and others were in an advanced state of decay. An interesting offering of Teotihuacan pieces found at Structure XIV is on display at the Yucatan Archaeology Museum (Merida).Other pieces found at Becan can be viewed at the Campeche Archaeology Museum.
Importance and relations
The concentration and quality of the monumental architecture at Becan prove its status as a political, economic and religious capital in ancient times. It was the most important city in the Rio Bec archaeological area, which is situated in the middle of the base of the Yucatan Peninsula, midway between the Gulf of Mexico and Chetumal Bay
From: ‘The Maya: an architectural and landscape guide’, produced jointly by the Junta de Andulacia and the Universidad Autonoma de Mexico, 2010, pp326-331.

Becan
- Plaza A; 2. Structure I; 3. Structure IV; 4. Plaza B; 5. Structure VIII; 6. Structure IX; 7. Stucco Frieze; 8. Plaza C; 9. Bal court.
Getting there:
From Xpujil. It’s possible to take colectivos that are heading toward Conhuas or the SUR bus heading towards Puerto Escárcega. Flag anything that looks like a colectivo to get back.
Entrance:
M$75
More on the Maya